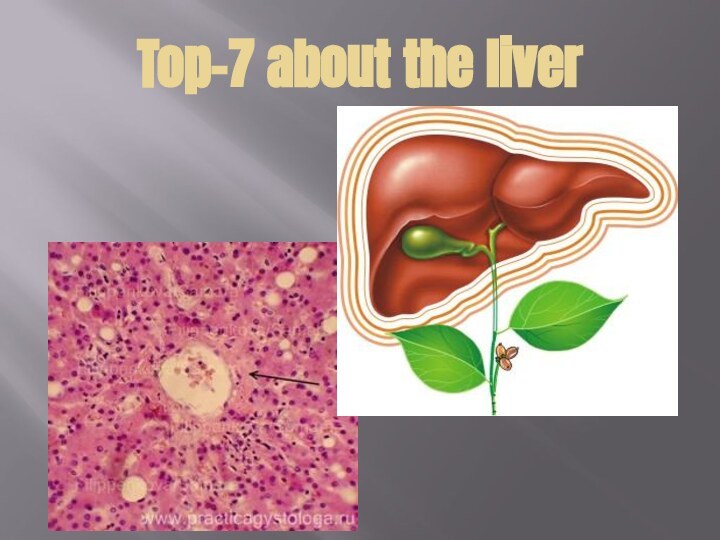
(or perisinusoidal space) is a location in the liver
between a hepatocyte and a sinusoid. It contains the blood plasma. Microvilli of hepatocytes extend into this space, allowing proteins and other plasma components from the sinusoids to be absorbed by the hepatocytes. Fenestration and discontinuity of the endothelium facilitates this transport. [1] This space may be obliterated in liver disease, leading to decreased uptake by hepatocytes of nutrients and wastes (like bilirubin, for example).The Space of Disse also contains Ito cells, also called hepatic stellate cells, which store fat or fat soluble vitamins (like vitamin A). A variety of insults that cause inflammation can result in Ito cells transforming to myofibroblasts, resulting in collagen production, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.