- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему The labour market
Содержание
- 2. Demand for labourMarginal Revenue ProductProductivitySupply of LabourThe factors influencing wage differentials
- 3. The market for a factor of production
- 4. Demand for LabourInfluenced by:Cost of hiring labourWages/salariesNational
- 5. Marginal Revenue ProductMRP = MPP x PMPP = Marginal Physical Product
- 6. DLThe demand for labour is downward sloping
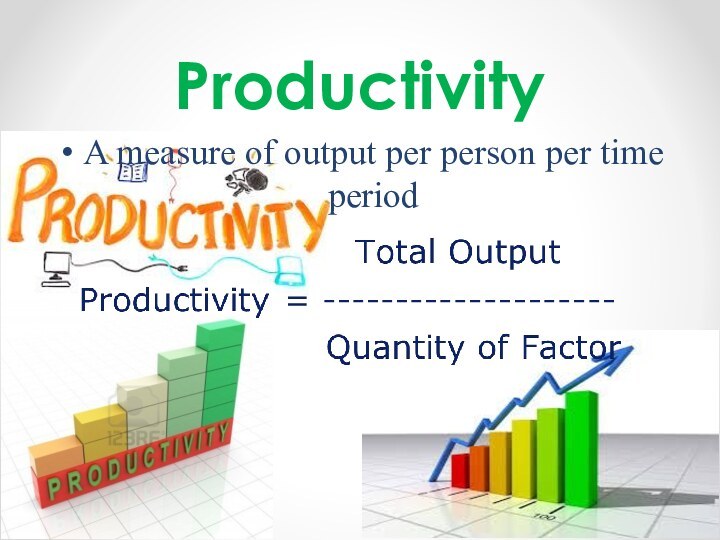
- 7. ProductivityA measure of output per person per time period
- 8. Supply of LabourThe amount of people offering their labour at different wage rates.
- 9. Supply of LabourSize and structure of the
- 10. Number EmployedDLSL30Q1Assume this is the market for
- 11. Other factors
- 13. Скачать презентацию
- 14. Похожие презентации









Слайд 2
Demand for labour
Marginal Revenue Product
Productivity
Supply of Labour
The factors
influencing wage differentials
Слайд 3 The market for a factor of production -
labour
Refers to the demand for labour – by
employers and the supply of labour (provided by potential employees)Demand for labour is a derived demand - not wanted for its own sake but for what it can contribute to production
Слайд 4
Demand for Labour
Influenced by:
Cost of hiring labour
Wages/salaries
National Insurance
contributions
Pension contributions
Administration costs associated with tax payments and adhering
to employment laws and regulations
Слайд 6
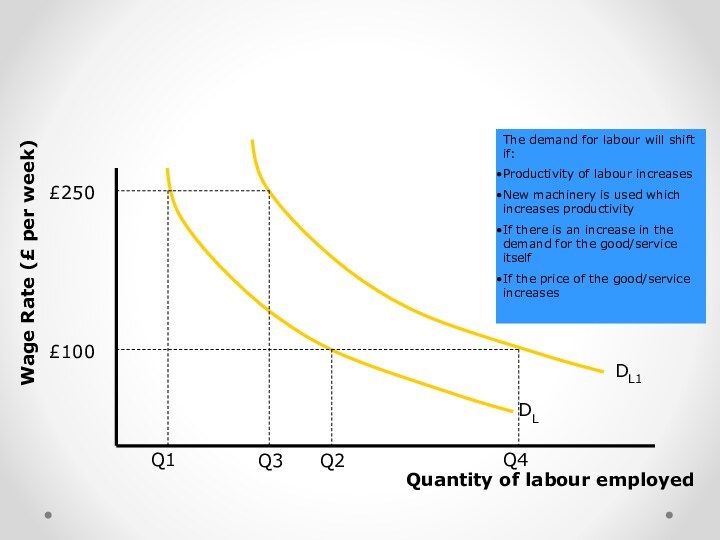
DL
The demand for labour is downward sloping from
left to right
£250
Q1
At a relatively high wage rate of
£250 per week, the value added by the worker must be greater to cover the cost of hiring that labour. Demand is likely to be lower.£100
Q2
At a lower wage rate the firm can afford to take on more workers. The demand for labour is inversely related to the wage rate
DL1
Q3
Q4
The demand for labour will shift if:
Productivity of labour increases
New machinery is used which increases productivity
If there is an increase in the demand for the good/service itself
If the price of the good/service increases
Quantity of labour employed
Wage Rate (£ per week)
Слайд 9
Supply of Labour
Size and structure of the population
– age, gender, etc.
Skill levels required
Education and training
Number
in higher educationSchool leaving age
Qualification types
Fashion
Time period
Opportunity cost of work – income and substitution effects
Слайд 10
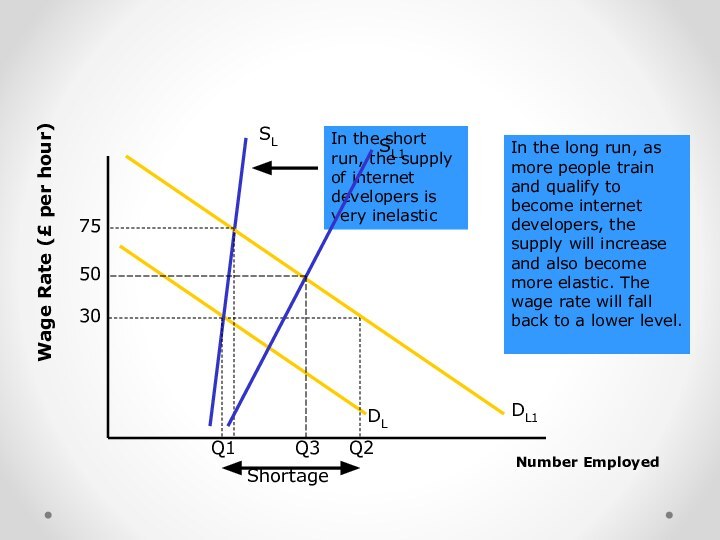
Number Employed
DL
SL
30
Q1
Assume this is the market for Internet
developers – the initial wage rate is £30 per
hourDL1
As businesses recognise the potential benefits of having a Web site, demand for their skills increases from D to D1
Q2
Shortage
The demand for developers at a wage rate of £30 per hour is now Q2 but there are still only Q1 available for employment. A shortage develops.
In the short run, the supply of internet developers is very inelastic
75
The shortage causes the wage rate to be forced up to £75 per hour as firms compete for the skills of those available. In the short run there is not the time for new workers to come onto the market because of the training time needed.
SL1
50
Q3
In the long run, as more people train and qualify to become internet developers, the supply will increase and also become more elastic. The wage rate will fall back to a lower level.
Wage Rate (£ per hour)
Слайд 11
Other factors influencing wage differentials:
Status attached to the
job
Discrimination
Race
Gender
Monopsony – a dominant buyer in the market
Sector –
public or privateTrade Union power or influence
Risk or danger involved
Social or unsocial hours
Shift patterns
Productivity





























