- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему It’s a network. (Chapter 11)
Содержание
- 2. Chapter 1111.0 Introduction11.1 Create and Grow11.2 Keeping
- 3. Chapter 11: ObjectivesUpon completion of this chapter,
- 4. Chapter 11: Objectives (Cont.)Use the basic host
- 5. 11.1 Create and Grow
- 6. Devices in a Small Network Small Network TopologiesTypical, Small Network Topology
- 7. Devices in a Small Network Device Selection
- 8. Devices in a Small Network Addressing
- 9. Devices in a Small Network Redundancy
- 10. Devices in a Small Network Design
- 11. Protocols in a Small Network Common
- 12. Protocols in a Small Network Common Protocols
- 13. Protocols in a Small Network Real-Time Applications
- 14. Growing to Larger Networks Scaling a Small
- 15. Growing to Larger Networks Protocol Analysis of
- 16. Growing to Larger Networks Evolving Protocol RequirementsNetwork
- 17. 11.2 Keeping the Network Safe
- 18. Network Device Security Measures Categories of Threats to Network SecurityCategories of Threats to Network Security
- 19. Network Device Security Measures Physical SecurityFour classes
- 20. Network Device Security Measures Types of Security VulnerabilitiesTypes of Security Weaknesses:TechnologicalConfigurationSecurity policyVulnerabilities - Technology
- 21. Vulnerabilities and Network Attacks Viruses, Worms, and
- 22. Vulnerabilities and Network Attacks Reconnaissance Attacks
- 23. Vulnerabilities and Network Attacks Access Attacks
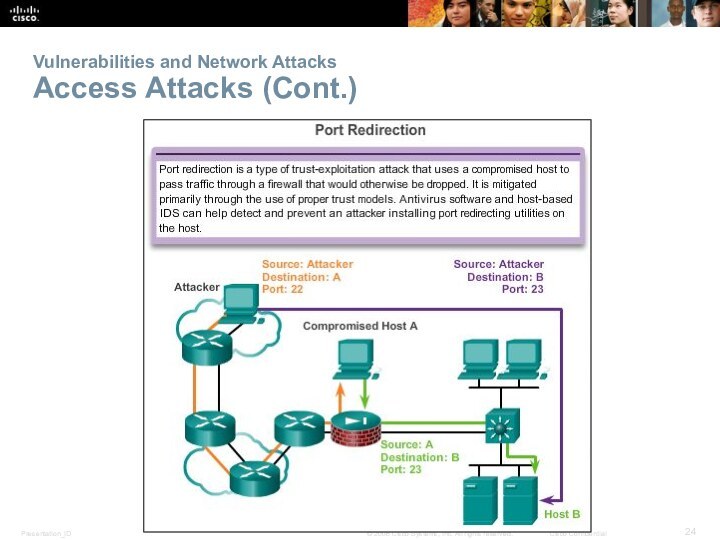
- 24. Vulnerabilities and Network Attacks Access Attacks (Cont.)
- 25. Vulnerabilities and Network Attacks Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
- 26. Mitigating Network Attacks Backup, Upgrade, Update,
- 27. Mitigating Network Attacks Authentication, Authorization, and
- 28. Mitigating Network Attacks FirewallsA Firewall resides
- 29. Mitigating Network Attacks Endpoint SecurityCommon endpoints
- 30. Securing Devices Introduction to Securing DevicesPart
- 31. Securing Devices PasswordsWeak and Strong Passwords
- 32. Securing Devices Basic Security PracticesEncrypt passwords.Require
- 33. Securing Devices Enabling SSHEnabling SSH
- 34. 11.3 Basic Network Performance
- 35. Ping Interpreting ICMP Messages! – indicates receipt
- 36. Ping Leveraging Extended PingThe Cisco IOS offers
- 37. Ping Network BaselineBaseline with ping
- 38. Ping Network Baseline (Cont.)
- 39. Tracert Interpreting Tracert Messages
- 40. Show Commands Common Show Commands RevisitedThe status
- 41. Show Commands Viewing Router Settings With Show
- 42. Show Commands Viewing Switch Settings with Show Versionshow version Command
- 43. Host and IOS Commands ipconfig Command Optionsipconfig
- 44. Host and IOS Commands arp Command Optionsarp Command Options
- 45. Host and IOS Commands show cdp neighbors
- 46. Host and IOS Commands Using the show
- 47. 11.4 Managing IOS Configuration Files
- 48. Router and Switch File Systems Router File
- 49. Router and Switch File Systems Switch File
- 50. Backup and Restore Configuration Files Backup and Restore Using Text Files
- 51. Backup and Restore Configuration Files Backup
- 52. Backup and Restore Configuration Files Using
- 53. Backup and Restore Configuration Files Backup and Restore Using USBBackup to USB Drive
- 54. 11.5 Summary
- 55. Chapter 11: SummaryIn this chapter, you learned:Good
- 56. Скачать презентацию
- 57. Похожие презентации
Chapter 1111.0 Introduction11.1 Create and Grow11.2 Keeping the Network Safe11.3 Basic Network Performance11.4 Managing IOS Configuration Files11.5 Summary























































Слайд 3
Chapter 11: Objectives
Upon completion of this chapter, you
will be able to:
Identify the devices and protocols used
in a small network.Explain how a small network serves as the basis of larger networks.
Explain the need for basic security measures on network devices.
Identify security vulnerabilities and general mitigation techniques.
Use the output of ping and tracert commands to establish relative network performance.
Use basic show commands to verify the configuration and status of a device interface.
Слайд 4
Chapter 11: Objectives (Cont.)
Use the basic host commands
to acquire information about the devices in a network.
Explain
the file systems on Routers and Switches.Apply the commands to back up and restore an IOS configuration file.
Слайд 7 Devices in a Small Network Device Selection for a
Small Network
Factors to be considered when selecting intermediate devices.
Слайд 8 Devices in a Small Network Addressing for a
Small Network
IP addressing scheme should be planned, documented, and
maintained based on the type of devices receiving the address.Examples of devices that should be part of the IP design:
End devices for users
Servers and peripherals
Hosts that are accessible from the Internet
Intermediary devices
Planned IP schemes help the administrator:
Track devices and troubleshoot
Control access to resources
Слайд 9 Devices in a Small Network Redundancy in a
Small Network
Redundancy helps to eliminate single points of failure.
Improves
the reliability of the network.Слайд 10 Devices in a Small Network Design Considerations for
a Small Network
The following should be included in the
network design:Secure file and mail servers in a centralized location.
Protect the location by physical and logical security measures.
Create redundancy in the server farm.
Configure redundant paths to the servers.
Слайд 11 Protocols in a Small Network Common Applications in
a Small Network
Network-Aware Applications – Software programs used to
communicate over the network. Application Layer Services – Programs that interface with the network and prepare the data for transfer.
Слайд 12 Protocols in a Small Network Common Protocols in a
Small Network
Network protocols define:
Processes on either end of a
communication sessionTypes of messages
Syntax of the messages
Meaning of informational fields
How messages are sent and the expected response
Interaction with the next lower layer
Слайд 13 Protocols in a Small Network Real-Time Applications for a
Small Network
Infrastructure – Should be evaluated to ensure it
supports proposed real-time applications.VoIP – Is implemented in organizations that still use traditional telephones.
IP telephony – The IP phone performs voice-to-IP conversions.
Real-time video protocols – Use the Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and the Real-Time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP).
Слайд 14
Growing to Larger Networks
Scaling a Small Network
Important considerations
when growing to a larger network:
Documentation – Physical and
logical topology.Device inventory – List of devices that use or comprise the network.
Budget – Itemized IT budget, including fiscal year equipment purchasing budget.
Traffic Analysis – Protocols, applications, services, and their respective traffic requirements should be documented.
Слайд 15 Growing to Larger Networks Protocol Analysis of a Small
Network
Information gathered by protocol analysis can be used to
make decisions on how to manage traffic more efficiently.
Слайд 16
Growing to Larger Networks
Evolving Protocol Requirements
Network administrator can obtain
IT “snapshots” of employee application utilization.
Snapshots track network utilization
and traffic flow requirements.Snapshots help inform network modifications needed to optimize employee productivity.
Слайд 18 Network Device Security Measures Categories of Threats to Network
Security
Categories of Threats to Network Security
Слайд 19
Network Device Security Measures
Physical Security
Four classes of physical
threats are:
Hardware threats – Physical damage to servers, routers, switches,
cabling plant, and workstations.Environmental threats – Temperature extremes (too hot or too cold) or humidity extremes (too wet or too dry).
Electrical threats – Voltage spikes, insufficient supply voltage (brownouts), unconditioned power (noise), and total power loss.
Maintenance threats – Poor handling of key electrical components (electrostatic discharge), lack of critical spare parts, poor cabling, and poor labeling.
Слайд 20
Network Device Security Measures
Types of Security Vulnerabilities
Types of
Security Weaknesses:
Technological
Configuration
Security policy
Vulnerabilities - Technology
Слайд 21
Vulnerabilities and Network Attacks
Viruses, Worms, and Trojan Horses
Virus
– Malicious software that is attached to another program
to execute a particular unwanted function on a workstation.Trojan horse – An entire application written to look like something else, when in fact it is an attack tool.
Worms – Worms are self-contained programs that attack a system and try to exploit a specific vulnerability in the target. The worm copies its program from the attacking host to the newly exploited system to begin the cycle again.
Слайд 26
Mitigating Network Attacks
Backup, Upgrade, Update, and Patch
Keep
current with the latest versions of antivirus software.
Install
updated security patches.Antivirus software can detect most viruses and many Trojan horse applications and prevent them from spreading in the network.
Слайд 27
Mitigating Network Attacks
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Authentication, Authorization,
and Accounting (AAA, or “triple A”)
Authentication – Users and
administrators must prove their identity. Authentication can be established using username and password combinations, challenge and response questions, token cards, and other methods.Authorization – Determines which resources the user can access and the operations that the user is allowed to perform.
Accounting – Records what the user accessed, the amount of time the resource is accessed, and any changes made.
Слайд 28
Mitigating Network Attacks
Firewalls
A Firewall resides between two
or more networks. It controls traffic and helps prevent
unauthorized access. Methods used are:Packet Filtering
Application Filtering
URL Filtering
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) – Incoming packets must be legitimate responses to requests from internal hosts.
Firewalls
Слайд 29
Mitigating Network Attacks
Endpoint Security
Common endpoints are laptops,
desktops, servers, smart phones, and tablets.
Employees must follow the
companies documented security policies to secure their devices.Policies often include the use of anti-virus software and host intrusion prevention.
Common Endpoint Devices
Слайд 30
Securing Devices
Introduction to Securing Devices
Part of network
security is securing devices, including end devices and intermediate
devices.Default usernames and passwords should be changed immediately.
Access to system resources should be restricted to only the individuals that are authorized to use those resources.
Any unnecessary services and applications should be turned off and uninstalled, when possible.
Update with security patches as they become available.
Слайд 32
Securing Devices
Basic Security Practices
Encrypt passwords.
Require minimum length
passwords.
Block brute force attacks.
Use Banner Message.
Set EXEC timeout.
Securing
Devices
Слайд 35
Ping
Interpreting ICMP Messages
! – indicates receipt of an
ICMP echo reply message
. – indicates a time expired
while waiting for an ICMP echo reply messageU – an ICMP unreachable message was received
Слайд 36
Ping
Leveraging Extended Ping
The Cisco IOS offers an "extended"
mode of the ping command:
R2# ping
Protocol [ip]:
Target IP address: 192.168.10.1
Repeat count
[5]:Datagram size [100]:
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Extended commands [n]: y
Source address or interface: 10.1.1.1
Type of service [0]:
Слайд 40
Show Commands
Common Show Commands Revisited
The status of nearly
every process or function of the router can be
displayed using a show command.Frequently used show commands:
show running-config
show interfaces
show arp
show ip route
show protocols
show version
Слайд 41
Show Commands
Viewing Router Settings With Show Version
Cisco
IOS Version
System Bootstrap
Cisco IOS Image
CPU and RAM
Configuration Register
Number and
Type of Physical Interfaces Amount of NVRAM
Amount of Flash
Слайд 43
Host and IOS Commands
ipconfig Command Options
ipconfig – Displays
ip address, subnet mask, default gateway.
ipconfig /all – Also
displays MAC address.ipconfig /displaydns – Displays all cached dns entries in a Windows system.
Слайд 45
Host and IOS Commands
show cdp neighbors Command Options
show
cdp neighbors command provides information about each directly connected
CDP neighbor device.Слайд 46 Host and IOS Commands Using the show ip interface
brief Command
The show ip interface brief command verifies the
status of all network interfaces on a router or a switch.
Слайд 48
Router and Switch File Systems
Router File Systems
show file
systems command – Lists all of the available file systems
on a Cisco 1941 route.The asterisk (*) indicates this is the current default file system.
Слайд 49
Router and Switch File Systems
Switch File Systems
The show
file systems command lists all of the available file systems
on a Catalyst 2960 switch.Слайд 51 Backup and Restore Configuration Files Backup and Restore
Using TFTP
Configuration files can be stored on a Trivial
File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server.copy running-config tftp – Saves the running configuration to a TFTP server.
copy startup-config tftp – Saves the startup configuration to a TFTP server.
Слайд 52 Backup and Restore Configuration Files Using USB Interfaces
on a Cisco Router
USB flash drive must be formatted
in a FAT16 format.Can hold multiple copies of the Cisco IOS and multiple router configurations.
Allows administrator to easily move configurations from router to router.
Слайд 55
Chapter 11: Summary
In this chapter, you learned:
Good network
design incorporates reliability, scalability, and availability.
Networks must be
secured from viruses, Trojan horses, worms and network attacks.Document Basic Network Performance.
Test network connectivity using ping and traceroute.
Use IOS commands to monitor and view information about the network and network devices.
Back up configuration files using TFTP or USB.