(escapable obligation)
Obligation (inescapable)
Request; Offer
Possibility
Absence of obligation
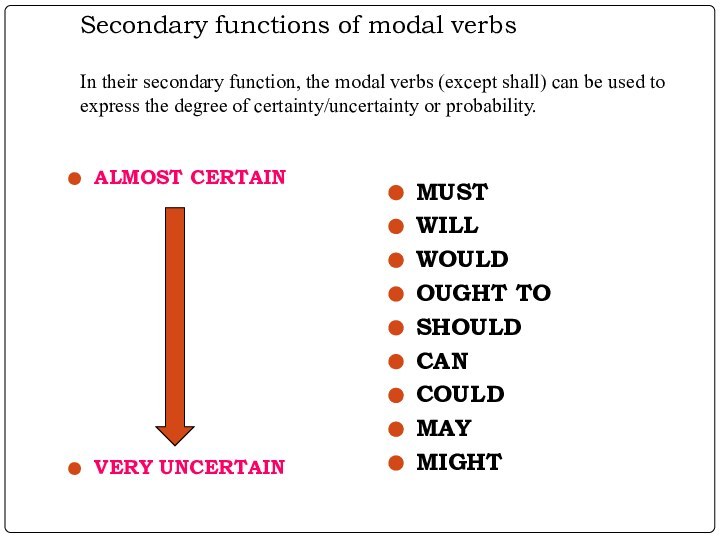
CAN
MAY (might)/ CAN
(could)MUSTN’T / CANNOT
WILL / SHALL / MAY
SHOULD
MUST
CAN / WILL
CAN / CANNOT
NEEDN’T