Слайд 4
Work analysis: any systematic gathering, documenting, and analyzing
of information about the content of work performed
Job
analysis: the process of collecting information about jobs “by any method for any purpose”
What is Work and Job Analysis?
Слайд 5
Job description: a written description of what job
occupants are required to do; how they are supposed
to do it; and the rationale for any required job procedures
Job specification: the knowledge, skills, abilities, and other attributes or competences that are needed by a job incumbent to perform well on the job
Work and Job Analysis – Key Terms
Слайд 6
Job: a collection of positions that are similar
in their significant duties
Position: a collection of duties assigned
to individuals in an organization at a given time
Job family: a set of different, but related jobs that rely on the same set of KSAOs
Work and Job Analysis – Key Terms
Слайд 7
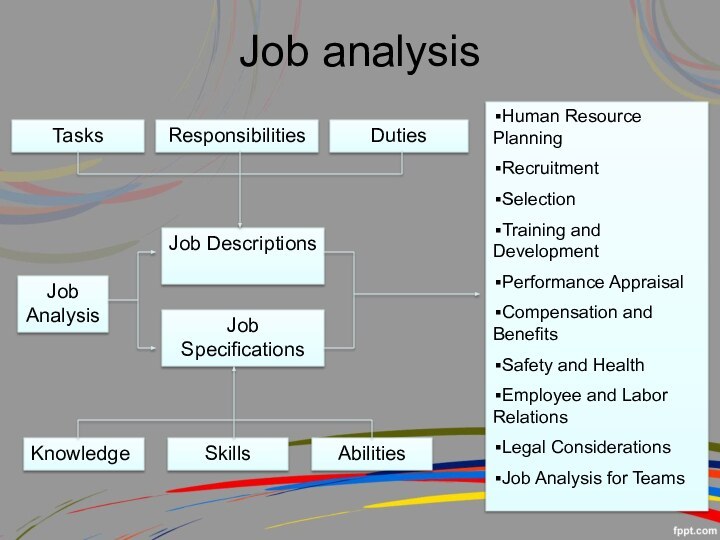
Job analysis
Tasks
Responsibilities
Duties
Job Analysis
Job Descriptions
Job Specifications
Knowledge
Skills
Abilities
Human Resource Planning
Recruitment
Selection
Training
and Development
Performance Appraisal
Compensation and Benefits
Safety and Health
Employee and
Labor Relations
Legal Considerations
Job Analysis for Teams
Слайд 8
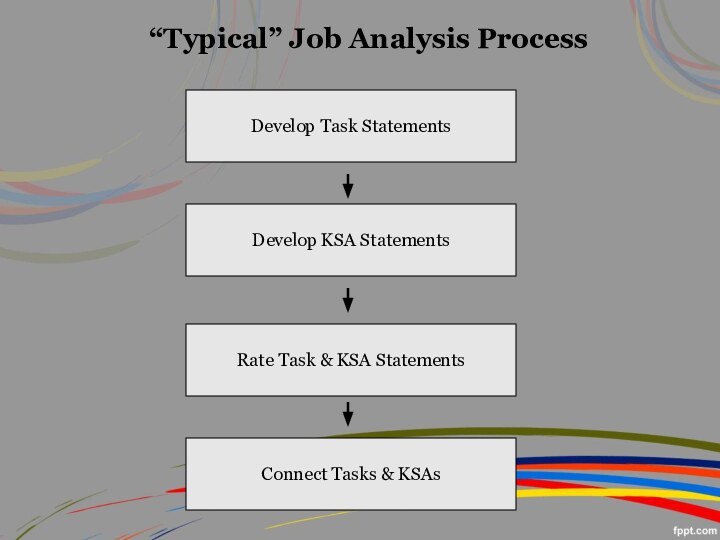
“Typical” Job Analysis Process
Develop Task Statements
Develop KSA Statements
Rate
Task & KSA Statements
Connect Tasks & KSAs
Слайд 9
Basic Methods to Collect Job Analysis Information
Interviews (Individual
or group)
Format: Individual or group with SME (Subject Matter
Experts)
SMEs: Employees and/or supervisors
Key Points:
Make purpose of the job analysis clear
Interviewers need to be trained
Use a structured format
Potential Limitations:
Employees may distort the responsibilities of their job
Supervisors may lack detailed information as to how the job is done
Слайд 10
On-Site Observation
Best used for structured jobs
Need
to get a representative sample
Need to be unobtrusive
Beneficial to use a structured format to record
observations
Note: Some suggest that it’s best to observe before conducting interviews. In some cases, observations may not be possible (e.g., safety concerns, union objections)
Слайд 11
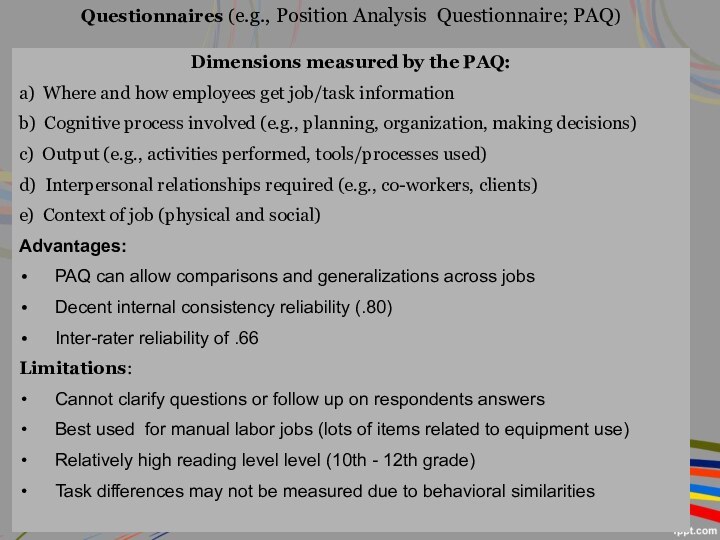
Dimensions measured by the PAQ:
a) Where and how
employees get job/task information
b) Cognitive process involved (e.g.,
planning, organization, making decisions)
c) Output (e.g., activities performed, tools/processes used)
d) Interpersonal relationships required (e.g., co-workers, clients)
e) Context of job (physical and social)
Advantages:
PAQ can allow comparisons and generalizations across jobs
Decent internal consistency reliability (.80)
Inter-rater reliability of .66
Limitations:
Cannot clarify questions or follow up on respondents answers
Best used for manual labor jobs (lots of items related to equipment use)
Relatively high reading level level (10th - 12th grade)
Task differences may not be measured due to behavioral similarities
Questionnaires (e.g., Position Analysis Questionnaire; PAQ)
Слайд 12
Job element Method
Definition of job element method (JEM
method)
Job element method is a method of job analysis,
developed by Ernest Primoff.
This method, like the critical incident technique, focuses on satisfactory workers. It attempts to identify the characteristics of satisfactory workers (job elements).
JEM method focuses on work behaviors and the results of this behavior rather than more abstract characteristics.
Слайд 13
Process of JEM method
The steps to perform a
Job Element job analysis are:
Step 1: Select a group
of experts
JEM is usually conducted by a professional analyst, who are project leader, and a team of six subject matter experts (SMEs), who are usually incumbents and supervisors.
Step 2: Conduct brainstorming sessions to identify job elements
• SMEs will make a list of element of job.
• When all of the elements have been listed, the analyst asks the SMEs to provide sub-elements. Sub-elements are specific behavioral examples that illustrate the meaning of the element
Слайд 14
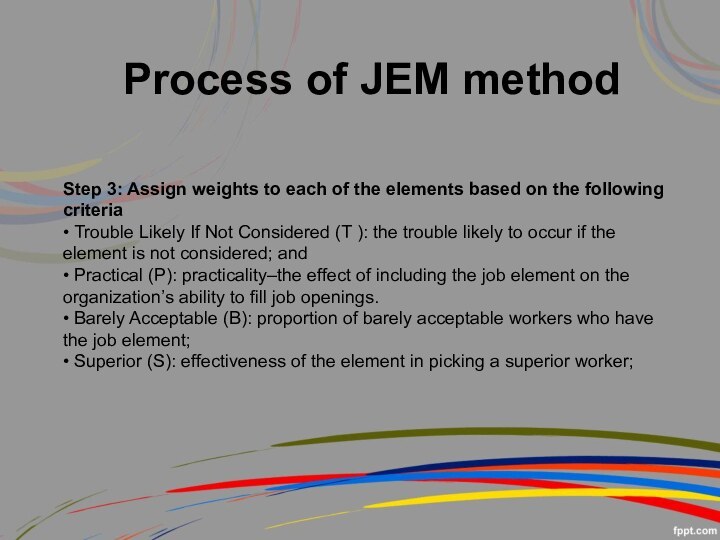
Step 3: Assign weights to each of the
elements based on the following criteria
• Trouble Likely If
Not Considered (T ): the trouble likely to occur if the element is not considered; and
• Practical (P): practicality–the effect of including the job element on the organization’s ability to fill job openings.
• Barely Acceptable (B): proportion of barely acceptable workers who have the job element;
• Superior (S): effectiveness of the element in picking a superior worker;
Process of JEM method
Слайд 15
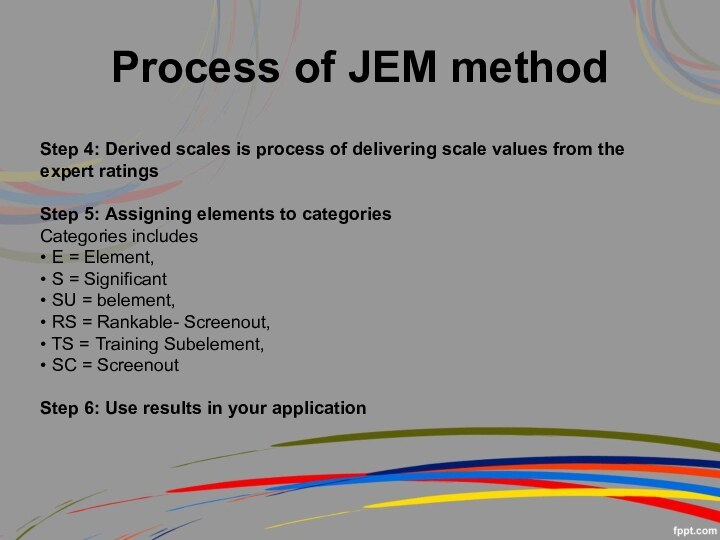
Step 4: Derived scales is process of delivering
scale values from the expert ratings
Step 5: Assigning elements
to categories
Categories includes
• E = Element,
• S = Significant
• SU = belement,
• RS = Rankable- Screenout,
• TS = Training Subelement,
• SC = Screenout
Step 6: Use results in your application
Process of JEM method
Слайд 16
Critical Incidents Technique
A worker-oriented method developed by Flanagan
(1954)
Worker oriented method of job analysis
Focuses on examples of
particularly successful/unsuccessful on-the-job behaviors
Basic Procedure:
SME’s are gathered to provide as many examples as possible.
Incidents are sorted into categories that make sense
Слайд 17
Critical Incidents Technique
Advantages: well suited for performance appraisal
Disadvantages:
focuses on extreme behaviors rather than typical behaviors, not
applied very systematically
Слайд 19
Functional job analysis: defines task statements as verbal
descriptions of activities that workers do; it is what
gets done on the job to facilitate recruitment, selection, and compensation
Functional Job Analysis
Слайд 20
Functional Job Analysis
A job-oriented method developed by Department
of Labor in the 1930’s and later refined by
Sydney Fine
Uses a variety of general methods of job analysis (e.g., interview, survey, observation)
The Dictionary of Occupational Titles was created with FJA
All jobs considered in 3 main dimensions:
Data: information, knowledge, concepts
People: amount and type of contact with people
Things: inanimate objects used on the job (MTEWA)
Слайд 21
Functional Job Analysis
Basic Procedure:
Break job down into tasks
Rate
each task in terms of Data, People, and Things
Sum
Scores to get a total composite on each dimension
Advantages: comprehensive and effective, suitable for a wide variety of purposes
Disadvantage: can be time-consuming and expensive
Слайд 22
Functional Job Analysis
Used beginning in the 1940’s
Seven scales
to describe what workers do in jobs:
(1) Things
(2)
Data
(3) People
(4) Worker Instructions
(5) Reasoning
(6) Math
(7) Language
Слайд 24
Position Analysis Questionnaire
A worker-oriented method developed by McCormick
and associates at Purdue U.
Standardized questioning containing 194 “job
elements” referring to a specific aspect of work behavior (e.g., use of measuring devices)
SME’s rate the relevance of the job elements that are organized into six categories
Слайд 25
Position Analysis Questionnaire
Advantages: can be used for any
job, good method for comparing jobs or classifying jobs,
relatively inexpensive and easy to use
Disadvantages: people may misrepresent their job, can take a lot of time to administer, must be interpreted at Purdue U., requires a high reading level
Слайд 26
Limiting Error/Bias in Job Analysis
Use multiple sources of
information about the job
Use more than one trained and
experienced analyst, if possible
Give analysts enough time to do the job right
Check and recheck information and results
Слайд 27
Job Evaluation
An assessment of the relative value of
jobs to determine appropriate compensation.
A process that allows one
to determine the financial worth of a job:
Setting wages
Determining comparable worth (whether jobs that require equivalent KSAOs are compensated equally)
Слайд 28
A Method of Job Evaluation
The Point System
Determine compensable
factors - important and common work factors across jobs
used to determine appropriate compensation (e.g., physical demands, responsibility, specialized knowledge, etc.)
Assign each job a score on each compensable factor.
Total scores on compensable factors and convert into dollar amounts.
Слайд 29
A Method of Job Evaluation
The Point System
Market value
of labor also may come into play (supply and
demand).
A wage trend line can be created by plotting point totals against current wages.
When wage discrepancy is determined, the underpaid is usually given a raise.
Exceptioning is the practice of ignoring pay discrepancies between particular jobs possessing equivalent duties and responsibilities.
Слайд 31
Common-Metric Questionnaire (CMQ)
Work Profiling System (WPS)
Threshold Traits Analysis
System
Fleishman Job Analysis Survey (F-JAS)
Cognitive Task Analysis (CTA)
Other Job
Analysis Methods
Слайд 32
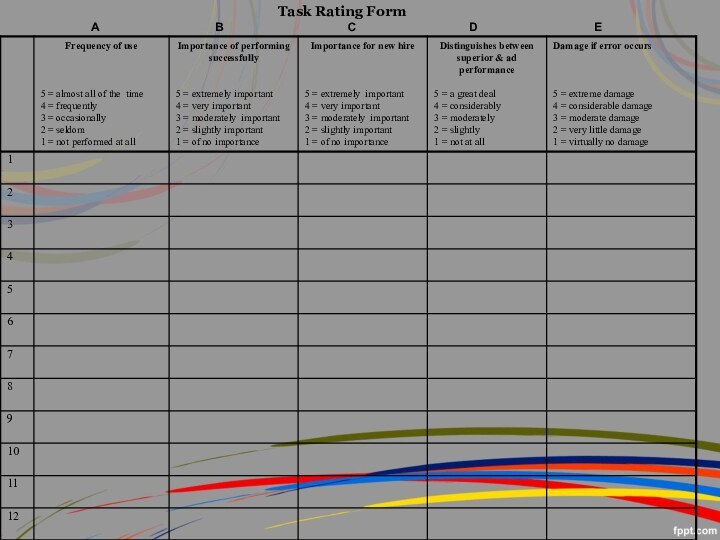
Basic Task Statement Components
1) What is the
action being performed? (using an action verb)
2) To
Whom/What is the action directed? (the object, or receiver, of the action verb)
3) How is the action performed? (e.g., use of certain procedures, equipment, tools). The “how” is arguably the most crucial part of the task statement in that it directly relates to KSAs
4) Why is the action being performed? (the purpose of the action). Often, it is preceded by words such as “in order to” or “so as to.” Be careful not to confuse the “why’ part of the statement with the “what” section
Слайд 35
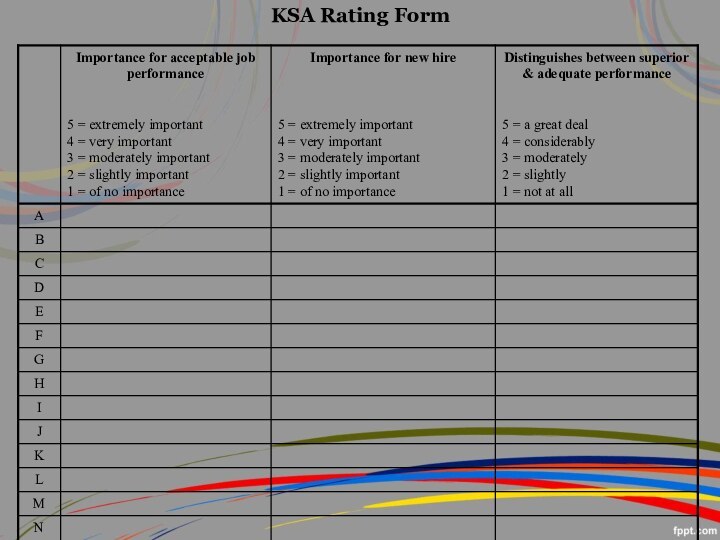
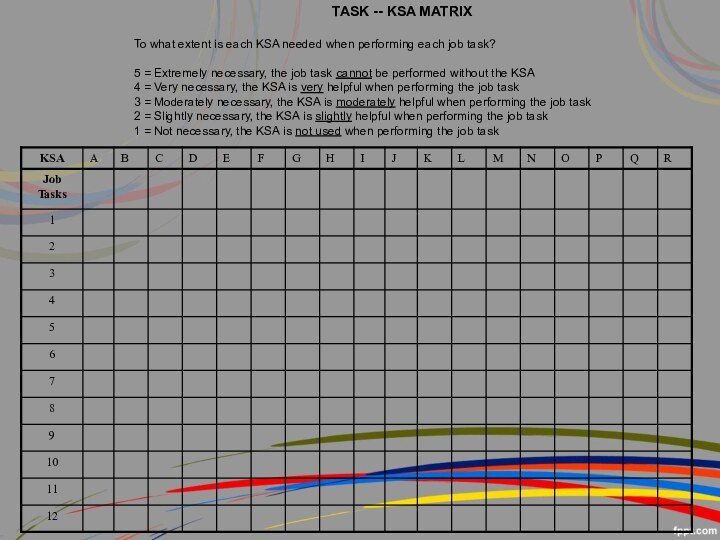
TASK -- KSA MATRIX
To what extent is each
KSA needed when performing each job task?
5 = Extremely
necessary, the job task cannot be performed without the KSA
4 = Very necessary, the KSA is very helpful when performing the job task
3 = Moderately necessary, the KSA is moderately helpful when performing the job task
2 = Slightly necessary, the KSA is slightly helpful when performing the job task
1 = Not necessary, the KSA is not used when performing the job task
Слайд 36
Kirkland v. Department of Correctional Services (1974)
"Without such
an analysis (job analysis) to single out the critical
knowledge, skills and abilities required by the job, their importance relative importance to each other, and the level of proficiency demanded as to each attribute, a test constructor is aiming in the dark and can only hope to achieve job relatedness by blind luck”
The KSAs tested for must be critical to successful job performance
Portions of the exam should be accurately weighted to reflect the relative importance to the job of the attributes for which they test
c) The level of difficulty of the exam material should match the level of difficulty of the job
Слайд 37
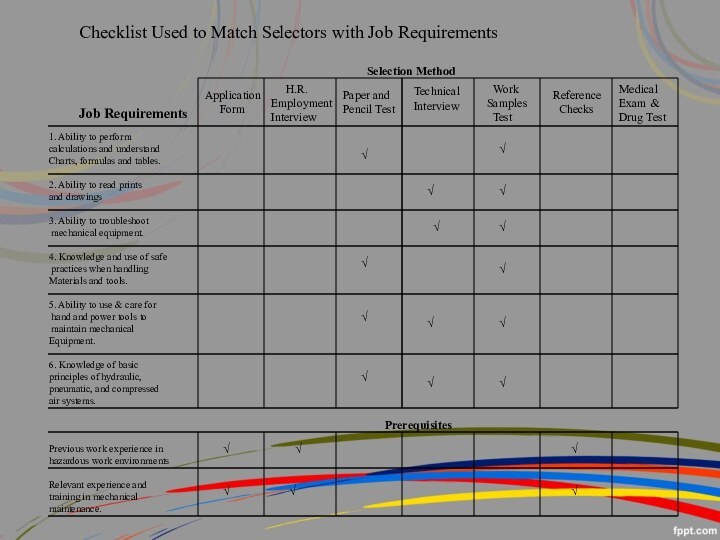
Checklist Used to Match Selectors with Job Requirements
Job
Requirements
1. Ability to perform
calculations and understand
Charts, formulas and tables.
2.
Ability to read prints
and drawings
3. Ability to troubleshoot
mechanical equipment.
4. Knowledge and use of safe
practices when handling
Materials and tools.
5. Ability to use & care for
hand and power tools to
maintain mechanical
Equipment.
6. Knowledge of basic
principles of hydraulic,
pneumatic, and compressed
air systems.
Previous work experience in
hazardous work environments
Relevant experience and
training in mechanical
maintenance.
Application
Form
H.R.
Employment
Interview
Paper and
Pencil Test
Technical
Interview
Work
Samples
Test
Reference
Checks
Medical
Exam &
Drug Test
Selection Method
Prerequisites
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
Слайд 38
Competency Modeling
[What is a competency?]
SME group in Schippman
et al (2000)
Recent definitions in the literature
Слайд 39
Traditional job analysis versus competency modeling
Overall, job
analysis is more rigorous on a multitude of criteria
(e.g., type of content, detail, data collection methods, ranking/prioritizing content)
Competency modeling was judged to be superior on “linking
research results to business goals”
>>> So, competency modeling may not be an adequate substitute for job analysis

























![Job analysis. Organizational psychology Competency Modeling[What is a competency?]SME group in Schippman et al (2000)Recent definitions in the literature](/img/tmb/15/1455381/3475b3e5964f2a078a39fbf190d514b0-720x.jpg)

