activities, that are involved in producing and delivering a
product or service to anywhere in the worldTypical Facilities:
Warehouses, Factories, Distribution Centers, Wholesalers, Resellers, Retail outlets
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть


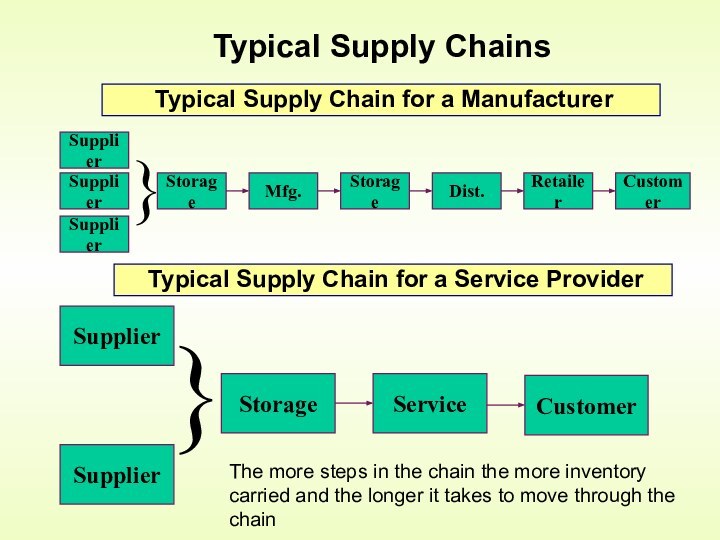






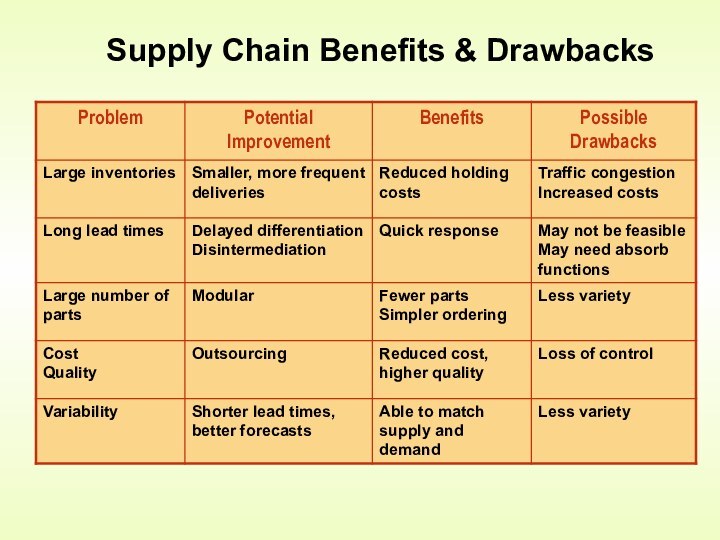







Need for Supply Chain Management
Outsourcing: Buying goods or services instead of producing or providing them in house
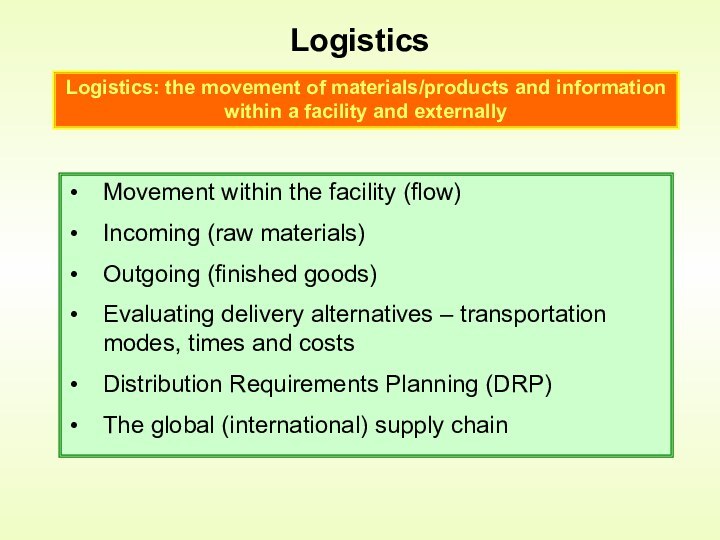
Logistics: the movement of materials/products and information within a facility and externally
Distribution Requirements Planning
Distribution Requirements Planning
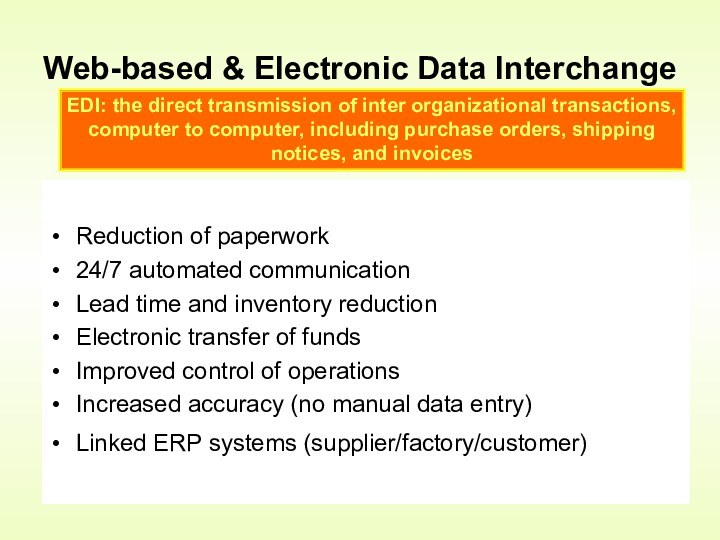
Web-based & Electronic Data Interchange
EDI: the direct transmission of inter organizational transactions, computer to computer, including purchase orders, shipping notices, and invoices
Advantages of E-Commerce
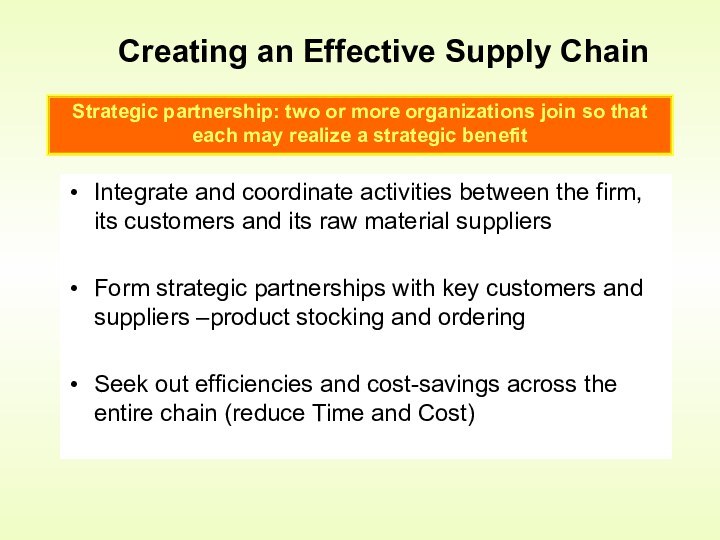
Creating an Effective Supply Chain
Strategic partnership: two or more organizations join so that each may realize a strategic benefit
Supply Chain Performance Metrics
Purchasing
Purchasing Cycle
Select an item that has a high annual dollar value. This can be a part, component, or product.
Identify the function of the item
Obtain answers to these kinds of questions
Can the function be performed in another way?
Could another material or part be used?
Can specifications be less stringent to save cost or time?
Can two or more parts of the item be combined?
Can a different process be used on the item to save cost or time?
Do supplier/providers have suggestions for improvements?
Can packaging be improved or made less costly?
Evaluate the answers obtained, and make recommendations
Make or Buy
Determining Prices