Слайд 2
Plan of the lecture
1. Definition of Rickets
2.
Biological activity of VitD metabolites
3. Exogene and endogene reasons
of Vit D deficiencies
4. Rickets classification
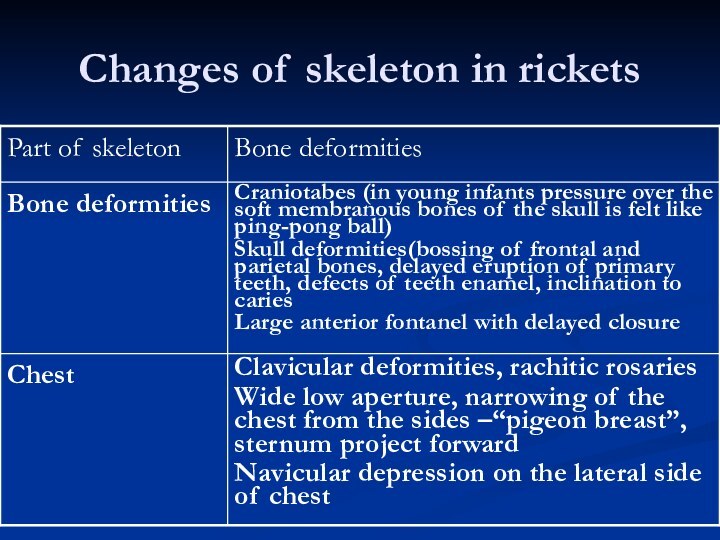
5. Changes of skeleton in rickets
6. Treatment fnd prevention of rickets
7. Hypervitaminosis D
8. Spasmophilia
Слайд 3
Rickets is the disease of growing organism characterized
by metabolism impairment, especially of phosphorus-calcium content abnormality that
leads for bone formation, bone growths mineralization failure.
Слайд 4
Necessity of Vit D
Vit D activity is measured
in IU. One IU contains 0,025 mcg of Vit
D. 400 IU contain 10 mcg of Vit D
Слайд 5
Biological activity of VitD metabolites
Enhancing of intestine
Ca absorbtion
Active Ca and P reabsorbtion in kidney
Mineralization
of cartilages and bone formation
Bone collagen and bone proteins synthesis activation ( osteocalcin, osteopontine)
Bone resorbtion stimulation
Immune response modulation, phagocytosis activation
Слайд 6
Vit D deficiency consequences
Слайд 7
Rickets predisposing factors
Слайд 8
Exogene reasons of Vit D deficiencies
Lack of
Vit D consumption with food. Poor containing of products
in diet that are rich in VitD ( yolk, fish, oil, milk, butter, liver)
Deficiency of insolation and rare outdoors walks that leads to poor production of Vit D in skin under influence of sun beams (UV spectrum 280-310 nm)
Inproper intake of phosphates and Ca with food
Слайд 9
Endogene reasons of Vit D deficiency
Malabsorption of Vit
D in intestine
Hydroxylation of Vit D precursors impairment into
active metabolites in liver, kidneys due to chronic diseases of theses organs
Genetic or inherited abnormalities of Vit D synthesizing process
Outstanding loosing of Ca and P by kidneys into urine or impairment of bone absorption of Ca and P.
Absence or degradation of Vit D receptors functional activity.
Слайд 10
Risk group of Vit D deficiency
Premature children with
low body weight
Neonates with signs of immaturity
Malabsorbtion syndrome (
celiac disease, food allergy, exudative enteropathy)
Convulsions that demand specific therapy (anticonvulsants)
Decreasing of motion activity ( paresis, paralysis, prolonged immobilization)
Chronic pathology of liver, bile ducts
Frequent respiratory pathology
Children fed by nonadapted formula
Abused by inherited abnormalities of Ca-P metabolism
Twins or neonates from pregnancies with short period between them.
Слайд 12
Criteria of rickets’ severity
!-st degree rickets is characterized
predominantly by neuro-muscular abnormalities and minimal disturbances of bone
formation (craniotabes, occiput flattening, minimal tissue signs in growing zones of metaphysic
2-nd degree rickets ( moderate) – beside neuro-muscular dystonia bone deformities of sculp, chest and limbs are present, moderate functional changes of inner organs
3-d degree rickets (severe) – prominent bone and muscular abnormalities, articular hypermobility, static and locomotor function retardation, impairment of inner organs function due to acidosis and concomitant microvasculature changes
Слайд 13
Criteria of rickets’ course
Acute course – prompt development
of all symptoms, clear neurologic and vegetative disorders, significant
hypophosphatemia, high level of alkaline phosphatase, osteomalacia symptoms prevelance
Subacute course –moderate and vague neurologic and vegetative abnormalities, not significant biochemical changes, osteoid hyperplasia predominance
Recurrent course – typical periods of exacerbation and remission with residual signs. X-ray reveals in methaphysis several calcification lines
Слайд 14
Criteria of rickets period
Initial period – signs of
disease can be seen in 2-3 mo old child
9 in premature children at the end of first mo). Behavior of child changes. He becomes irritated, jerky. Neuro-vegetative symptoms become visible. Ca level is slightly elevated or normal ( N-2,37-2,62 mmols/l), P level is decreased (N- 1,45-1,77 mmols/l), alkaline phosphatase is slightly elevated, acidosis is present, hyperphosphateuria, hyperaminoaciduria can be find. Initial period elongation in rickets acute course can be 2-6 weeks, in subacute course – 2-3 month
Слайд 15
Criteria of rickets period
Swing period ( clinically
obvious) (6 mo of life) – is characterized by
more prominent neuro-muscular and vegetative disorders, retrardation of psychomotor and somatic development, visible skeletal disorders especially in growing zones of bones. Hypophosphatemia become obvious, moderate hypocalcaemia, elevated level of alkaline phosphatase
Слайд 16
Criteria of rickets period
Reconvalescence period – condition
improves, neurologic ad vegetative disorders disappear, static function improves,
new reflexes appear but muscular hypotonia and skeletal deformities can be present for long time. The levels of Ca, P, alkaline phosphatase normalize
Residual period – all reversible changes in skeleton disappear ( muscular hypotonia, joint and ligament dysfunction) biochemical indexes normalize, but nonreversible changes of skeleton are present (deformities, osteoid hyperplasia symptoms).
Слайд 19
Main treatment goal
Restoration of Ca-P metabolism
Normalizing of peroxydative
process in lipids
Elimination of metabolic acidosis and hypokaliemia
Elimination of
VitD deficiency
Слайд 20
Treatment must include
Proper regimen for child. Infant must
spend not less than 2-3 hours outdoors, room of
child must be aired.
Proper feeding. Diet must contain products rich in vit D and mustn’t be overloaded by wheat or semolina porridge because it absorb Ca and P and decrease it penetration through intestine
Medication with vit D
Hygienic bathing, massage, physical exercises
Слайд 21
Antinatal nonspecific prevention of rickets
Pregnant woman must spend
outdoors not less than 2-4 hours every day, must
be active, get proper diet with high containing of vit D and C and other micro and macro nutrients, proteins
Specific antenatal prophylaxis : Pregnant woman must take vit D 400-500 IU daily from 28-32 week of pregnancy beside summer month. If woman has chronic nephropathy or another extragenital pathology like diabetus mellitus, rheumatic fever, hypertension dosage of vit D increases to 1000-1500 IU daily for 8 weeks. Another way can be performed UV radiation of skin.
Слайд 22
Postnatal nonspecific preventive efforts
Consist of performing everyday massages
and exercises, walking outdoors, bathing, proper feeding ( breast
feeding is preferable. In the case of hypogalactia –proper formula feeding must substitute breast milk) Mother’s breast milk contain the most suitable quantity of Ca and P in most rational rate of these electrolytes to be absorbed in gut.
Слайд 23
Specific preventive activity
For full term children with
natural feeding vit D is proposed from 3-4 week
after birth in fall, winter period in daily dosage 400-500 IU. If child was born in spring or summer you needn’t prescribe vit D.
Premature neonates with 1 degree of immaturity are prescribed vit D 500-1000 IU from 10-14 day old for 2 mo with 2 mo intervals.
Premature neonates with 2-3 degree of immaturity must get 1000-2000IU of vit D from 10-20 day old daily for 1 year, except summer months. When they get 1 year dosage of vit D must be 500-1000 IU daily. You must also add treatment with medications of Ca and P. UV radiation can be prescribed 1-2 times per year. Course consist of 10-12 radiations starting from 1/8 biodosages of UV with steady elevation to 1,5 – 2 biolog. dosages.
Слайд 24
Rickets’ treatment
Prescribing specific treatment you must take
into account period and course of disease. Daily dosage
differs from 2000to 5000 IU for 30-45 days. After gaining therapeutic effect child is proposed preventive dosage (500IU) daily for 3 years.
Such medications can be used
Videchol (0,125% oil solution of cholecalciferolum (D3). 1 ml of solution contain 25000 IU, 1 drop – 500IU.
Vit D2 ( 0,125% oil solution of ergocalciferoli; 1 ml of it contain 50 000IU, 1 drop-1000 IU
AQUADETRIM water solution of vit D3 1 drop contain 500 IU
Слайд 25
Main biological functions of Ca in organism
Mineralization of
bones and formation of skeleton
Generate electrical potential of cell
Regulate
activity of cells, biologically active substance
Take part in integrity of organism function
Maintain normal neuro-muscular excitability and contractility
Maintain homeostasis
Activate big quantity of enzymes and biologically active substance
Слайд 26
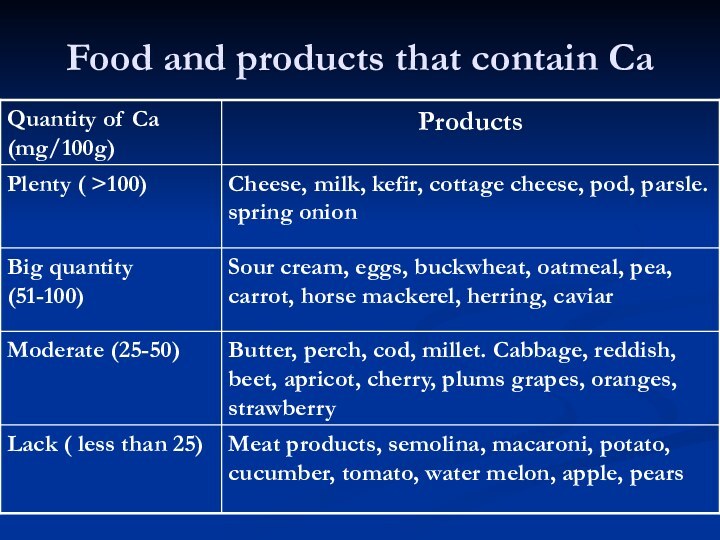
Food and products that contain Ca
Слайд 27
Contraindications for Vit D treatment
Intrapartum intracranium trauma or
hypoxia
Jaundice
Little sizes of anterior fountanella.
If child
is fed by adopted formula that contain vit D.
Слайд 28
Hyper-VitD treatment
Stop intake of Vit D
Decrease Ca intake
Eliminate
milk, cheese from diet
Plants, cereals are recommended because they
fix Vit D and Ca in intestine and help eliminate it
In severe conditions is recommended IV injections of albumin, 5% solution of glucose, Ringer solution, Vit C. Prednisone (2 mg/kg) is recommended. It can decrease absorbtion of Ca from intestine and induce resorbtion of Ca from bone and thus accelerate loses of this macroelement from organism.
Слайд 29
Vit D antagonists
Vit A
- Vit E
Furosemide (1 mg/kg)
Myocalcic
(synthetic thyrocalcitonin – 5-10 U/kg IV)
Слайд 30
Medication that bind Ca in intestine
Cholestiramine (o,5 g/kg
bid)
Almagel (50-100 mg/kg daily)
Trilon B (50 mg/kg daily IV
)
Слайд 31
Diagnostic approach
Principle approach is monitoring of ionized Ca
( normal one is 1,1-1,4 mmols/l; in spasmophilia less
than 0,85 mmol/l)
Decreasing of common Ca level ( less than 1,75 mmols/l)
ECG –elongation of QT and ST intervals
Metabolic alkalosis
Слайд 32
Spasmophilia treatment
Latent form
Regimen normalization
Diet restrict of cow milk
and milkfish products
Ca containing medication
Necessity of Ca in infants
is 50-55 mg/kg daily
Neonates -400mg daily
Infants – 600 mg
Children from 1 to 5 years old – 800-1200 mg
Adolescents – 1200-15000mg
Adults -1000-1200-1500 mg
Слайд 33
To restore Ca level can be used
10% solution
of Ca gluconates ( I ml of solution contain
9 mg of CA)
5% sol. Of Ca gluconatis, Ca lactis
To eliminate alkalosis by 10% sol. Of ammonii chloride ( 1 teaspoon tid)