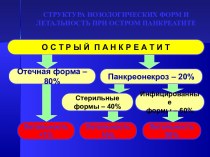
- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Injury of genitourinary organs
Содержание
- 2. Emergency Diagnosis & ManagementAbout 10% of all
- 3. Many of them are subtle and difficult
- 4. Emergency Diagnosis & ManagementInitial assessment should include
- 5. Emergency Diagnosis & ManagementThe history should include
- 6. Emergency Diagnosis & ManagementThe abdomen and genitalia
- 7. Fractures of the lower ribs are often
- 8. Patients who do not have life-threatening injuries
- 9. Emergency Diagnosis & ManagementWhen genitourinary tract injury
- 10. Assessment of Injury Assessment of the injury
- 11. Catheterization Blood at the urethral meatus in
- 12. CatheterizationIf no blood is present at the
- 13. CatheterizationIf catheterization is traumatic despite the greatest
- 14. Computed Tomography (CT)Abdominal CT with contrast media
- 15. Computed Tomography (CT)It can define the size extent of the retroperitoneal hematoma
- 16. Computed Tomography (CT)Spiral CT scanning, now common,
- 17. Retrograde CystographyFilling of the bladder with contrast
- 18. Retrograde CystographyA film should be obtained with
- 19. Retrograde CystographyCystography with CT is excellent for establishing bladder injury.
- 20. UrethrographyA small (12F) catheter can be inserted
- 21. Urethrography After retrograde injection of 20
- 22. ArteriographyArteriography may help define renal parenchymal and renal vascular injuries.
- 23. Intravenous UrographyIntravenous urography can be used to detect renal and ureteral injury.
- 24. Cystoscopy and Retrograde UrographyCystoscopy and retrograde urography
- 25. Abdominal SonographyAbdominal sonography has not been shown
- 26. Injuries to the KidneyRenal injuries are the most common injuries of the urinary system.
- 27. Injuries to the KidneyMost injuries occur from
- 28. Injuries to the KidneyEtiologyBlunt trauma directly to
- 29. Injuries to the KidneyVehicle collisions at high
- 30. Injuries to the KidneyAssociated abdominal visceral injuries are present in 80% of renal penetrating wounds.
- 31. Pathology & Classification Early Pathologic FindingsLacerations
- 32. Pathology & Classification Early Pathologic FindingsIn
- 33. Pathology & Classification Early Pathologic FindingsAcute
- 34. Pathology & Classification HydronephrosisFollow-up excretory
- 35. Pathology & Classification Arteriovenous FistulaArteriovenous
- 36. Pathology & Classification Renal Vascular
- 37. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesMicroscopic or
- 38. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesSome cases
- 39. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesThe degree
- 40. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesMiller and
- 41. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesHowever, should
- 42. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesSymptomsThere is
- 43. Clinical Findings & Indications for StudiesCatheterization usually reveals hematuria.
- 44. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 45. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 46. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies SignsThe abdomen may be distended and bowel sounds absent.
- 47. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Laboratory FindingsMicroscopic or gross hematuria is usually present.
- 48. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 49. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 50. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 51. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 52. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 53. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 54. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 55. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 56. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 57. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 58. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 59. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 60. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 61. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 62. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies ComplicationsHeavy late bleeding may occur 4 weeks after injury.
- 63. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 64. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 65. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 66. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 67. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 68. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 69. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 70. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 71. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 72. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 73. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 74. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 75. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 76. Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
- 77. Clinical Findings SymptomsIf the ureter has been
- 78. Clinical Findings SymptomsUreteral injuries from external violence
- 79. Clinical Findings SymptomsSignsThe acute hydronephrosis of a
- 80. Clinical Findings SymptomsWatery discharge from the wound
- 81. Laboratory FindingsUreteral injury from external violence is manifested by microscopic hematuria in 90% of cases.
- 82. Imaging FindingsDiagnosis is by excretory urography.
- 83. Imaging FindingsPartial transection of the ureter results
- 84. Imaging FindingsIn acute injury from external violence,
- 85. Ultrasonography Ultrasonography outlines hydroureter or urinary extravasation
- 86. Radionuclide ScanningRadionuclide scanning demonstrates delayed excretion on
- 87. Differential Diagnosis Postoperative bowel obstruction and peritonitis
- 88. Differential DiagnosisDeep wound infection must be considered
- 89. Differential DiagnosisAcute pyelonephritis in the early postoperative
- 90. ComplicationsUreteral injury may be complicated by stricture
- 91. Treatment Prompt treatment of ureteral injuries is
- 92. TreatmentProximal urinary drainage by percutaneous nephrostomy or
- 93. TreatmentThe goals of ureteral repair are to
- 94. Lower Ureteral InjuriesInjuries to the lower third of the ureter allow several options in management.
- 95. Lower Ureteral InjuriesAn antireflux procedure should be done when possible.
- 96. Lower Ureteral InjuriesTransureteroureterostomy may be used in
- 97. Midureteral InjuriesMidureteral injuries usually result from external
- 98. Upper Ureteral InjuriesInjuries to the upper third
- 99. Stenting Most anastomoses after repair of ureteral injury should be stented.
- 100. Stenting After 3-4 weeks of healing, stents can be endoscopically removed from the bladder.
- 101. Prognosis The prognosis for ureteral injury is
- 102. Injuries to the BladderBladder injuries occur most
- 103. Injuries to the BladderIatrogenic injury may result
- 104. Injuries to the Bladder Pathogenesis &
- 105. Injuries to the Bladder Pathogenesis & PathologyWhen
- 106. Injuries to the Bladder Pathogenesis & PathologyIf
- 107. Injuries to the Bladder Clinical FindingsPelvic fracture accompanies bladder rupture in 90% of cases.
- 108. Injuries to the Bladder Symptoms There is usually a history of lower abdominal trauma.
- 109. Injuries to the Bladder SignsHeavy bleeding
- 110. Injuries to the Bladder SignsAn acute abdomen may occur with intraperitoneal bladder rupture.
- 111. Injuries to the Bladder Laboratory FindingsCatheterization
- 112. Injuries to the Bladder Laboratory FindingsWhen
- 113. Injuries to the Bladder X-Ray FindingsA plain abdominal film generally demonstrates pelvic fractures.
- 114. Injuries to the Bladder X-Ray FindingsBladder disruption is shown on cystography.
- 115. Injuries to the Bladder X-Ray FindingsThe
- 116. Injuries to the Bladder X-Ray FindingsCT
- 117. Injuries to the Bladder X-Ray FindingsIncomplete
- 118. Injuries to the Bladder ComplicationsA pelvic
- 119. Injuries to the Bladder ComplicationsPartial incontinence
- 120. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentEmergency MeasuresShock and hemorrhage should be treated.
- 121. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentSurgical MeasuresA lower midline abdominal incision should be made.
- 122. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentThe bladder
- 123. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentExtraperitoneal Bladder
- 124. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentAs the
- 125. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentExtraperitoneal bladder
- 126. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentIntraperitoneal RuptureIntraperitoneal
- 127. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentThe bladder
- 128. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentPelvic FractureStable fracture of the pubic rami is usually present.
- 129. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentPelvic HematomaThere
- 130. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentIf bleeding
- 131. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentPrognosisWith appropriate treatment, the prognosis is excellent.
- 132. Injuries to the Bladder TreatmentPatients with
- 133. Injuries to the UrethraUrethral injuries are uncommon
- 134. Injuries to the UrethraVarious parts of the urethra may be lacerated, transected, or contused.
- 135. Injuries to the Posterior UrethraEtiologyThe membranous urethra
- 136. Injuries to the Posterior UrethraThe urethra can
- 137. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Clinical
- 138. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Clinical
- 139. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Clinical
- 140. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Clinical
- 141. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Clinical
- 142. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Clinical
- 143. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra X-Ray
- 144. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra X-Ray
- 145. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Instrumental ExaminationThe only instrumentation involved should be for urethrography.
- 146. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra Differential
- 147. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra ComplicationsStricture,
- 148. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra ComplicationsStricture
- 149. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra ComplicationsThe
- 150. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentEmergency MeasuresShock and hemorrhage should be treated.
- 151. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentSurgical MeasuresUrethral catheterization should be avoided.
- 152. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentImmediate
- 153. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentThe
- 154. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentThe
- 155. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentThis approach involves no urethral instrumentation or manipulation.
- 156. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentIncomplete
- 157. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentDelayed
- 158. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentThis
- 159. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentA
- 160. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentImmediate
- 161. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentGeneral
- 162. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentTreatment
- 163. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentIf
- 164. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentStricture,
- 165. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentThe
- 166. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentIncontinence
- 167. Injuries to the Posterior Urethra TreatmentPrognosisIf complications can be avoided, the prognosis is excellent.
- 168. Injuries to the Anterior UrethraEtiologyThe anterior urethra is the portion distal to the urogenital diaphragm.
- 169. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Pathogenesis
- 170. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Pathogenesis
- 171. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Clinical
- 172. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Clinical
- 173. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Clinical
- 174. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Clinical
- 175. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Clinical
- 176. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra Laboratory
- 177. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra X-Ray FindingsA contused urethra shows no evidence of extravasation.
- 178. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra ComplicationsHeavy
- 179. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra ComplicationsThe
- 180. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra ComplicationsStricture
- 181. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentGeneral
- 182. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentSpecific
- 183. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentUrethral
- 184. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentIf
- 185. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentMost
- 186. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentUrethral
- 187. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentImmediate
- 188. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentTreatment
- 189. Injuries to the Anterior Urethra TreatmentPrognosisUrethral
- 190. Injuries to the PenisDisruption of the tunica
- 191. Injuries to the PenisGangrene and urethral injury
- 192. Injuries to the PenisInjuries to the penis
- 193. Injuries to the ScrotumSuperficial lacerations of the
- 194. Injuries to the ScrotumTotal avulsion of the
- 195. Injuries to the ScrotumLater reconstruction of the
- 196. Скачать презентацию
- 197. Похожие презентации
Emergency Diagnosis & ManagementAbout 10% of all injuries seen in the emergency room involve the genitourinary system to some extent.



































































































































































































Слайд 3 Many of them are subtle and difficult to
define and require great diagnostic expertise.
Early diagnosis is
essential to prevent serious complications.Emergency Diagnosis & Management
Слайд 4
Emergency Diagnosis & Management
Initial assessment should include control
of hemorrhage and shock along with resuscitation as required.
Слайд 5
Emergency Diagnosis & Management
The history should include a
detailed description of the accident. In cases involving gunshot
wounds, the type and caliber of the weapon should be determined, since high-velocity projectiles cause much more extensive damage.
Слайд 6
Emergency Diagnosis & Management
The abdomen and genitalia should
be examined for evidence of contusions or subcutaneous hematomas,
which might indicate deeper injuries to the retroperitoneum and pelvic structures.Слайд 7 Fractures of the lower ribs are often associated
with renal injuries, and pelvic fractures often accompany bladder
and urethral injuries.Emergency Diagnosis & Management
Слайд 8 Patients who do not have life-threatening injuries and
whose blood pressure is stable can undergo more deliberate
radiographic studies.Emergency Diagnosis & Management
Слайд 9
Emergency Diagnosis & Management
When genitourinary tract injury is
suspected on the basis of the history and physical
examination, additional studies are required to establish its extent.
Слайд 10
Assessment of Injury
Assessment of the injury should
be done in an orderly fashion so that accurate
and complete information is obtained.
Слайд 11
Catheterization
Blood at the urethral meatus in men
indicates urethral injury; catheterization should not be attempted if
blood is present, but retrograde urethrography should be done immediately.
Слайд 12
Catheterization
If no blood is present at the meatus,
a urethral catheter can be carefully passed to the
bladder to recover urine; microscopic or gross hematuria indicates urinary system injury.
Слайд 13
Catheterization
If catheterization is traumatic despite the greatest care,
the significance of hematuria cannot be determined, and other
studies must be done to investigate the possibility of urinary system injury.
Слайд 14
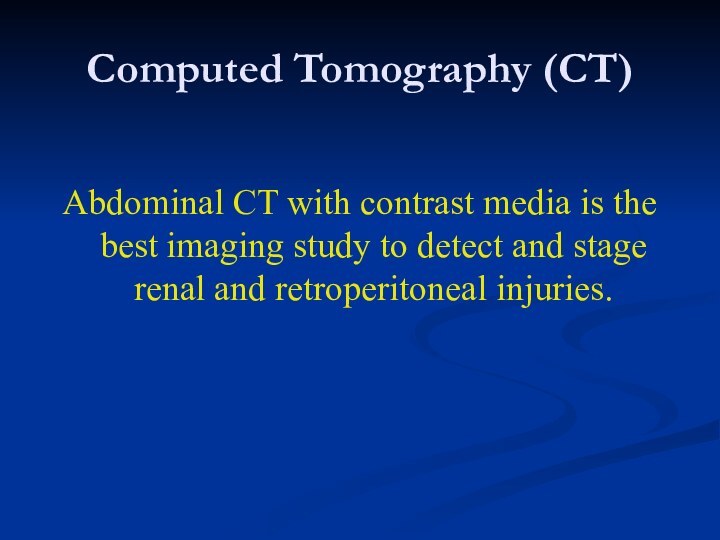
Computed Tomography (CT)
Abdominal CT with contrast media is
the best imaging study to detect and stage renal
and retroperitoneal injuries.
Слайд 16
Computed Tomography (CT)
Spiral CT scanning, now common, is
very rapid, but it may not detect renal parenchymal
lacerations, urinary extravasation, or ureteral and renal pelvic injuries.
Слайд 17
Retrograde Cystography
Filling of the bladder with contrast material
is essential to establish whether bladder perforations exist.
Слайд 18
Retrograde Cystography
A film should be obtained with the
bladder filled and a second one after the bladder
has emptied itself by gravity drainage.
Слайд 20
Urethrography
A small (12F) catheter can be inserted into
the urethral meatus and 3 mL of water placed
in the balloon to hold the catheter in position.
Слайд 21
Urethrography
After retrograde injection of 20 mL
of water-soluble contrast material, the urethra will be clearly
outlined on film, and extravasation in the deep bulbar area in case of straddle injury or free extravasation into the retropubic space in case of prostatomembranous disruption will be visualized.
Слайд 23
Intravenous Urography
Intravenous urography can be used to detect
renal and ureteral injury.
Слайд 24
Cystoscopy and Retrograde Urography
Cystoscopy and retrograde urography may
be useful to detect ureteral injury, but are seldom
necessary, since information can be obtained by less invasive techniques.
Слайд 25
Abdominal Sonography
Abdominal sonography has not been shown to
add substantial information during initial evaluation of severe abdominal
trauma.
Слайд 27
Injuries to the Kidney
Most injuries occur from automobile
accidents or sporting mishaps, chiefly in men and boys..
Слайд 28
Injuries to the Kidney
Etiology
Blunt trauma directly to the
abdomen, flank, or back is the most common mechanism,
accounting for 80-85% of all renal injuries.
Слайд 29
Injuries to the Kidney
Vehicle collisions at high speed
may result in major renal trauma from rapid deceleration
and cause major vascular injury.
Слайд 30
Injuries to the Kidney
Associated abdominal visceral injuries are
present in 80% of renal penetrating wounds.
Слайд 31
Pathology & Classification
Early Pathologic Findings
Lacerations from blunt
trauma usually occur in the transverse plane of the
kidney.
Слайд 32
Pathology & Classification
Early Pathologic Findings
In injuries from
rapid deceleration, the kidney moves upward or downward, causing
sudden stretch on the renal pedicle and sometimes complete or partial avulsion.
Слайд 33
Pathology & Classification
Early Pathologic Findings
Acute thrombosis of
the renal artery may be caused by an intimal
tear from rapid deceleration injuries owing to the sudden stretch.
Слайд 34
Pathology & Classification
Hydronephrosis
Follow-up excretory urography is
indicated in all cases of major renal trauma.
Слайд 35
Pathology & Classification
Arteriovenous Fistula
Arteriovenous fistulas may
occur after penetrating injuries but are not common
Слайд 36
Pathology & Classification
Renal Vascular Hypertension
The blood
flow in tissue rendered nonviable by injury is compromised;
this results in renal vascular hypertension in less than 1% of cases.
Слайд 37
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Microscopic or gross
hematuria following trauma to the abdomen indicates injury to
the urinary tract.
Слайд 38
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Some cases of
renal vascular injury are not associated with hematuria.
Слайд 39
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
The degree of
renal injury does not correspond to the degree of
hematuria, since gross hematuria may occur in minor renal trauma and only mild hematuria in major trauma
Слайд 40
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Miller and McAninch
(1995) made the following recommendations based on findings in
over 1800 blunt renal trauma injuries.
Слайд 41
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
However, should physical
examination or associated injuries prompt reasonable suspicion of a
renal injury, renal imaging should be undertaken.
Слайд 42
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Symptoms
There is usually
visible evidence of abdominal trauma. Pain may be localized
to one flank area or over the abdomen.
Слайд 44
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Signs
Initially, shock
or signs of a large loss of blood from
heavy retroperitoneal bleeding may be noted.
Слайд 45
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Signs
Diffuse abdominal
tenderness may be found on palpation; an "acute abdomen"
usually indicates free blood in the peritoneal cavity. A palpable mass may represent a large retroperitoneal hematoma or perhaps urinary extravasation.
Слайд 46
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Signs
The abdomen
may be distended and bowel sounds absent.
Слайд 47
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Laboratory Findings
Microscopic
or gross hematuria is usually present.
Слайд 48 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
Staging of renal injuries allows a systematic approach
to these problems. Слайд 49 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
For example, blunt trauma to the abdomen associated
with gross hematuria and a normal urogram requires no additional renal studies; however, nonvisualization of the kidney requires immediate arteriography or CT scan to determine whether renal vascular injury exists. Слайд 50 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
Ultrasonography and retrograde urography are of little use
initially in the evaluation of renal injuries.Слайд 51 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
Staging begins with an abdominal CT scan, the
most direct and effective means of staging renal injuries. Слайд 52 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
This noninvasive technique clearly
defines parenchymal lacerations and
urinary extravasation, Слайд 53 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
Arteriography defines major arterial and parenchymal injuries when
previous studies have not fully done so. Слайд 54 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
The major causes of nonvisualization on an excretory
urogram are total pedicle avulsion, arterial thrombosis, severe contusion causing vascular spasm, and absence of the kidney (either congenital or from operation).Слайд 55 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Staging and
X-Ray Findings
Radionuclide renal scans have been used in staging
renal trauma.
Слайд 56
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Differential Diagnosis
Trauma
to the abdomen and flank areas is not always
associated with renal injury.
Слайд 57
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Complications
Early Complications
Hemorrhage
is perhaps the most important immediate complication of renal
injury.
Слайд 58
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Complications
The size
and expansion of palpable masses must be carefully monitored.
Слайд 59
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Complications
Urinary extravasation
from renal fracture may show as an expanding mass
(urinoma) in the retroperitoneum.
Слайд 60
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Complications
A resolving
retroperitoneal hematoma may cause slight fever (38.3 °C), but
higher temperatures suggest infection.
Слайд 61
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Complications
Late Complications
Hypertension,
hydronephrosis, arteriovenous fistula, calculus formation, and pyelonephritis are important
late complications.
Слайд 62
Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies
Complications
Heavy late
bleeding may occur 4 weeks after injury.
Слайд 63 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Emergency
Measures
The objectives of early management are prompt treatment of
shock and hemorrhage, complete resuscitation, and evaluation of associated injuries.Слайд 64 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Blunt Injuries
Bleeding stops spontaneously with bed rest and hydration.
Слайд 65 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Cases in which operation is indicated include those associated
with persistent retroperitoneal bleeding, urinary extravasation, evidence of nonviable renal parenchyma, and renal pedicle injuries (less than 5% of all renal injuries). Aggressive preoperative staging allows complete definition of injury before operation.Слайд 66 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Penetrating Injuries
Penetrating injuries should be surgically explored.
Слайд 67 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
In 80% of cases of penetrating injury, associated organ
injury requires operation; thus, renal exploration is only an extension of this procedure.Слайд 68 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Treatment of Complications
Hydronephrosis may require surgical correction or nephrectomy.
Слайд 69 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Prognosis
With careful follow-up, most renal injuries have an excellent
prognosis, with spontaneous healing and return of renal function. Слайд 70 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Injuries to the Ureter
Ureteral injury is rare but may
occur, usually during the course of a difficult pelvic surgical procedure or as a result of gunshot wounds. Слайд 71 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Etiology
Large pelvic masses (benign or malignant) may displace the
ureter laterally and engulf it in reactive fibrosis. Слайд 72 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Extensive carcinoma of the colon may invade areas outside
the colon wall and directly involve the ureter; thus, resection of the ureter may be required along with resection of the tumor mass. Слайд 73 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Devascularization may occur with extensive pelvic lymph node dissections
or after radiation therapy to the pelvis for pelvic cancer. Слайд 74 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Endoscopic manipulation of a ureteral calculus with a stone
basket or ureteroscope may result in ureteral perforation or avulsion.Слайд 75 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Pathogenesis & Pathology
The ureter may be inadvertently ligated and
cut during difficult pelvic surgery. Слайд 76 Clinical Findings & Indications for Studies Treatment: Surgical
Measures
Intraperitoneal extravasation of urine can also occur, causing ileus
and peritonitis.
Слайд 77
Clinical Findings
Symptoms
If the ureter has been completely or
partially ligated during operation, the postoperative course is usually
marked by fever of 38.3-38.8 °C as well as flank and lower quadrant pain.
Слайд 78
Clinical Findings
Symptoms
Ureteral injuries from external violence should be
suspected in patients who have sustained stab or gunshot
wounds to the retroperitoneum.
Слайд 79
Clinical Findings
Symptoms
Signs
The acute hydronephrosis of a totally ligated
ureter results in severe flank pain and abdominal pain
with nausea and vomiting early in the postoperative course and with associated ileus. Signs and symptoms of acute peritonitis may be present if there is urinary extravasation into the peritoneal cavity.
Слайд 80
Clinical Findings
Symptoms
Watery discharge from the wound or vagina
may be identified as urine by determining the creatinine
concentration of a small urine has many times the creatinine concentration found in serum and by intravenous injection of 10 mL of indigo carmine, which will appear in the urine as dark blue.
Слайд 81
Laboratory Findings
Ureteral injury from external violence is manifested
by microscopic hematuria in 90% of cases.
Слайд 83
Imaging Findings
Partial transection of the ureter results in
more rapid excretion, but persistent hydronephrosis is usually present,
and contrast extravasation at the site of injury is noted on delayed films.
Слайд 84
Imaging Findings
In acute injury from external violence, the
excretory urogram usually appears normal, with very mild fullness
down to the point of extravasation at the ureteral transection.Retrograde ureterography demonstrates the exact site of obstruction or extravasation.