Слайд 3
Introduction
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is categorized as a
vasculitis of large- and medium-sized vessels
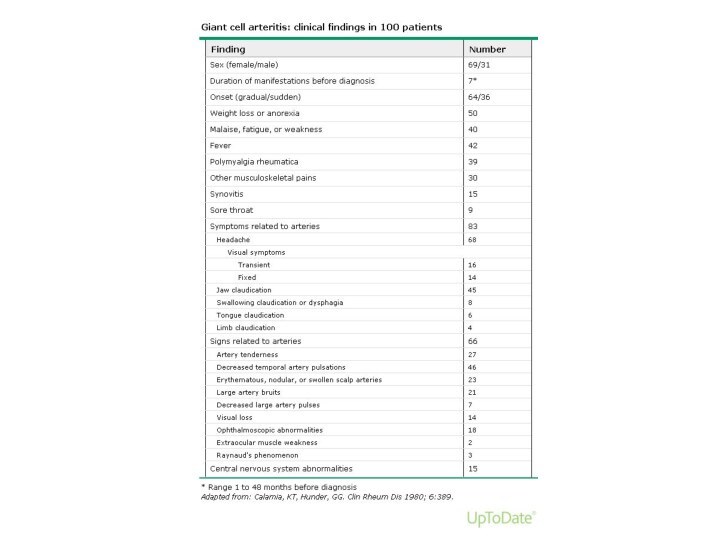
Systemic symptoms are common
in GCA and vascular involvement can be widespread
Targeting of the muscular arteries from cranial branches of the aortic arch gives rise to the most characteristic symptoms of GCA
The most feared complication of GCA, visual loss, is one potential consequence of such cranial arteritis
Слайд 5
Epidemiology
GCA is the most common systemic vasculitis
The lifetime
risk of developing GCA is ~1% in women and
0.5% in men
The greatest risk factor for developing GCA is aging
The disease almost never occurs before age 50
Over 80 percent of patients are older than 70 years
Ethnicity is a major risk factor for GCA. The highest incidence figures are found in Scandinavian countries
F>M
Слайд 6
Clinical findings
The onset of symptoms tends to be
subacute
Abrupt presentations occurs less frequently
Systemic symptoms are frequent and
include fever, fatigue, and weight loss
Fever occurs in up to one-half of patients with GCA and is usually low-grade
In ~ 10% of patients constitutional symptoms and/or laboratory evidence of inflammation dominate the clinical presentation and can be the only clues to the diagnosis
Слайд 8
Clinical findings - Headache
Located over the temples, but
can also be frontal or occipital or generalized
The headaches
can progressively worsen, or wax and wane, sometimes subsiding temporarily before treatment is started
Tenderness of the scalp to touch
Слайд 10
Jaw Claudication
Trismus-like symptoms
Fatigue of the muscles of mastication
Rapid
onset after the start of chewing and the ensuing
severity of pain
Patients seldom recognize the significance of symptoms of jaw claudication and must be questioned directly about this symptom
Claudication-like symptoms occasionally occur with repeated swallowing and in the tongue during eating
Jaw claudication is the symptom most highly associated with a positive temporal artery biopsy
Слайд 11
Vision
Transient visual loss (amaurosis fugax) — Transient monocular (and, rarely,
binocular) impairment of vision can be an early manifestation
of GCA.
Permanent vision loss — The most feared complication of GCA. Commonly is painless and sudden, may be partial or complete, and may be unilateral or bilateral. Even in the era of effective therapy, permanent partial or complete loss of vision in one or both eyes is reported 20% of patients
Risk factors — prior transient visual loss as the strongest predictor for subsequent permanent visual loss
Diplopia
Слайд 12
Large vessel GCA
Involvement of the aorta and its
major proximal branches - especially in the upper extremities
The clinical
consequences comprise aneurysms and dissections of the aorta, particularly the thoracic aorta, as well as stenosis, occlusion and ectasia of large arteries
Axillary arteries, proximal brachial arteries - arterial bruits, diminished or absent blood pressures, and arm claudication may ensue. Cold intolerance is common, but explicit digital ulcerations and gangrene are rare because of the adequacy of collateral arterial supply
Upper-extremity disease is bilateral, though not symmetric,
Слайд 14
External carotid artery- branches
Maxillary and dental pain
Facial swelling
Throat
pain
Tongue pain
Слайд 16
Physical examination
Pulses – carotid, brachial, radial, femoral, pedal
Blood
pressure
Bruits – carotid or supraclavicular areas; over the axillary,
brachial, or femoral arteries; over the abdominal aorta
Cardiac auscultation
Temporal a. examination
Слайд 19
Laboratory findings
Normochromic anemia is often present prior to
therapy and improves promptly after the institution of glucocorticoids
Thrombocytosis
The leukocyte count is usually normal, even in the setting of widespread systemic inflammation.
Serum albumin — moderately decreased at diagnosis but responds quickly to the institution of glucocorticoids
Hepatic enzymes — Elevated serum concentrations of hepatic enzymes, especially the alkaline phosphatase, occur in 25 to 35 percent of patients
ESR and C-reactive protein — elevated
Слайд 20
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of giant cell arteritis (GCA) should
be considered in a patient over the age of
50 who complains of:
New headaches
Abrupt onset of visual disturbances
Symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica
Jaw claudication
Unexplained fever or anemia
High ESR/CRP
Слайд 21
Diagnosis
Patient suspected of having GCA should undergo temporal
artery biopsy
~85% sensitivity
Other arteries can also be sampled
Scheduling of
the biopsy should NOT interfere with the start of glucocorticoid therapy when there is a significant concern about the possibility of GCA
Слайд 22
Biopsy-negative GCA
The patient may not have GCA. If
the clinical story is equivocal, then alternative diagnoses should
be given more weight
The patient may have GCA involving only the great vessels. Among patients with suggestive symptoms (most often arm claudication), an imaging study should be performed
An empiric trial of glucocorticoid therapy may be helpful. Failure of the patient’s symptoms to resolve within one week of high-dose glucocorticoids argues strongly against the diagnosis of GCA
Слайд 23
Imaging
MRI/MRA
USD
Angiography
PET-CT
Слайд 24
Treatment
Uncomplicated GCA - 40 to 60 mg of prednisone in
a single dose
After achieving a daily dose of 10
mg, the prednisone taper should be slow, such that patients remain on some prednisone for 9 to 12 months. Tapering in 1 mg decrements per month once the daily dose is less than 10 mg is appropriate