Слайд 2
At rest, the light rays focus behind instead
of on the retina.
This type of eye defect
is termed hypermetropia.
This condition can be corrected by convex lenses.
Слайд 3
Red-green color blindness is the inability to distinguish
red and green colors in dim light (and sometimes
bright light) due to a lack of red and green cone cells.
Malformed eye parts cause common focusing problems.
In astigmatism, one or both corneas have uneven curvature and cannot bend light to the same focal point.
Слайд 4
Nearsightedness (myopia) results when the image is focused
in front of the retina.
Farsightedness (hyperopia) is due to
an image focused behind the retina.
Слайд 5
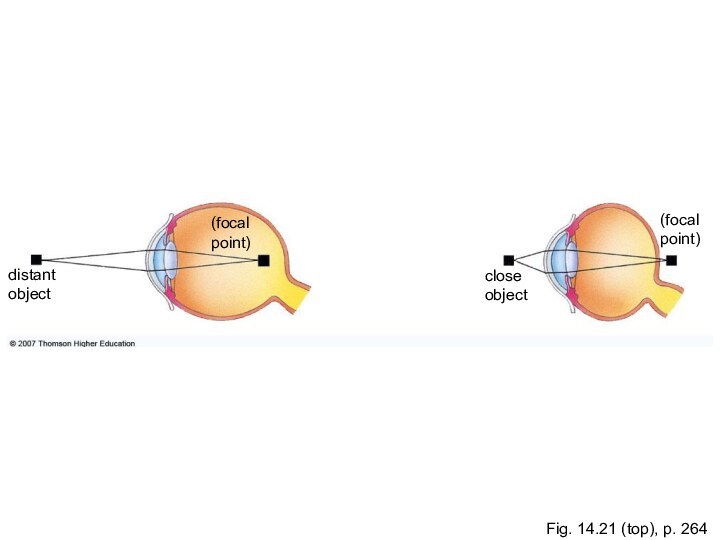
Fig. 14.21 (top), p. 264
(focal
point)
distant
object
(focal
point)
close
object
Слайд 7
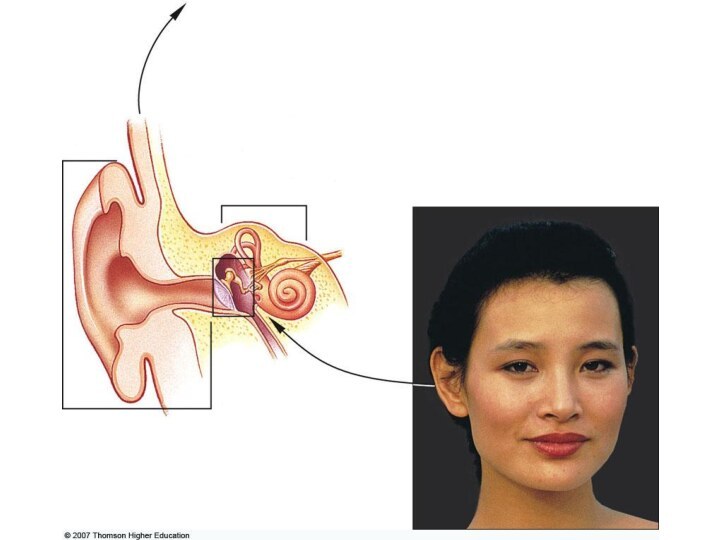
The human ear has 2 sensory functions.
One
of them is hearing.
Other is maintaning balance or equilibrium.
THE
EARS
Слайд 8
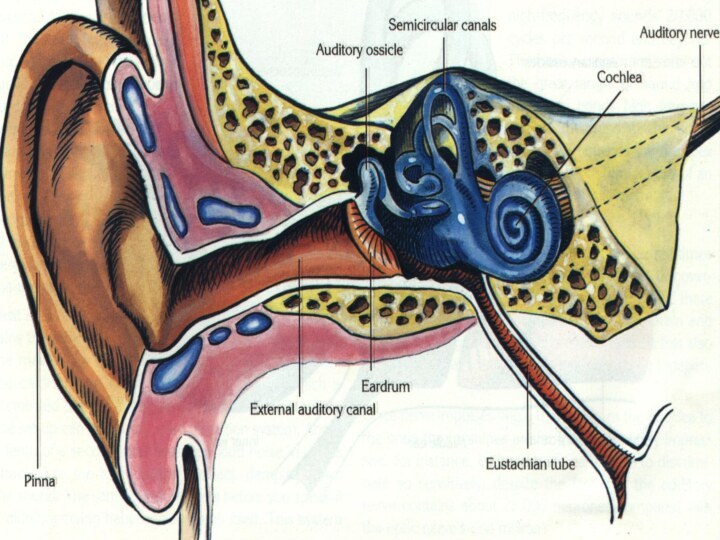
Structure of ears
Ears contains 3 main parts;
Outer ear,
The middle ear
Inner ear
Слайд 10
OUTER EAR
Outer ear is composed of 3 parts.
These
are pinna, auditory canal and eardrum.
Pinna is a cartilaginous
tissue which collects sound waves and determines the source of voices.
Слайд 11
Auditory canal is a canal which is found
between pinna and eardrum.
It has hairs and produces wax-like
substance to filter solid partcicles.
The eardrum separates outer ear from the middle ear.
It is thin half transparent.
Слайд 12
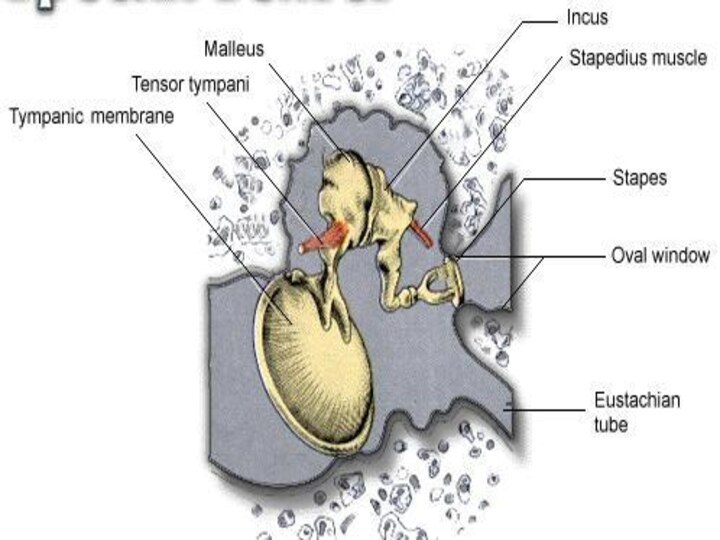
MIDDLE EAR
It contains three small bones which are
called the hammer, anvil and stirrup.
These bones form a
chain across the middle ear linking the eardrum to another membrane, the oval window.
Слайд 14
The hammer attached to the eardrum, the anvil
connects the hammer to the stirrup.
Stirrup is connected to
the oval window.
Слайд 16
EUSTACHIAN TUBE
It is located between pharynx and the
middle ear.
It equalizes in the middle ear and atmosphere.
Слайд 18
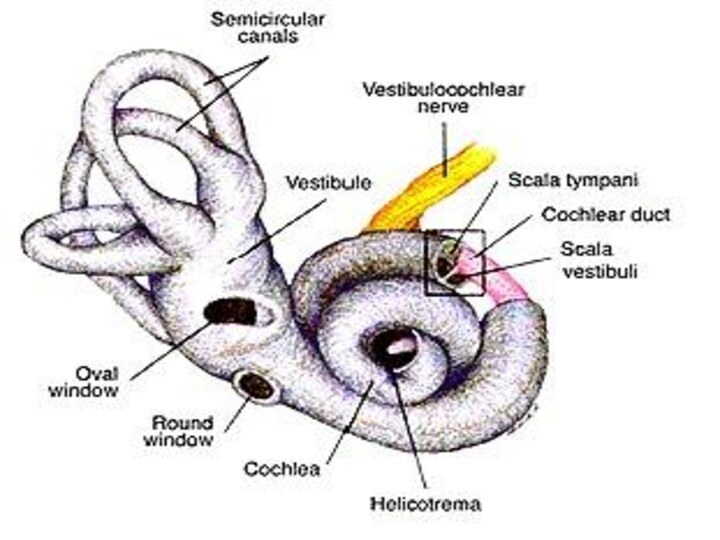
THE INNER EAR
It consists of the cochlea and
semicircular canals.
Cochlea is organ of hearing which consists of
coiled, liquid-filled tubes.
Слайд 19
They are separated from another by membranes.
Lining of
the membranes are specialized hair cells that are sensitive
to vibration.
Слайд 20
Semicircular canals enable the body to maintain balance.
These
canals contain fluid and hairlike projenctions that detect changes
in body position.
Слайд 21
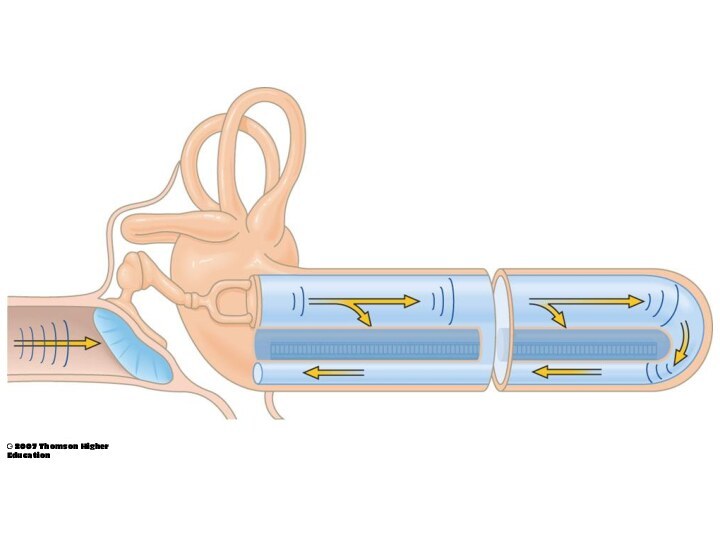
Sound waves collected by outer ear pass down
the auditory canal to the eardrum.
They cause the
eardrum to vibrate.
The vibrations are transmitted across the middle ear by the hammer, onvil and stirrup.
HEARING
Слайд 22
Vibration of stirrup cause vibrations in the oval
window which in turn cause the fluid within the
cochlea.
The initiates in nerve endings around the hair cells.
These impulses are carried to the cerebral cortex, where their meaning is interpreted.
Слайд 26
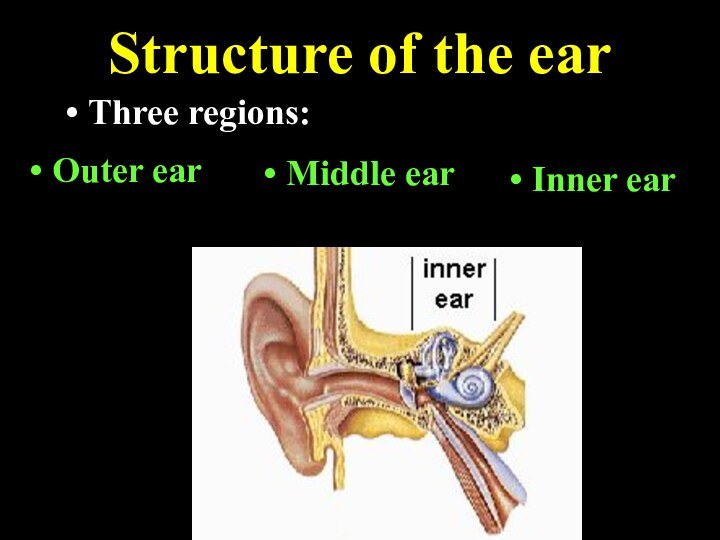
Structure of the ear
Three regions:
Outer ear
Middle ear
Inner ear
Слайд 27
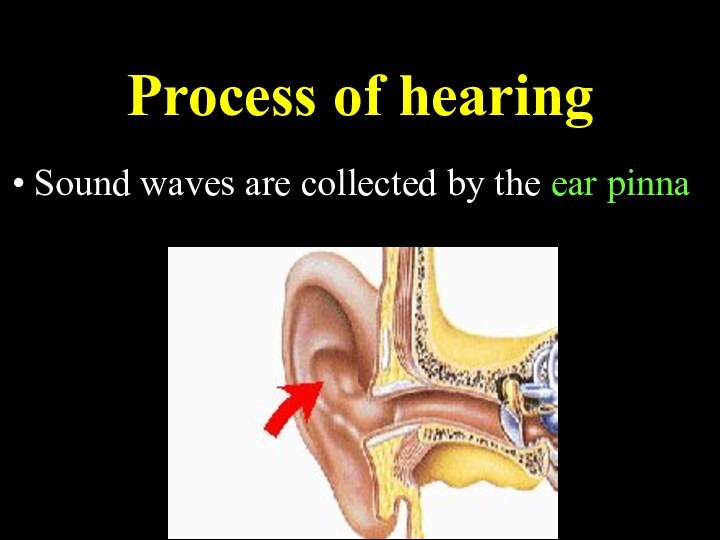
Process of hearing
Sound waves are collected by the
ear pinna
Слайд 28
Process of hearing
Sound waves pass along the external
auditory canal to the ear drum
Слайд 29
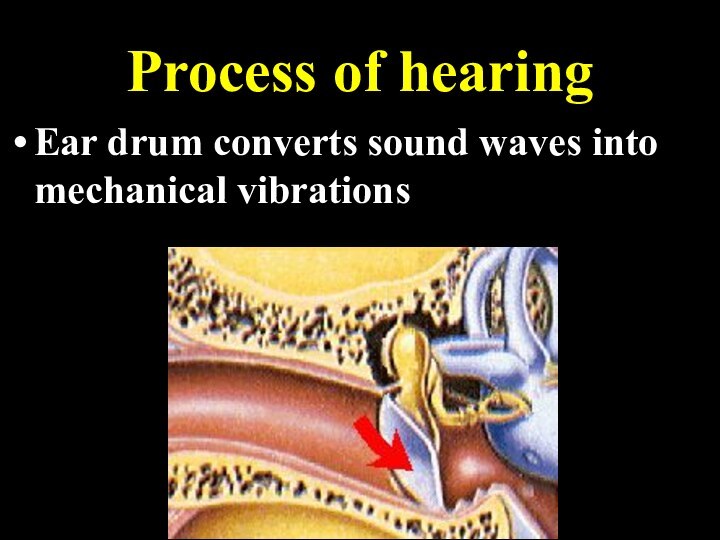
Process of hearing
Ear drum converts sound waves into
mechanical vibrations
Слайд 30
Process of hearing
Ear drum transmits vibration to the
ear bones
Слайд 31
Process of hearing
Ear bones transmit vibration to the
oval windows
Слайд 32
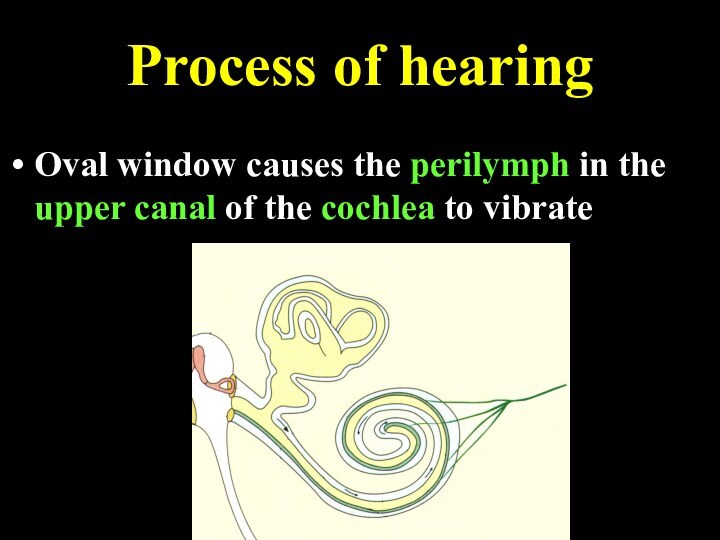
Process of hearing
Oval window causes the perilymph in
the upper canal of the cochlea to vibrate
Слайд 33
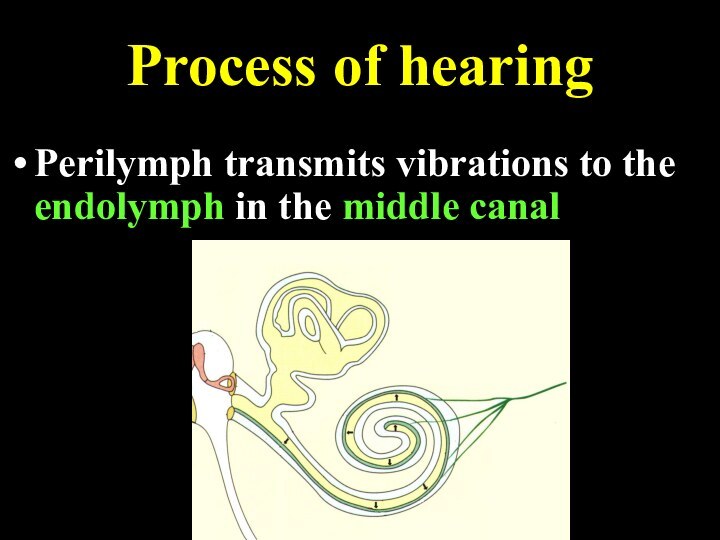
Process of hearing
Perilymph transmits vibrations to the endolymph
in the middle canal
Слайд 34
Process of hearing
The sensory hair cells on the
bottom membrane of the middle canal are stimulated
The sensory
hair cells send off nerve impulses
Слайд 35
Process of hearing
The auditory nerve transmits the impulses
to the auditory centre of the cerebral cortex
The auditory
centre interprets the nerve impulses and produce the sensation of hearing
Слайд 36
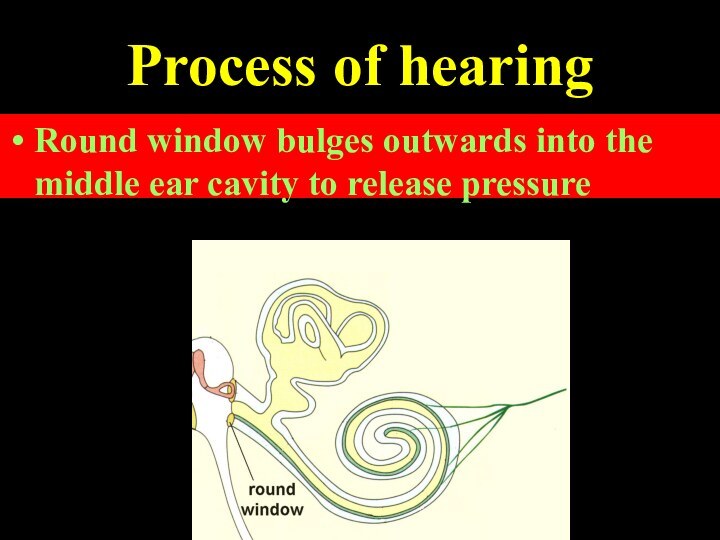
Process of hearing
The vibrations of perilymph are transmitted
to the round window
Round window bulges outwards into the
middle ear cavity to release pressure
Слайд 37
All multicellular organisms have a skin composed of
one or more layers.
THE SKIN
Слайд 38
Functions of Skin
It protects the inner layers of
the body from physical and chemical effects.
It prevents body
from enterance of microbes
It prevents water loss in terrestial organisms.
It prevents cell from ultraviolet light.
Слайд 39
Structure of the skin
Epidermis
Dermis
Accesory structure of the skin
Skin gland
Hair follicles
Nails
Skin pigment
Слайд 40
EPIDERMIS is outermost layer of skin.
This layer composed
of keratinised epithelial cells.
Epidermis contains no blood vessels.
Upper section
of epidermis is composed of non-living cells.
The color of skin is conferred by melanin pigment.
Слайд 41
DERMIS is rich in blood vessels and nerve
ending.
The receptors located in the skin are connected to
these nerve ending.
Dermis also contain smooth muscle, sweat glands, hair follicles, toch receptors and lymph vessels.
Слайд 43
RECEPTORS
Meisner corpuscles: They are involved in reception of
touch of the palm sole and lips.
Paccinian corpuscles: They
are involved in recption of mechanical stimuli.
Krouse corpuscles: They are involved in reception of cold and pressure.
Слайд 44
Ruffini corpuscles: They are involved in recption of
heat, touch and pressure.
Sweat glands: They are present in
all regions of the skin. They open onto the surface of skin by pores.
Слайд 46
They are involved in removal of water, minerals,
urea and other substances.
The main function of sweat glands
is the regulation of body temperature by evaporation of water.
Слайд 47
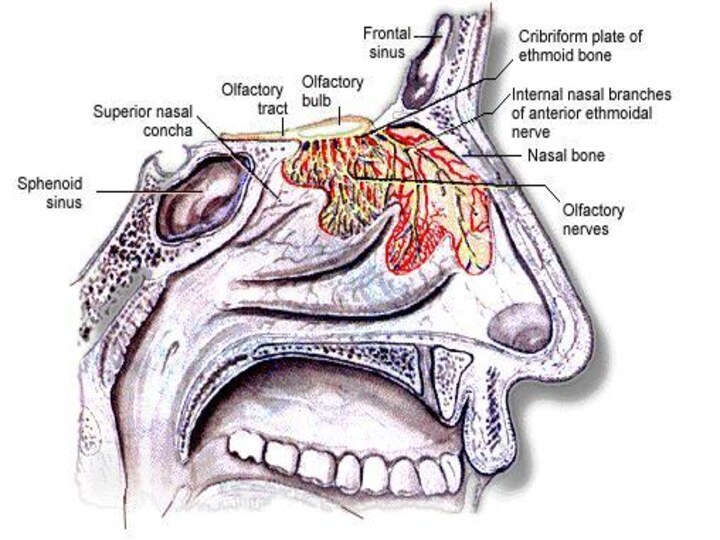
Nose is the organ of the body involved
in both respiration and smell.
The reception of smell takes
place in chemoreceptors located in nasal cavity.
THE NOSE
Слайд 49
Smelling is fundemantal in the detection of food,
maintenance of relationship, reproduction and communication of some animals.
Nose
also provides the control of temperature
The control of humidity and the elemination of infectious organisms.
Слайд 51
The surface of the tongue is covered with
small projections called papillae.
There are the taste receptors or
taste buds within the papillae.
Nerve fibers branch among the cells of the taste bud and each cell is in contact with one or more neurons.
THE TASTE
Слайд 52
The taste buds are sensitive to only four
basic tastes;
SWEET, SOUR, SALT AND BITTER
Each taste bud is
particularly sensitive to one of these tastes.
Taste and smell are chemical senses; they begin at chemoreceptors
Слайд 53
Tend to be localized on specific areas of
the tongue, taste buds for sourness are found along
the sides of the tongue
Taste buds for bitterness at the back of the tongue
Taste buds for sweetness and saltiness at the back of the tongue
Слайд 54
Taste buds for sweetness and saltiness on the
tip of the tongue.
When taste buds are stimulated, impulses
are initiated by the sensory cells of the structure and carried to the brain.
Слайд 55
Tongue - the taste organ
Detected by taste buds
on the upper surface of the tongue which are
stimulated by chemicals dissolved in saliva
Different regions detect different tastes
sweet
salty
sour
bitter
Flavour of food is given by both the sense of taste and odour of it