- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Java technology classes and objects
Содержание
- 2. Start and finishBreakFacilities, telephones and messagesQuestions and discussions LOGISTICS
- 3. CLASSClassFields…MethodsAttributesFunctionsClass is abstact data type. Class denotes
- 4. OBJECTAn object has identity (it acts as
- 5. EXAMPLES Objects Non-objectsA pen The upper 37 % of
- 6. EXERCISEConsider a tube of four yellow tennis
- 7. SOFTWARE OBJECTS Question: What are software objects
- 8. SOFTWARE CLASS A class is a description
- 9. CLASS EXAMPLEInternet MerchandiseFields“Name”, “Price“, “Producer”, “Type”, “Photo” Methods“Make discount”, “Set name”, “Add photo”
- 10. OBJECT EXAMPLESHOTGUNFields“FAIR X-Light”“120000 rubles”“Italy”“Sporting Goods”“http://www.fair.it/media/img/prodotti/xlight_prestige_b.jpg”Methods“Make discount”, “Set
- 11. class { field; method; } A class in java can contain:fieldmethodconstructorblockclass and interfaceCLASS IN JAVA
- 12. EXAMPLEWrite class Vehicle that have attributes (fields)
- 13. Code that is outside the object's class
- 14. EXERCISEWrite program that sets different values for
- 15. Use an object reference to invoke an
- 16. EXERCISEAdd method to calculate effectiveness into Vehicle
- 17. CLASS STRING String is a very special
- 18. STRING METHODSString machine = “pentium”;int comp =
- 19. EXAMPLEclass stringTester { public static void main
- 20. Java API provides wrapper classes for each
- 21. There are three reasons that you might
- 22. To convert the value of this Number
- 23. To compare this Number object to the
- 24. Each Number class contains other methods that
- 25. INTEGER TO STRINGString toString()Returns a String object
- 26. Write program which gets input of the
- 27. Write class to represent Radio that have
- 28. Скачать презентацию
- 29. Похожие презентации













![Java technology classes and objects EXAMPLEclass stringTester { public static void main ( String[] args ) {](/img/tmb/14/1398941/8576d0ab29909a3b13faf357d589faac-720x.jpg)









Слайд 3
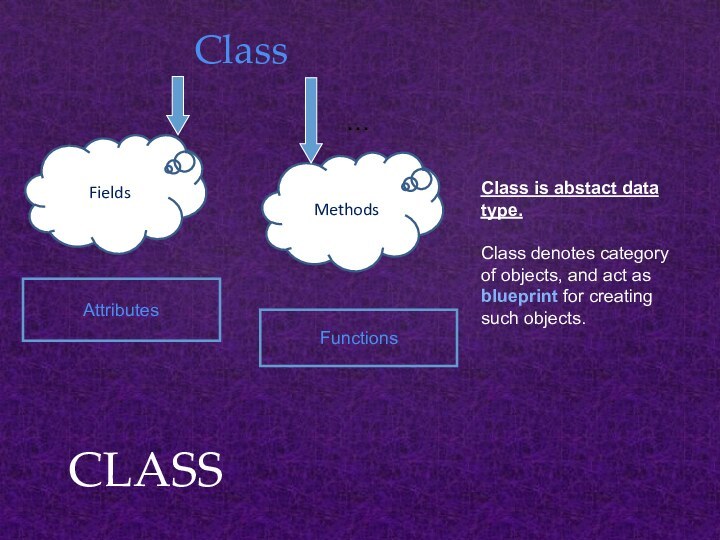
CLASS
Class
Fields
…
Methods
Attributes
Functions
Class is abstact data type.
Class denotes category
Слайд 4
OBJECT
An object has identity (it acts as a
single whole).
An object has state (it has various properties,
which might change). An object has behavior (it can do things and can have things done to it).
Object is entity that has the following features:
Слайд 5
EXAMPLES
Objects Non-objects
A pen The upper 37 % of the
pen
A Computer The air above Keyboard the keyboard
A shoe The color blackA desk All desks in the world
Слайд 6
EXERCISE
Consider a tube of four yellow tennis balls.
Is the tube of tennis balls an object?
Is
each tennis ball an object? Could the top two balls be considered a single object?
Is the color of the balls an object?
Is your understanding of tennis balls an object?
Слайд 7
SOFTWARE OBJECTS
Question: What are software objects made
out of?
Answer: Computer memory.
Software objects have
identity because each is a separate chunk of memory having name.Software objects have state. Some of the memory that makes a software object is used for attributes which contain values.
Software objects have behavior. Some of the memory that makes a software object is used to contain programs (called methods) that enable the object to "do things." The object does something when one of its method runs.
Слайд 8
SOFTWARE CLASS
A class is a description of
a kind of object.
A programmer may define
a classor may use predefined classes that come in class libraries.
A class is merely a plan for a possible object (or objects.). It does not by itself create any objects.
When a programmer wants to create an object the new operator is used with the name of the class.
Creating an object is called instantiation.
Слайд 9
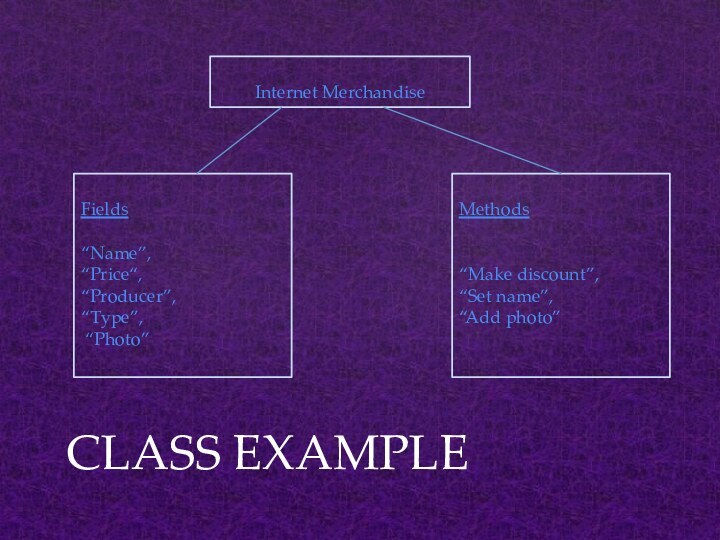
CLASS EXAMPLE
Internet Merchandise
Fields
“Name”,
“Price“,
“Producer”,
“Type”,
“Photo”
Methods
“Make discount”,
“Set name”,
“Add photo”
Слайд 10
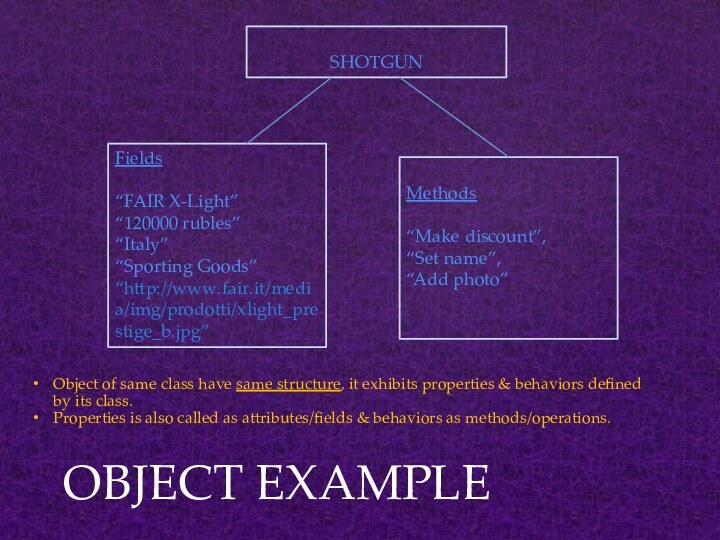
OBJECT EXAMPLE
SHOTGUN
Fields
“FAIR X-Light”
“120000 rubles”
“Italy”
“Sporting Goods”
“http://www.fair.it/media/img/prodotti/xlight_prestige_b.jpg”
Methods
“Make discount”,
“Set name”,
“Add photo”
Object of same class have same
structure, it exhibits properties & behaviors defined by its class.Properties is also called as attributes/fields & behaviors as methods/operations.
Слайд 11
class {
field;
method;
}
A class in java can contain:
field
method
constructor
block
class and
interface
CLASS IN JAVA
Слайд 12
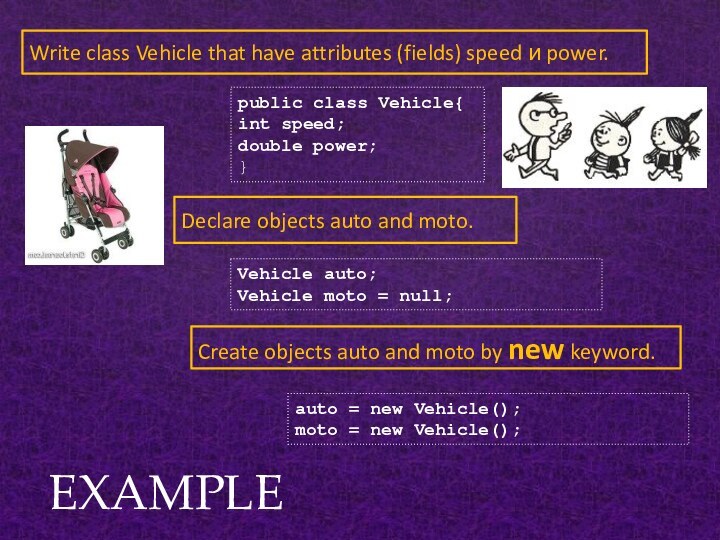
EXAMPLE
Write class Vehicle that have attributes (fields) speed
и power.
Declare objects auto and moto.
public class Vehicle{
int
speed;double power;
}
Vehicle auto;
Vehicle moto = null;
Create objects auto and moto by new keyword.
auto = new Vehicle();
moto = new Vehicle();
Слайд 13 Code that is outside the object's class must
use an object reference or expression, followed by the
dot (.) operator, followed by a simple field name, as in:objectReference.fieldName
GET & SET ATTRIBUTES
To get: variable = object.field;
To set: object.field = variable;
Слайд 14
EXERCISE
Write program that sets different values for the
fields:
auto.power = 88.7;
auto.speed = 150;
moto.power = 24;
moto.speed =
120;System.out.println(auto.power +” “+ auto.speed);
System.out.println(moto.power +” “+ moto.speed);
auto.speed = 180;
System.out.println(auto.power +” “+ auto.speed);
System.out.println(moto.power +” “+ moto.speed);
Every object has independent fields.
Слайд 15 Use an object reference to invoke an object's
method. Append the method's simple name to the object
reference, with an intervening dot operator (.). Provide, within enclosing parentheses, any arguments to the method. If the method does not require any arguments, use empty parentheses.objectReference.methodName(argumentList);
or:
objectReference.methodName();
CALLING METHODS
Слайд 16
EXERCISE
Add method to calculate effectiveness into Vehicle class
double
eff() {
return power/speed;
}
Compare 2 objects
System.out.print(auto.eff()>moto.eff());
The objects must
be created to use method eff().
Слайд 17
CLASS STRING
String is a very special class
in Java.
Strings are constants, their values cannot
be changed after they are created. But they can be reinitialized.String here=“I am here”;
here=“I am there”;//previous one is completely deleted
Our rules and dictionaries can be stored string class.
This class is armed with useful methods
compareTo(String str),
concate(String str),
endsWith(String str),
indexOf(int ch),
length(),
startsWith(String str),
lastIndexOf(String str).
Слайд 18
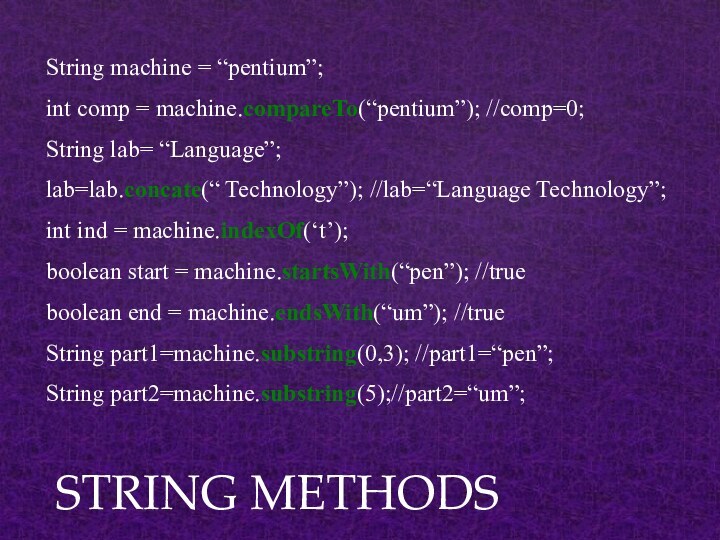
STRING METHODS
String machine = “pentium”;
int comp = machine.compareTo(“pentium”);
//comp=0;
String lab= “Language”;
lab=lab.concate(“ Technology”); //lab=“Language Technology”;
int ind = machine.indexOf(‘t’);
boolean
start = machine.startsWith(“pen”); //trueboolean end = machine.endsWith(“um”); //true
String part1=machine.substring(0,3); //part1=“pen”;
String part2=machine.substring(5);//part2=“um”;
Слайд 19
EXAMPLE
class stringTester {
public static void main (
String[] args ) {
String str1;
// str1 is a variable that refers to an object, // but the object does not exist yet.
int len; // len is a primitive variable of type int
str1 = new String(“Bullet is waiting…"); // create an object of type String
len = str1.length(); // invoke the object's method length() System.out.println("The string is " + len + " characters long");
}
}
Слайд 20 Java API provides wrapper classes for each of
the primitive data types. These classes "wrap" the primitive
in an object.NUMBER WRAPPERS
int x = 25;
Integer y = new Integer(33);
Слайд 21 There are three reasons that you might use
a Number object rather than a primitive:
As an argument
of a method that expects an object (often used when manipulating collections of numbers).To use constants defined by the class, such as MIN_VALUE and MAX_VALUE, that provide the upper and lower bounds of the data type.
To use class methods for converting values to and from other primitive types, for converting to and from strings, and for converting between number systems (decimal, octal, hexadecimal, binary).
REASONS
Слайд 22 To convert the value of this Number object
to the primitive data type returned.
CONVERT TO PRIMITIVE TYPES
byte
byteValue()
short shortValue()
int intValue()
long longValue()
float floatValue()
double doubleValue()Double Var = new Double (3.1415);
int i = Var.intValue();
Слайд 23
To compare this Number object to the argument.
COMPARATION
int
compareTo(Byte anotherByte) int compareTo(Double anotherDouble) int compareTo(Float anotherFloat) int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) int compareTo(Long
anotherLong) int compareTo(Short anotherShort)Integer Var = new Integer (5);
int i = 3;
if(Var.compareTo(i)) System.out.println (“They are the same!”);
else System.out.println (“They are different!”);
Слайд 24 Each Number class contains other methods that are
useful for converting numbers to and from strings and
for converting between number systems.STRING INTO INTEGER
static Integer decode(String s)
Decodes a string into an integer. Can accept string representations of decimal, octal, or hexadecimal numbers as input.
Integer iVar = Integer.decode(“3”);
static int parseInt(String s)
Returns an integer (decimal only).
int i = Integer.parseInt(“3”);
static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
Returns an integer, given a string representation of decimal, binary, octal, or hexadecimal (radix equals 10, 2, 8, or 16 respectively) numbers as input.
int i = Integer.parseInt(“3”,16);
Слайд 25
INTEGER TO STRING
String toString()
Returns a String object representing
the value of this Integer.
Integer y = 125;
String
s1 = y.toString(); //"125”static String toString(int i)
Returns a String object representing the specified integer.
String s1 = Integer.toString(25); //"25”
static String toBinaryString(int i)
public static String toOctalString(int i)
public static String toHexString(int i)
Returns a String object representing the specified integer in binary, octal or hexadecimal form.
String s1 = Integer.toBinaryString(12); //“1100”
Слайд 26 Write program which gets input of the user
in decimal integer form and which prints the result
in binary, octal and hexadecimal form.EXERCISE
Слайд 27 Write class to represent Radio that have name,
frequency and mode (switched on/off). Have methods to change
the mode and to change frequency. In main() method create Radio object and then get user input to change and to print mode & frequency.HOMEWORK





























