Слайд 2
Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems
Effective means of protecting
LANs
Internet connectivity is essential
For organization and individuals
But creates a
threat (enabling the outside world to reach and interact with local network assets)
Could secure all workstations and servers (but this is not a practical approach)
Also use firewall as perimeter defence
Single choke point to impose security
Слайд 3
Firewall Access Policy
A critical component in the planning
and implementation of a firewall is specifying a suitable
access policy
Types of traffic authorized to pass through the firewall
Includes address ranges, protocols, applications and content types
The policy should be developed from the organization’s security risk assessment and policy
Should be developed from a broad specification of which traffic types the organization needs to support
Then refined to detail the filter elements which can then be implemented within an appropriate firewall topology
Слайд 4
Firewall Capabilities & Limits
Capabilities
Defines a single choke point
Provides
a location for monitoring security events
Convenient platform for some
Internet functions such as NAT, usage monitoring, IPSEC, VPNs
Limitations
Cannot protect against attacks bypassing firewall (from dial-out, or a modem pool dial-in capability for traveling employees and telecommuters)
May not protect fully against internal threats
Improperly secure wireless LAN
Laptop, PDA, portable storage device infected outside then used inside
Слайд 5
Firewall Filter Characteristics
Слайд 6
Types of Firewalls
Positive (negative) filter:
Allow (reject) packets that
meet
a criteria
Stateful inspection: Keeps track of
TCP connections
Слайд 7
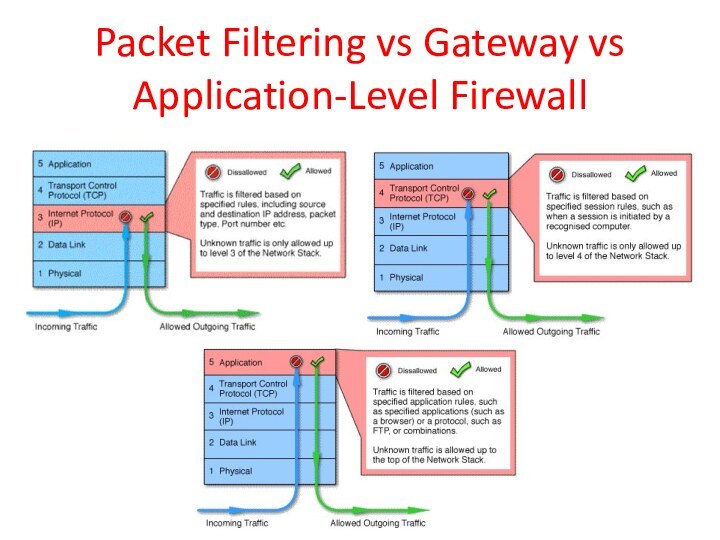
Packet Filtering Firewall
Applies rules to packets in/out of
firewall
based on information in packet header
src/dest IP addr &
port, IP protocol, interface
Typically a list of rules of matches on fields
If match rule says if forward or discard packet
Two default policies:
Discard: prohibit unless expressly permitted
more conservative, controlled, visible to users
Forward: permit unless expressly prohibited
easier to manage/use but less secure
Слайд 8
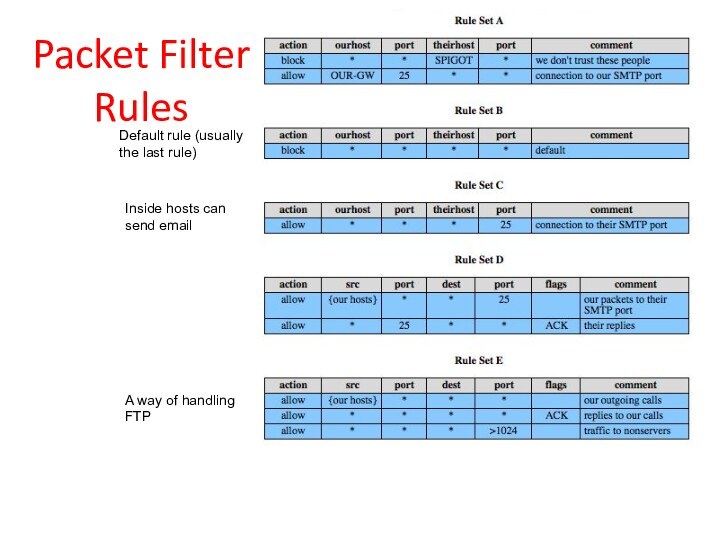
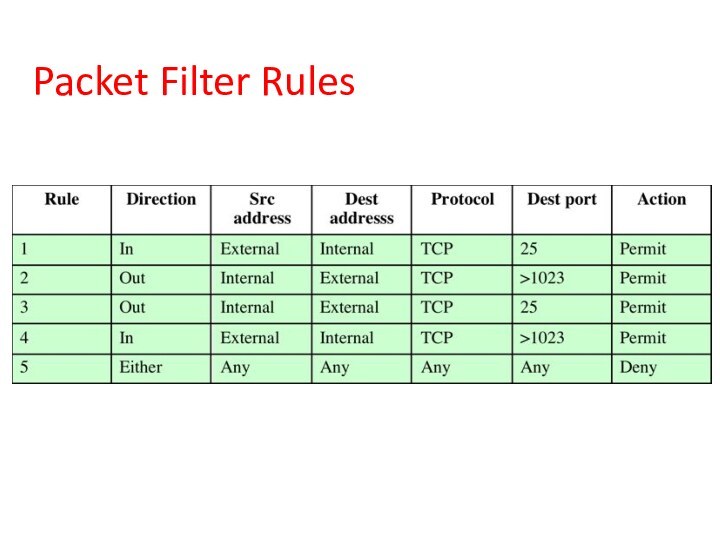
Packet Filter Rules
Default rule (usually
the last rule)
Inside hosts
can
send email
A way of handling
FTP
Слайд 10
Packet Filter Weaknesses
Weaknesses
Cannot prevent attack on application bugs
Limited
logging functionality
Do no support advanced user authentication
Vulnerable to attacks
on TCP/IP protocol bugs (e.g., IP address spoofing)
Improper configuration can lead to breaches
Attacks
IP address spoofing
Source route attacks (srs dictates the pkt route)
Tiny fragment attacks (to circumvent filtering rules that depend on TCP header info)
Слайд 11
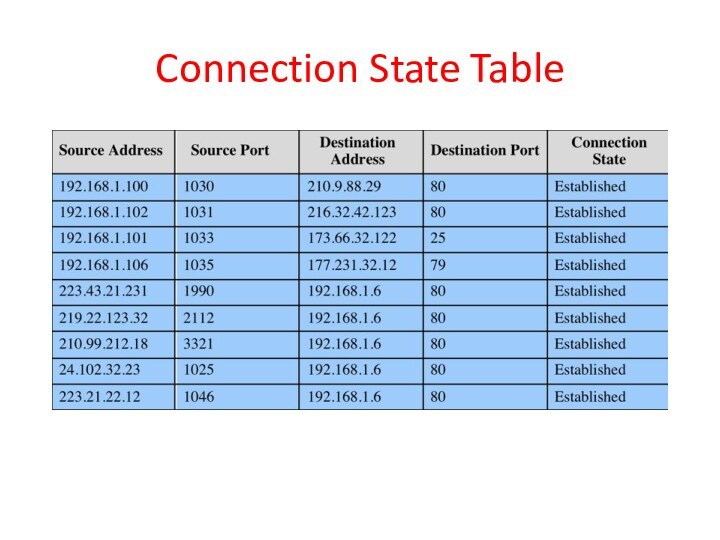
Stateful Inspection Firewall
Reviews packet header information but also
keeps info on TCP connections
Typically have low, “known” port
# for server and high, dynamically assigned (ephemeral) client port #
Stateful inspection packet firewall tightens rules for TCP traffic using a directory of TCP connections
only allow incoming traffic to high-numbered ports for packets matching an entry in this directory
may also track TCP seq numbers as well
Слайд 13
Application-Level (Proxy) Gateway
Acts as a relay of application-level
traffic
User contacts gateway with remote host name
Authenticates themselves
Gateway contacts
application on remote host and relays TCP segments between server and user
Must have proxy code for each application
May restrict application features supported
Some services may not be available
More secure than packet filters
But have higher overheads
Слайд 14
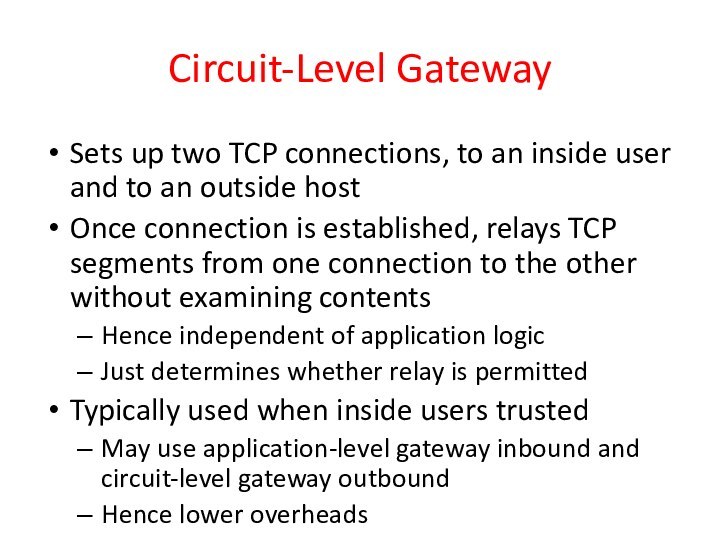
Circuit-Level Gateway
Sets up two TCP connections, to an
inside user and to an outside host
Once connection is
established, relays TCP segments from one connection to the other without examining contents
Hence independent of application logic
Just determines whether relay is permitted
Typically used when inside users trusted
May use application-level gateway inbound and circuit-level gateway outbound
Hence lower overheads
Слайд 15
Packet Filtering vs Gateway vs Application-Level Firewall
Слайд 16
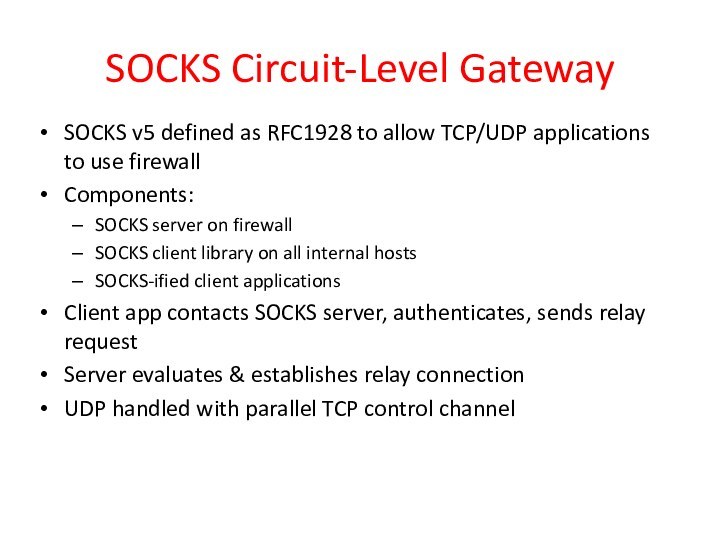
SOCKS Circuit-Level Gateway
SOCKS v5 defined as RFC1928
to allow TCP/UDP applications to use firewall
Components:
SOCKS server on
firewall
SOCKS client library on all internal hosts
SOCKS-ified client applications
Client app contacts SOCKS server, authenticates, sends relay request
Server evaluates & establishes relay connection
UDP handled with parallel TCP control channel
Слайд 17
Firewall Basing
Several options for locating firewall:
Bastion host
Individual host-based
firewall
Personal firewall
Слайд 18
Bastion Hosts
Critical strongpoint in network
Hosts application/circuit-level gateways
Common characteristics:
Runs
secure O/S, only essential services
May require user auth to
access proxy or host
There may be many proxy services
Each proxy can restrict features, hosts accessed
Each proxy small, simple, checked for security
Each proxy is independent, can be uninstalled
Слайд 19
Host-Based Firewalls
Used to secure individual host
Available in/add-on for
many O/S
Filter packet flows
Often used on servers
Advantages:
Tailored filter rules
for specific host needs
Protection from both internal/external attacks
Additional layer of protection to org firewall when used with a standalone firewall
Слайд 20
Personal Firewall
Controls traffic flow to/from PC/workstation
For both home
or corporate use
May be software module on PC
Or in
home cable/DSL router/gateway
Typically much less complex
Primary role to deny unauthorized access
May also monitor outgoing traffic to detect/block worm/malware activity
Слайд 21
Firewall Locations
Internal firewall:
more stringent filtering capability
to provide
protection from external
attacks
(b) provides two way protection wrt
the DMZ
network
External firewall: protection for the
DMZ consistent with their need for
external connectivity
Слайд 22
Virtual Private Networks
Encryption and similar services
but transparent to
the user
Слайд 23
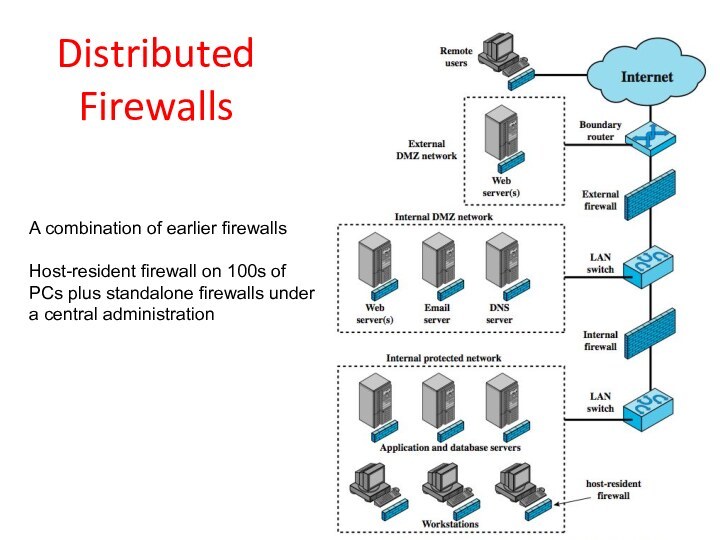
Distributed Firewalls
A combination of earlier firewalls
Host-resident firewall on
100s of
PCs plus standalone firewalls under
a central administration
Слайд 24
Firewall Topologies
Host-resident firewall: personal firewall and firewall on
servers (used alone or part of a defense in-depth)
Screening
router: a single router between internal and external networks, e.g., SOHO apps)
Single bastion inline: single firewall device between an internal and external router (stateful or app proxies)
Single bastion T: similar to above but has a 3rd NIC on bastion to a DMZ (for medium to large organizations)
Double bastion inline: DMZ is between (for large organizations)
Distributed firewall configuration
Слайд 25
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Recent addition to security products
which
Inline network-/host-based IDS that can block traffic
Functional addition to
firewall that adds IDS capabilities
Using IDS algorithms but can block or reject packets like a firewall
May be network or host based
Слайд 26
Host-Based IPS
Identifies attacks using both:
Signature techniques
malicious application packets
Anomaly
detection techniques
behavior patterns that indicate malware
Example of malicious behavior:
buffer overflow, access to email contacts, directory traversal
Can be tailored to the specific platform
e.g. general purpose, web/database server specific
Can also sandbox applets to monitor behavior
May give desktop file, registry, I/O protection
Слайд 27
Network-Based IPS
inline NIDS that can discard packets or
terminate TCP connections
uses signature and anomaly detection
may provide flow
data protection
monitoring full application flow content
can identify malicious packets using:
pattern matching (for specific byte seq)
stateful matching (to stop attack streams rather than a single pkts)
protocol anomaly (deviations from stds)
traffic anomaly (unusual traffic like a UDP floods)
Слайд 28
Unified Threat Management Products
Reduce admin burden by replacing
network
products (firewall, IDS, IPS, …)
With a single device