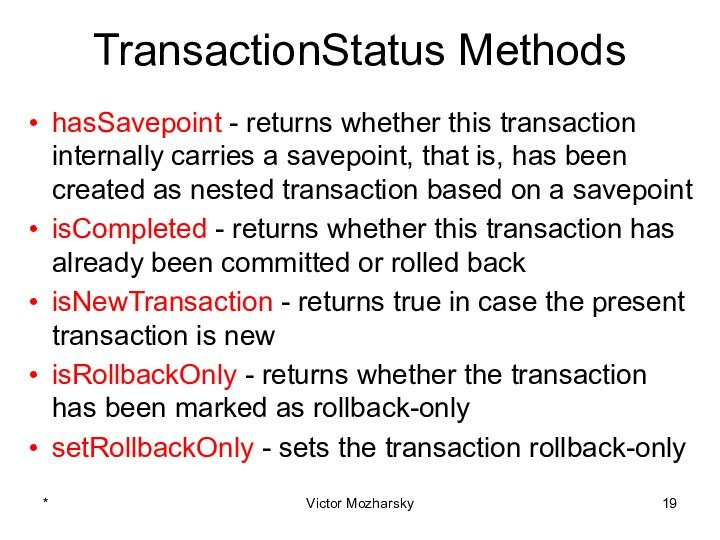
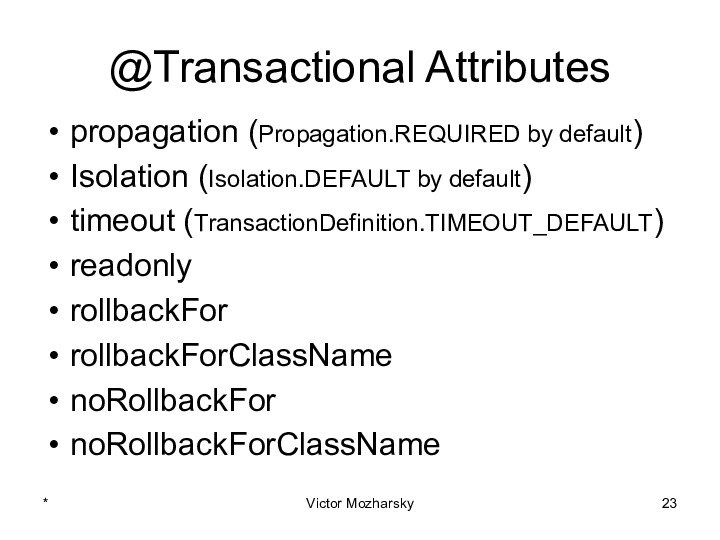
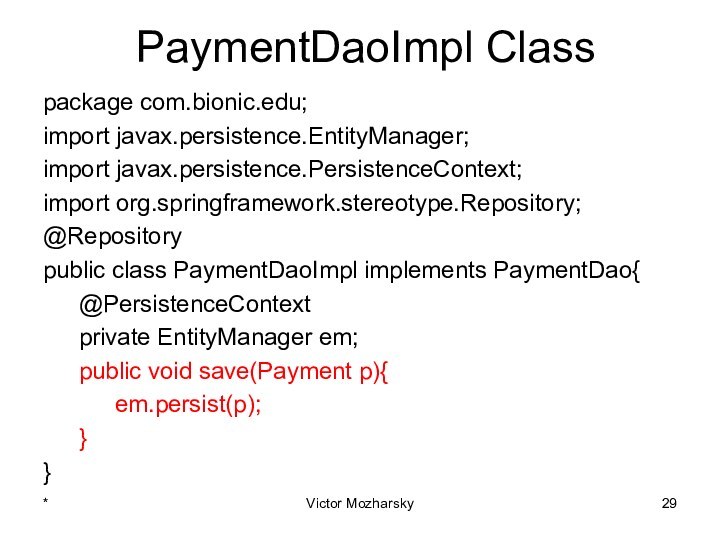
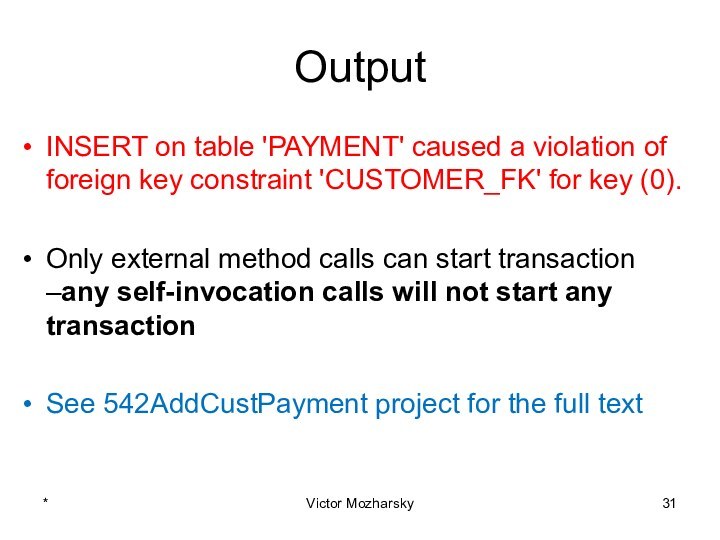
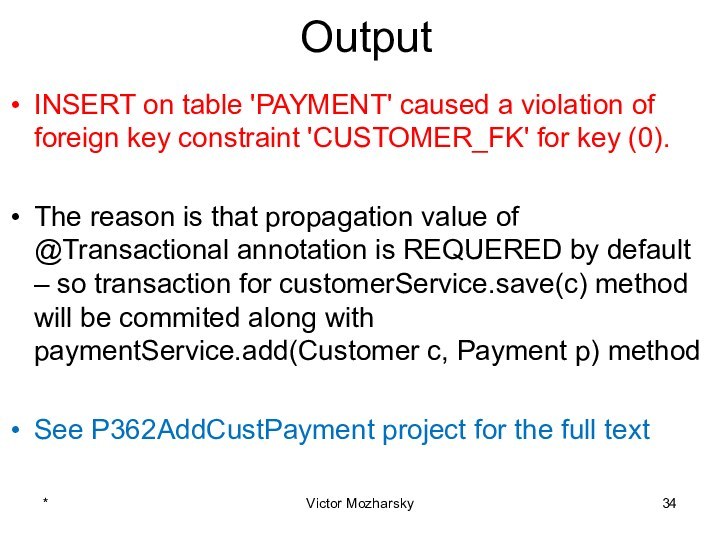
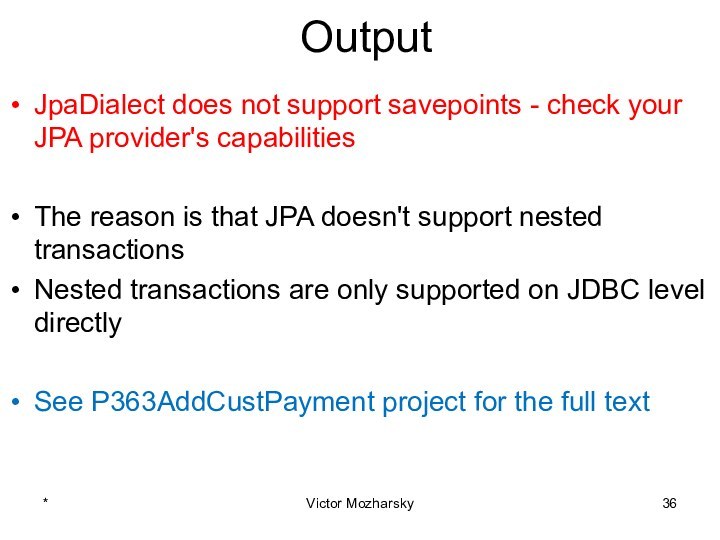
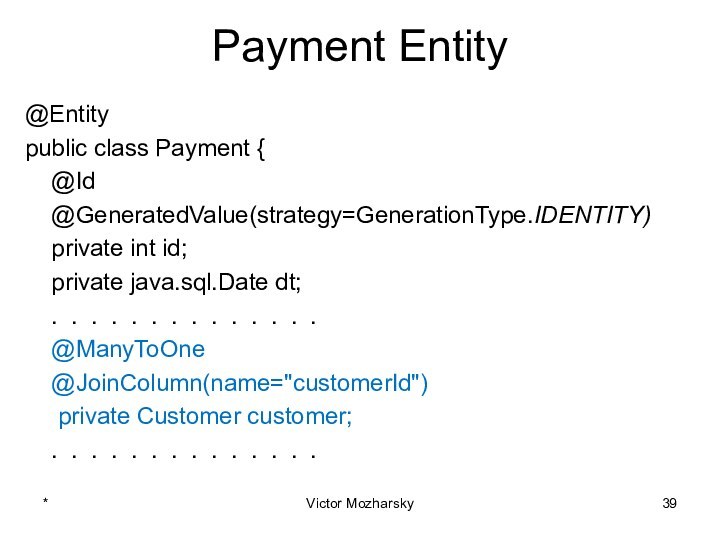
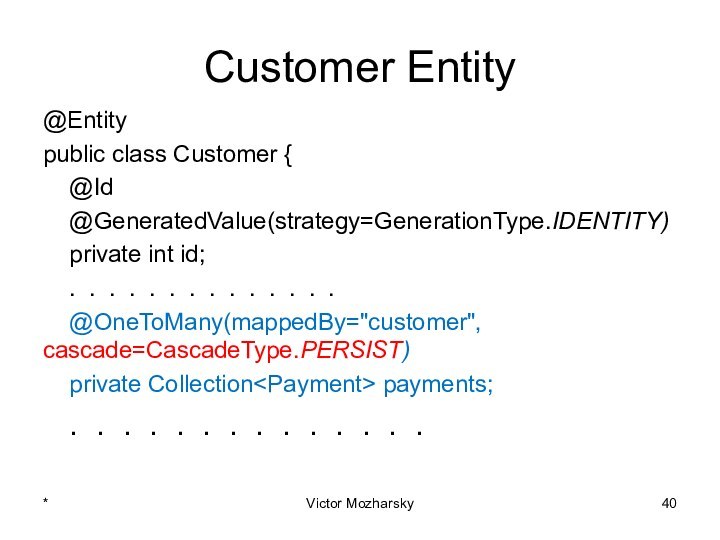
actions that are treated as a single unit of
workThese actions should either complete entirely or take no effect at all
Transaction management is an important part of RDBMS oriented enterprise applications to ensure data integrity and consistency.
*
Victor Mozharsky