Слайд 2
LESSON OBJECTIVES:
Water and its structure
To explore the unique
properties of water as the cohesion, adhesion, capillary water
and surface tension
Chemical properties of water as solvent
Water Hardness
Слайд 3
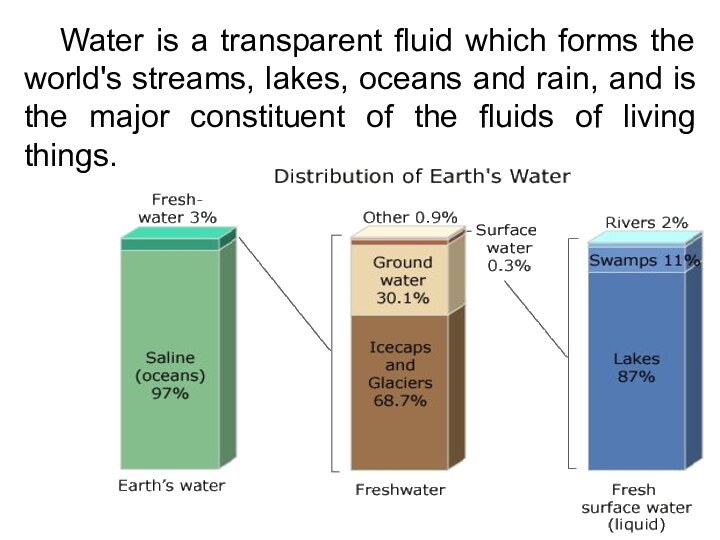
Water is a transparent fluid which forms the
world's streams, lakes, oceans and rain, and is the
major constituent of the fluids of living things.
Слайд 4
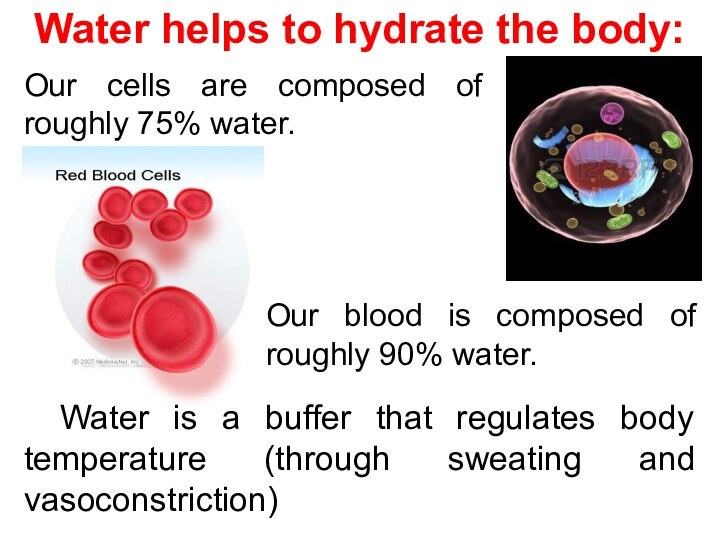
Water is a buffer that regulates body temperature
(through sweating and vasoconstriction)
Water helps to hydrate the body:
Our cells are composed of roughly 75% water.
Our blood is composed of roughly 90% water.
Слайд 5
Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature
and pressure, but it often co-exists on Earth with
its solid state, ice; and gaseous state, steam (water vapor). It also exists as snow, fog, dew and cloud.
snow
fog
dew
clouds
Слайд 7
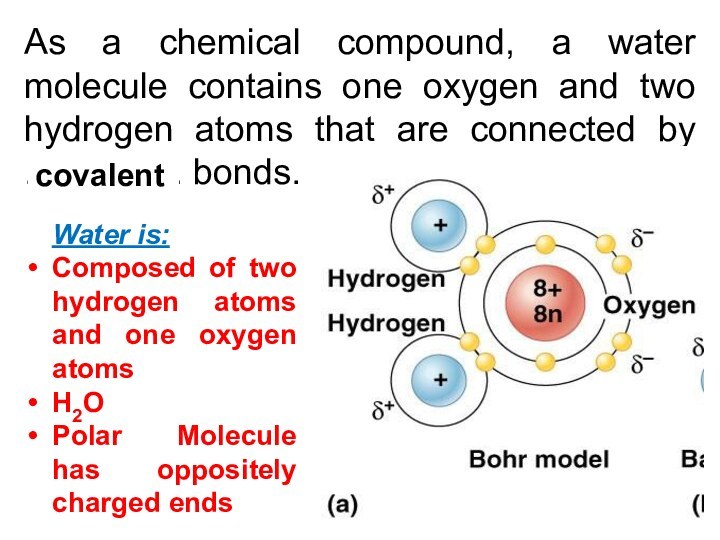
As a chemical compound, a water molecule contains
one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected
by ................ bonds.
Water is:
Composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atoms
H2O
Polar Molecule has oppositely charged ends
covalent
Слайд 8
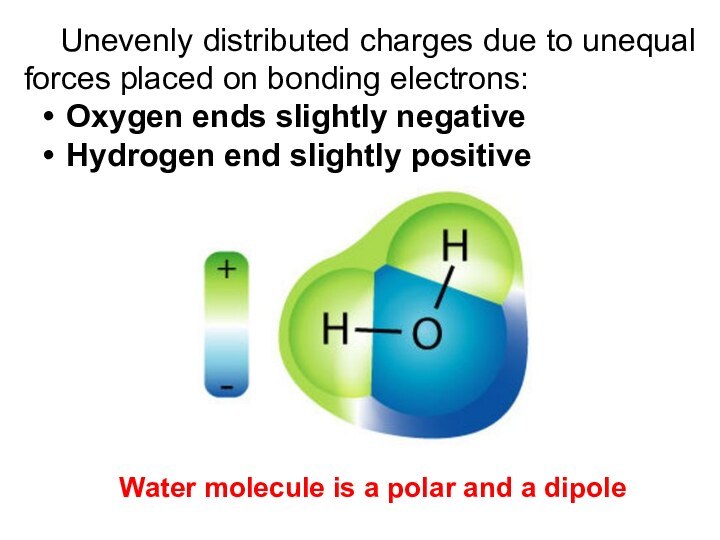
Unevenly distributed charges due to unequal forces placed
on bonding electrons:
Oxygen ends slightly negative
Hydrogen end slightly positive
Water
molecule is a polar and a dipole
Слайд 9
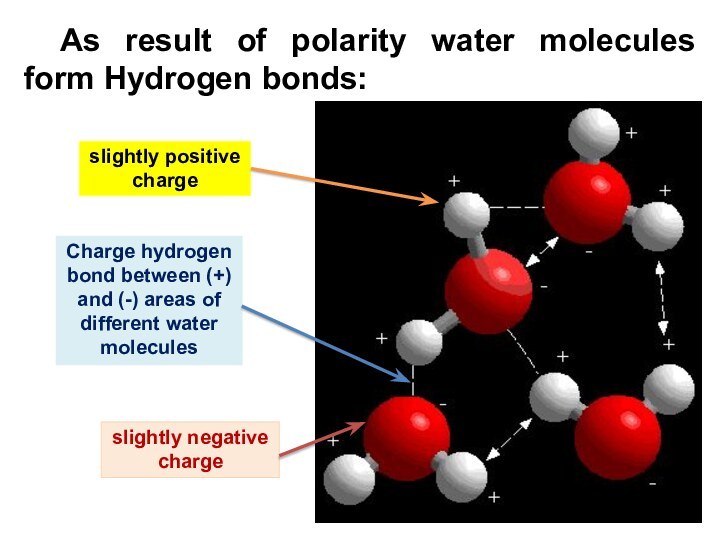
As result of polarity water molecules form Hydrogen
bonds:
slightly positive
charge
Charge hydrogen bond between (+) and (-)
areas of different water molecules
slightly negative
charge
Слайд 10
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF WATER:
Water has a high specific heat.
Water in a pure state has a neutral pH. As
a result, pure water is neither acidic nor basic. Water changes its pH when substances are dissolved in it.
Water conducts heat more easily than any liquid except mercury.
Water molecules exist in liquid form over an important range of temperature from 0 - 100° Celsius.
Water has a high surface tension.
Water is a universal solvent.
Слайд 11
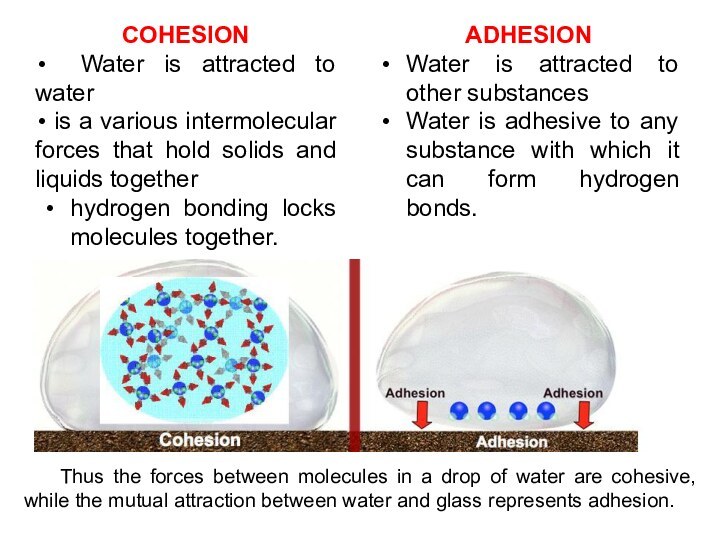
COHESION
Water is attracted to water
is
a various intermolecular forces that hold solids and liquids
together
hydrogen bonding locks molecules together.
ADHESION
Water is attracted to other substances
Water is adhesive to any substance with which it can form hydrogen bonds.
Thus the forces between molecules in a drop of water are cohesive, while the mutual attraction between water and glass represents adhesion.
Слайд 13
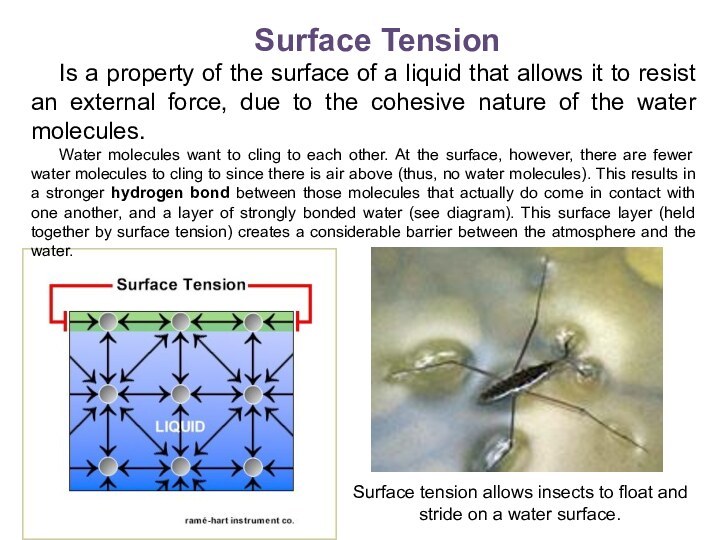
Surface Tension
Is a property of the surface
of a liquid that allows it to resist an
external force, due to the cohesive nature of the water molecules.
Water molecules want to cling to each other. At the surface, however, there are fewer water molecules to cling to since there is air above (thus, no water molecules). This results in a stronger hydrogen bond between those molecules that actually do come in contact with one another, and a layer of strongly bonded water (see diagram). This surface layer (held together by surface tension) creates a considerable barrier between the atmosphere and the water.
Surface tension allows insects to float and stride on a water surface.
Слайд 14
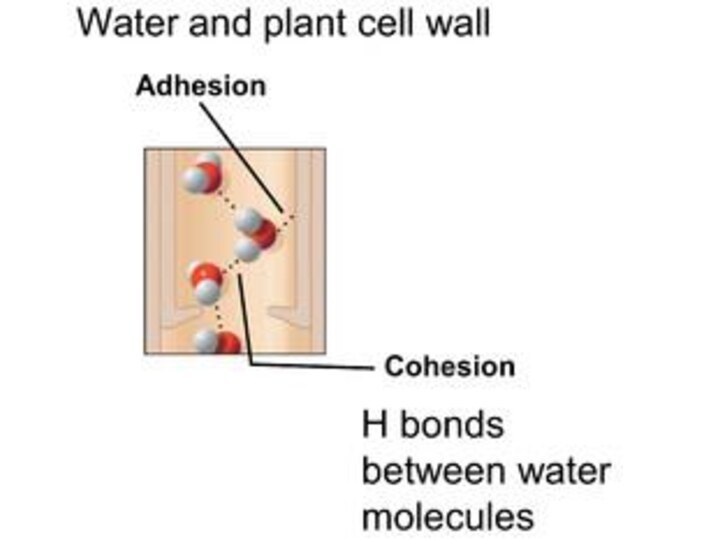
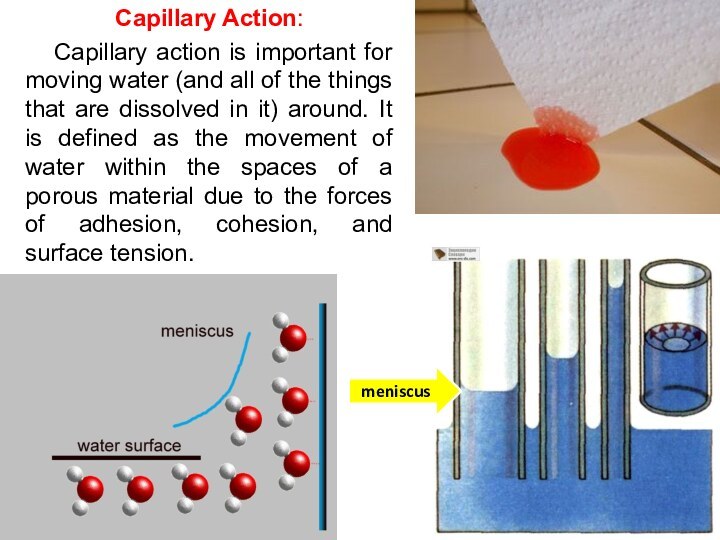
Capillary Action:
Capillary action is important for moving water
(and all of the things that are dissolved in
it) around. It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous material due to the forces of adhesion, cohesion, and surface tension.
meniscus
Слайд 15
Density:
Water has a density of 1g/mL at 4 °C
Water
is the one of the few substances that is
less dense as a solid than liquid
Due to hydrogen bonding and resultant pockets
ice floats on water because
it is less dense
Слайд 16
Properties of Water
At sea level, pure water boils
at 100 °C and freezes at 0 °C.
The
boiling temperature of water decreases at higher elevations (lower atmospheric pressure).
For this reason, an egg will take longer to boil at higher altitudes
Слайд 17
Water is Universal Solvent:
Ions and polar molecules readily
dissolve in water
Substances such as salt are pulled
apart by attraction of opposite charges due to polar structures
Слайд 18
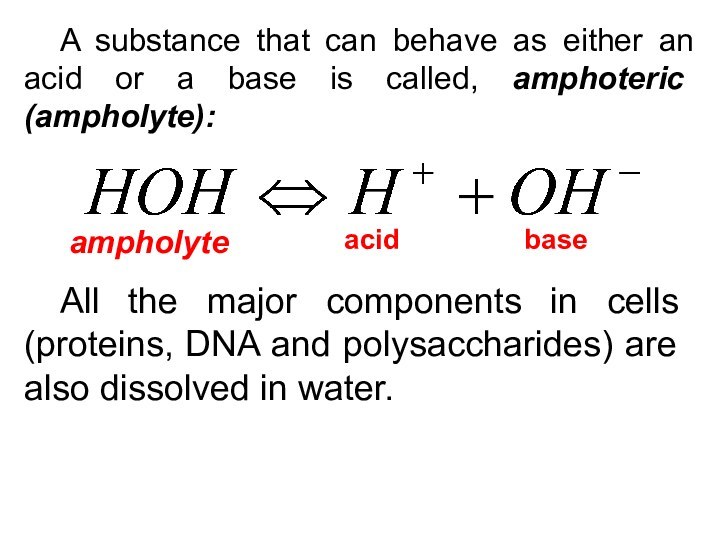
A substance that can behave as either an
acid or a base is called, amphoteric (ampholyte):
acid
base
ampholyte
All the
major components in cells (proteins, DNA and polysaccharides) are also dissolved in water.
Слайд 19
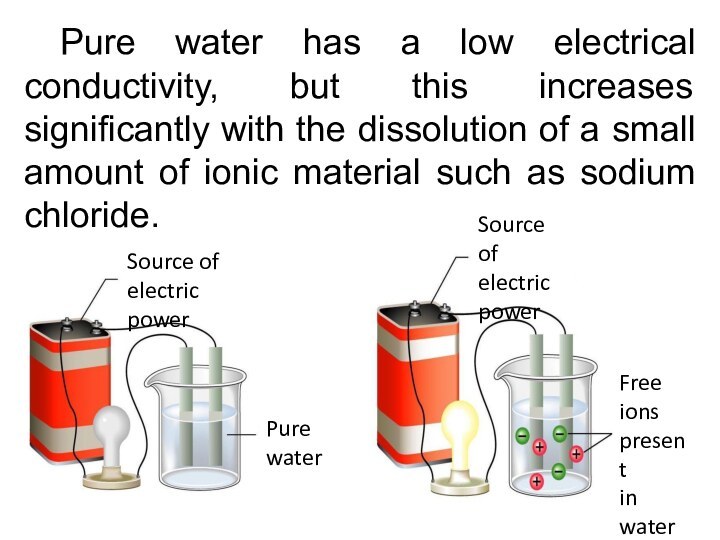
Pure water has a low electrical conductivity, but
this increases significantly with the dissolution of a small
amount of ionic material such as sodium chloride.
Слайд 20
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF WATER:
pH (activity acidity)
Total Acidity
Alkalinity
Total Hardness
Chemical
reactivity: water can participate in chemical reactions. Example: involvement
of water molecules in dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, electrolysis.
Metals – Iron, Manganese, Zinc, Copper, Chromium, Lead
Nitrate/ Nitrite
Arsenic, Selenium, Fluoride
Chloride
Total and Free Chlorine
In practice, the chemical properties of water are determined by analytical methods.
Слайд 21
REACTION OF WATER WITH METALS
Not all metals react with water.
Metals
of Group 1 (IA or alkali) react vigorously with cold
water forming hydroxide and hydrogen gas:
Metals from magnesium to iron in the activity series of metals, react with steam (but not H2O) to form the metal oxide and hydrogen gas:
Noble metals, such as gold and silver, do not react with water at all.
Слайд 22
DISSOLVING ELECTROLYTES IN WATER
Solid electrolytes are composed of
ions which are held together by electrostatic forces of
attraction. When an electrolyte is dissolved in water, these forces are weakened and the electrolyte undergoes dissociation into ions. The ions are solvated.
acid: HCl (g) + H2O (aq) = H+ (aq) + Cl-(aq)
base: NaOH (s) + H2O (aq) = Na+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
salt: NaCl(s) + H2O (aq) = Na+ (aq) + Cl-(aq)
The process of splitting of the molecules into ions of an electrolyte is called dissociation .
Слайд 23
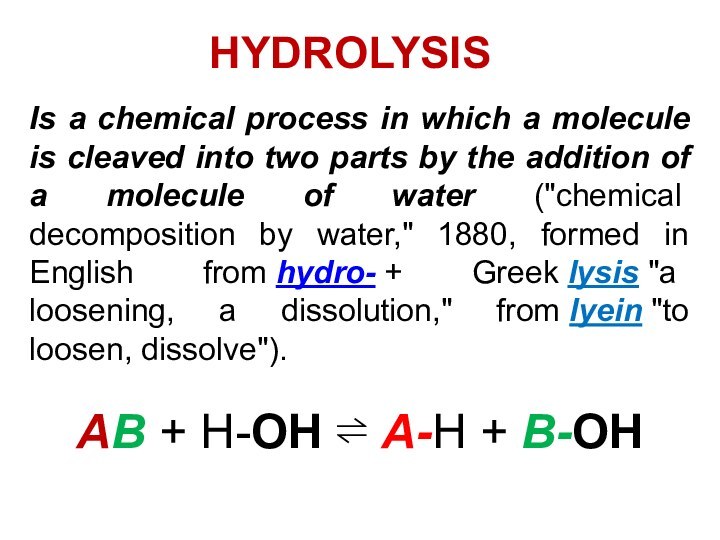
Is a chemical process in which a molecule
is cleaved into two parts by the addition of
a molecule of water ("chemical decomposition by water," 1880, formed in English from hydro- + Greek lysis "a loosening, a dissolution," from lyein "to loosen, dissolve").
AB + H-OH ⇌ A-H + B-OH
HYDROLYSIS
Слайд 24
TOTAL HARDNESS
One important indicators of water quality is
its hardness. General hardness (GH) is caused by the
presence of a certain concentration of calcium (Са2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions in 1 liter of water:
Слайд 25
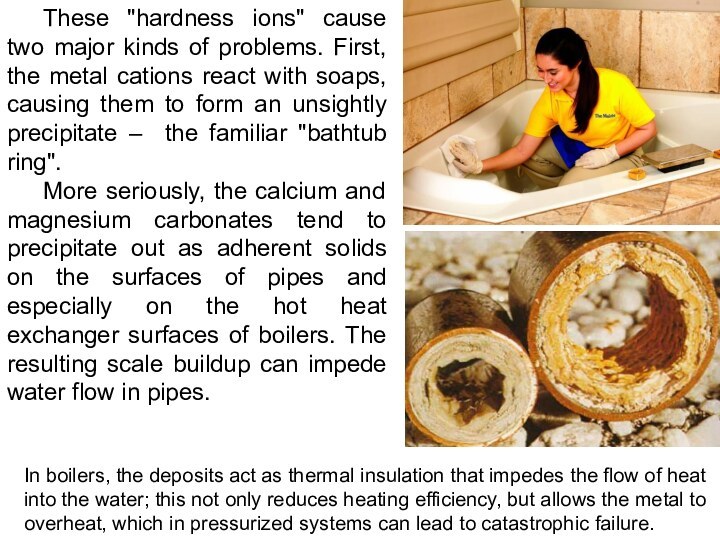
These "hardness ions" cause two major kinds of
problems. First, the metal cations react with soaps, causing
them to form an unsightly precipitate – the familiar "bathtub ring".
More seriously, the calcium and magnesium carbonates tend to precipitate out as adherent solids on the surfaces of pipes and especially on the hot heat exchanger surfaces of boilers. The resulting scale buildup can impede water flow in pipes.
In boilers, the deposits act as thermal insulation that impedes the flow of heat into the water; this not only reduces heating efficiency, but allows the metal to overheat, which in pressurized systems can lead to catastrophic failure.
Слайд 26
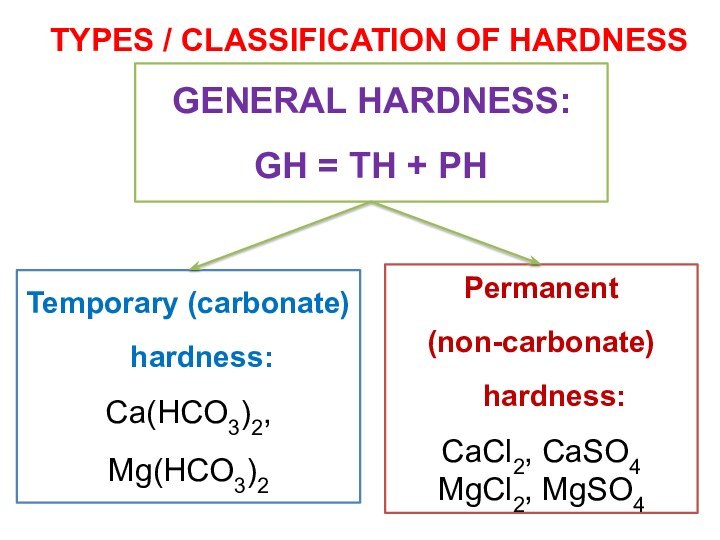
TYPES / CLASSIFICATION OF HARDNESS
Temporary (carbonate) hardness:
Ca(HCO3)2,
Mg(HCO3)2
Permanent
(non-carbonate) hardness:
CaCl2, CaSO4
MgCl2, MgSO4
GENERAL HARDNESS:
GH = TH + PH
Слайд 27
Temporary hardness is due to the presence of
bi-carbonates of calcium and magnesium. It can be removed
by easy means like boiling. When temporary hard water is boiled, the carbonates decompose with liberation of carbon-dioxide and precipitation of the insoluble Carbonates which are reformed:
MgCO3 is slightly soluble in water but heating will cause its hydrolysis into the much less soluble Mg(OH)2
So simple boiling and filtering of water remove temporary hardness.
TEMPORARY HARDNESS
Слайд 28
It is due to the presence of chlorides
and sulphates of calcium and magnesium. These salts do
not decompose on boiling. So permanent hardness can’t be removed easily. It can be removed by soda (Na2CO3), surfactants (Na3PO4) or lime (Ca(OH)2) when MgSO4 is responsible for hardness:
PERMANENT HARDNESS
Surfactant a substance that tends to reduce the surface tension of a liquid in which it is dissolved.
Слайд 29
Removal of Hardness
Boiling
Addition of lime
Addition of sodium carbonates
Base exchange process
Addition of Sodium carbonate
Base exchange process:
Sodium Permutit is used ( Na2Al2 Si2O H2O )
Exchange Na ions for Ca and Mg ions
Ca and Mg Permutit is formed .
Removes 100% hardness
Some raw water is added to protect against corrosive action of 100% soft water
Temporary Hardness
Permanent Hardness
Слайд 30
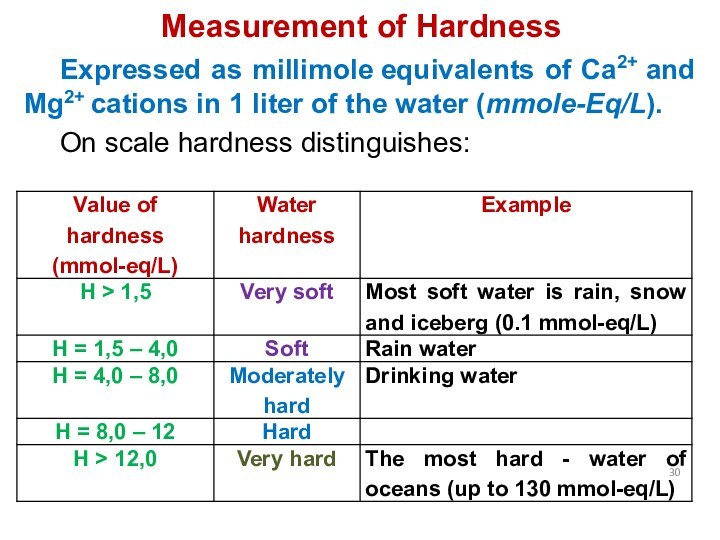
Measurement of Hardness
Expressed as millimole equivalents of Ca2+ and
Mg2+ cations in 1 liter of the water (mmole-Eq/L).
On
scale hardness distinguishes:
Слайд 31
ESTIMATION OF WATER HARDNESS
Water hardness can be determined
by the following 2 analytical methods:
By titration with HCl:
In this method temporary hardness can be measured.
By titration with EDTA: In this method general hardness can be measured.
Слайд 32
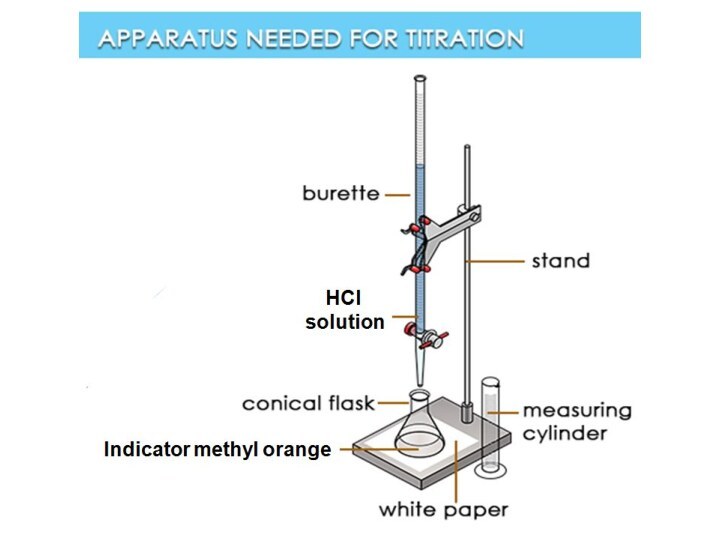
ESTIMATION OF TEMPORARY HARDNESS BY TITRATION WITH HCL:
For
determining temporary hardness: 100 ml hard water is taken
into a 250 ml conical flask. Then few 3-4 drops of methyl orange is added in it as an indicator. Now titration is carried out by adding 0.1N cold HCl until the yellow color of methyl orange turns red.
Here, each meal 0.1N HCl is equivalent to 0.005 gm of CaCO3. The associated reactions are as follows:
Слайд 33
Add 1ml of buffer solution (NH4OH+NH4Cl) to 100
ml of the original water sample. Add 3-4 drops
of Eriochrome Black T indicator. Titrate against 0.05N prepared EDTA solutions in burette until the color charges from wine red (or violet) to pure blue (or turquoise) with no reddish tone; then calculate the general hardness:
ESTIMATION OF GENERAL HARDNESS BY TITRATION WITH EDTA:
Слайд 34
Eriochrome Black Indicator reacted with metal ions in
water and changed its color:
Lab # 3 Water Hardness
Слайд 35
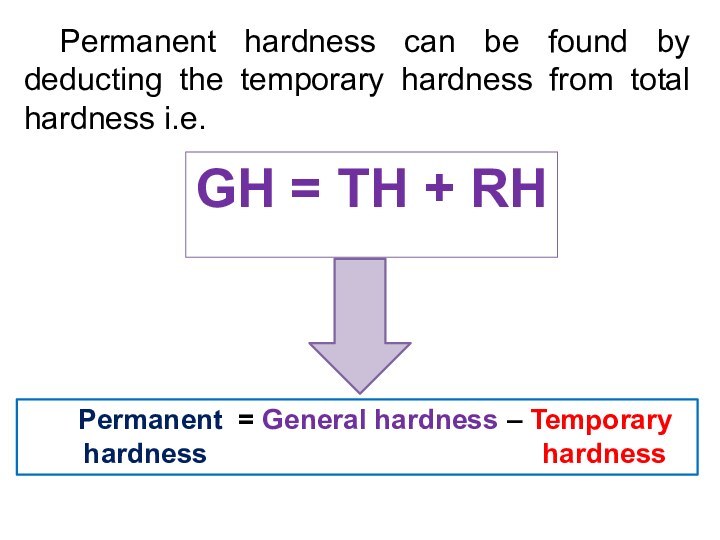
Permanent hardness can be found by deducting the
temporary hardness from total hardness i.e.
Permanent = General hardness
– Temporary
hardness hardness
GH = TH + RH
Слайд 36
CONCLUSION:
The safe drinking water is recognized water:
with pH
of 7 to 7.5 mmol / L
hardness not
more than 7 mmol / L,
the total amount of minerals in which not more than 1 g / l,
harmful chemical impurities do not exceed the maximum allowable concentrations,
and lacking pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
Слайд 38
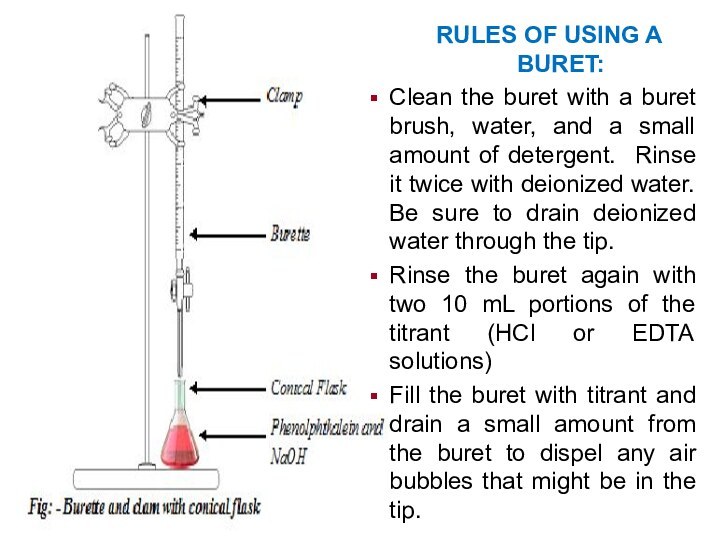
RULES OF USING A BURET:
Clean the buret with
a buret brush, water, and a small amount of
detergent. Rinse it twice with deionized water. Be sure to drain deionized water through the tip.
Rinse the buret again with two 10 mL portions of the titrant (HCl or EDTA solutions)
Fill the buret with titrant and drain a small amount from the buret to dispel any air bubbles that might be in the tip.
Слайд 39
Use a marker pen to create a black
area on a white note card. This will be
used to help locate the bottom of the meniscus when reading the buret.
Place the note card with the black mark behind the buret and just below the meniscus. This will make the bottom of the meniscus much easier to see. Record the volume reading to the nearest 0.01 mL.
Слайд 40
If you need to dispense less than a
full drop of titrant, open the stopcock slightly to
allow a small amount of titrant to accumulate on the tip of the buret.
Rinse the titrant on the tip into the flask using deionized water from your wash bottle.
Слайд 41
КИПЯЧЕНИЕ ВОДЫ
Жесткость снижается на 30 - 40%.
Слайд 42
ВЫМОРАЖИВАНИЕ ВОДЫ
Общая жесткость снижается на 70-80%.
Слайд 43
ФИЛЬТРАЦИЯ
Общая жесткость понижается на 80%.
Слайд 45
Что такое бытовой фильтр?
Внутри картриджа фильтра содержится смесь
из активированного угля (черные частицы) и катионообменники (гранулы смолы
белого цвета).
Уголь адсорбирует вредные органические вещества и хлориды.
Катионообменники снижают общую жесткость.