Слайд 2
Module logistics
See the module outline for details.
Some highlights:
Textbooks:
Lipczynski, Wilson and Goddard
Church
Assessment: 1.5 hour exam (70%), and
an individual coursework (30%)
The seminar will take place during teaching weeks 9 and 10 (depending on your group).
Слайд 3
Module structure
Structure
? Conduct ? Performance
Market definition
Concentration measures
Concentration determinants
Testing
SCP, NEIO
Advertising
R&D
Market power & welfare
Product Differentiation
Слайд 4
IO is the application of microeconomic theory to
the analysis of firms, markets and industries
In IO
(unlike microeconomics), the industry structure is entirely modelled and is dynamic.
Number and size distribution of firms
Barriers to entry
Product differentiation
Vertical integration and diversification
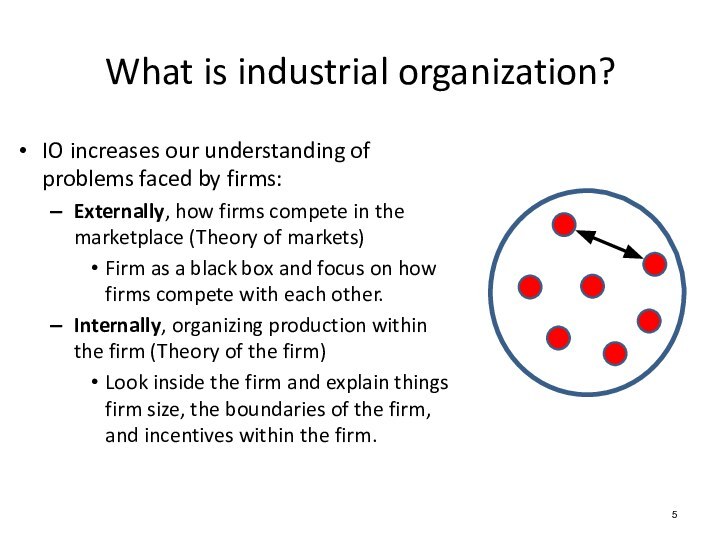
What is industrial organization?
Слайд 5
IO increases our understanding of problems faced by
firms:
Externally, how firms compete in the marketplace (Theory of
markets)
Firm as a black box and focus on how firms compete with each other.
Internally, organizing production within the firm (Theory of the firm)
Look inside the firm and explain things firm size, the boundaries of the firm, and incentives within the firm.
What is industrial organization?
Слайд 6
For policy makers:
Competition policy aims to prevent firms
from abusing market power. [Sherman Act 1890, China antitrust
law 2007]
How to measure market power and excess profit?
How competitive is a specific industry?
What types of firm behavior can make an industry less competitive?
What type of market structure is most conductive of innovation?
IO and policymaking
Слайд 7
2010: The EU commission accuses Google of promoting
its shopping service in internet search at the expense
of rival services
Google is accused of systematically favouring its own comparison shopping product in its general search results pages
http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_IP-15-4780_en.htm
Google’s response:
“Economic data (…), and statements from complainants all confirm that product search is robustly competitive”.
Google claims that Google shopping is operating in a field that includes Amazon and eBay, where shoppers go to compare prices.
IO and policymaking: The Google
antitrust case
Слайд 8
Google could face a 3bn euros fine.
Related to
that case, IO provides answers to the following questions.
How
to define a market?
How to measure market power?
How to stop dominant firms from abusing market power?
IO and policymaking: The Google
antitrust case
Слайд 9
Typology of market structures
Слайд 10
Dynamic theory where markets are changing due to
the activities of entrepreneurial and profit-seeking innovators.
“Creative destruction” (Schumpeter,
1928): Competition is driven by innovation
Innovation destroys old products and processes and replaces them with new ones.
Innovators earn profits and imitation gradually erodes these profits by cutting prices and raising input costs.
Abnormal profits and market power are necessary to motivate firms to innovate, and improve products in the long run
Austrian School: Schumpeter
Слайд 11
Creative destruction:
The music industry
1850
1900
1950
2000
Wind-up gramophone
Barrel organ
Pianola
Hi-Fi stereo
LP
records
Tape cassette
MP3
Compact Discs
Electrical gramophone
Слайд 12
The Chicago School
The Chicago School (1970-80s): Also argues
against government intervention
Large firms are large because they are
more efficient
In the long run abuse of market power is unlikely, e.g. collusive agreements are unstable
Markets have a tendency to revert towards competition, without the need for government intervention
Слайд 13
Concentrates on empirical analysis rather than on theoretical
analysis.
Bain (1956): There is a causal relationship between concentration
and profitability:
The SCP paradigm
Слайд 14
Structure ? Conduct ? Performance
The SCP paradigm
The
number and size distribution of firms
Entry conditions
Vertical integration and
diversification
Pricing strategies
Advertising
R&D
Differentiation
Collusion
Mergers
Profitability
Growth
Quality of products
Technical progress
Productive efficiency
SCP assumes a causal relationship between structure, conduct, and performance.
Most influential during the 1950-1970s.
Слайд 15
According to SCP, relationships between structural variables and
market performance hold across industries.
The line of causality
is from structure through performance. If a stable relationship is established between structure and market power, it is assumed that structure determines market power.
The SCP paradigm
Слайд 16
SCP & European banking: Structure
1980s: European banking was
fragmented. Banks did not operate in other countries [high
entry barriers]. Domestic banks did not face competition from foreign banks.
Deregulation made EU banking more competitive
Second Banking Directive, 1990
Creation of the euro
As a consequence: Banks able to trade throughout Europe.
Lowered entry barriers.
Do this make the industry more competitive or less competitive?
Слайд 17
SCP & European banking: Structure
1990-2009: decline in the
number of banks
Слайд 18
SCP & European banking: Structure
1990-2009: increased level of
seller concentration
Слайд 19
SCP & European banking: Conduct
Following the deregulation, many
banks have consolidated (M&A), e.g.
Unicredito (Italy) and HVB (Germany)
BNP
Paribas (France) Banco Nazionale de Lavoro (Italy)
Banco Santander (Spain) and Alliance of Leicester (UK)
Large banks have adapted their structures, risk management and strategic planning functions to deal with pan-European activity.
Слайд 20
SCP & European banking: Performance
1990-2006: increased profitability despite
the lowering of entry barriers.
How to explain the increased
profits?
Increased consolidation; Product diversification; Cost-cutting
Слайд 21
Structure ? Conduct ? Performance
Conduct
to structure? R&D, advertising, differentiation
Performance to structure? Growth and
changing market shares
Performance to conduct? Profitability and capacity to invest in R&D, or cut prices
SCP: Reverse causality?
Слайд 22
Structure ? Conduct ? Performance
Public
policies that aim to prevent the abuse of market
power
Preventing mergers beyond a certain scale [STRUCTURE]
Price controls, restrictions on collusion [CONDUCT]
Policies that also affect firms’ PERFORMANCE
Competition policy and SCP
Not allowing M&As
Taxation
Price controls
Слайд 23
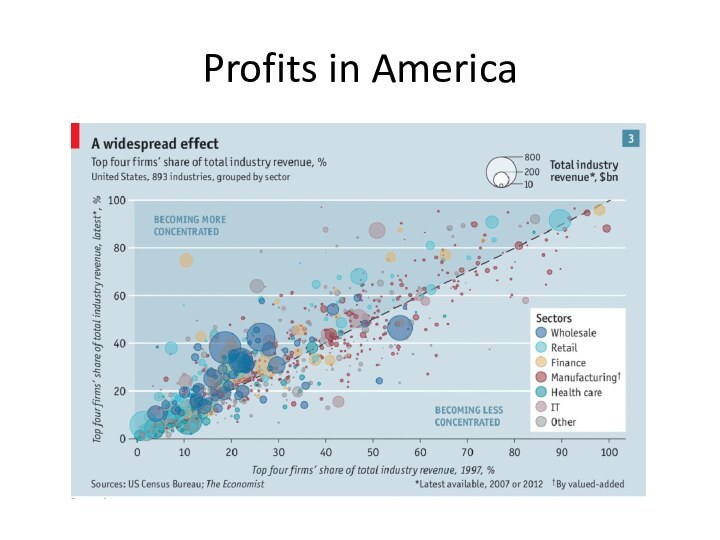
Profits in America and the
practical relevance of
IO
Source: ‘Too much of a good thing’. The Economist,
2016.
Profits have risen in most rich countries over the past ten years.
E.g. America Airlines: Used to make losses; but made $24bn profit in 2015.
How? The falling price of fuel has not been passed on to the consumers.
Why not? Consolidations has left the industry with 4 dominant firms with many shareholders in common.
Слайд 25
Profits in America
- Historical developments
In the 1990s American
firms faced a wave of competition from low-cost competitors
abroad.
In 1998, Joel Klein (DoJ), declared that “our economy is more competitive today than it has been in a long, long time.”
How to explain the recent increase in corporate earnings?
Since 2008 American firms have engaged in mergers worth $10 trillion, allowing the merged companies to increase market shares and cut costs.
Two-thirds of the industry sectors became more concentrated between 1997 and 2012. The average share of the top 4 firms has risen from 26% to 32%.
Слайд 28
Profits in America
About 25% of America’s abnormal profits
are spread across a wide range of sectors.
Another 25%
comes from the health-care industry (pharmaceutical and medical-equipment). Patent rules allow temporary monopolies on new drugs and inventions. Much of health-care purchasing is controlled by insurance firms. Four of the largest, Anthem, Cigna, Aetna and Humana, are planning to merge into two larger firms.
The remaining 50% abnormal profits are in the technology sector, where firms such as Google and Facebook enjoy market shares of 40% or more.
Слайд 33
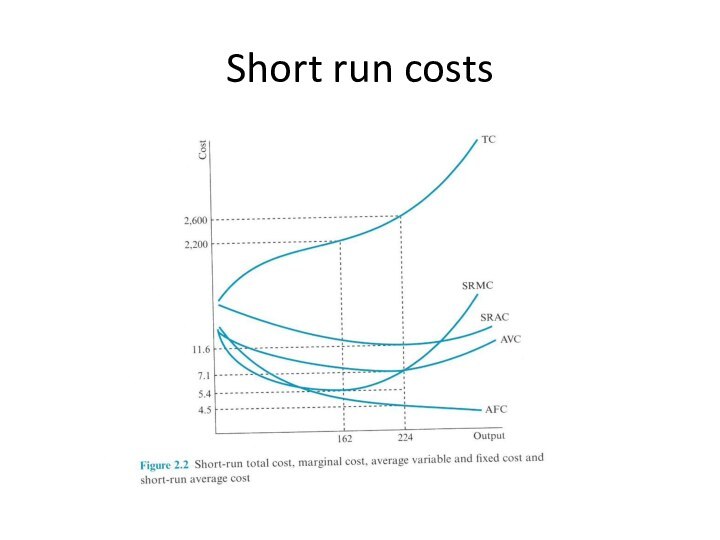
Long run costs
In the long-run, firms can change
their usage of all the inputs, including capital, number
and size of factories etc.
LRAC: Lowest cost of producing any given output level when the firm can vary both K and L.
Draw SRAC for all possible levels of K. The curve that enfolds these curves from below is the LRAC.
Compared to SRAC, LRAC decline longer before finally increasing
LRMC: long-run marginal cost
Слайд 35
Application to oil pipelines
Costs associated with construction and
operation:
Planning and design
Acquisition of clearing the right-of-way
Construction costs
Steel for
the pipeline
Pumps (One time fixed costs)
Electricity to power the pumps (variable costs)
Labor (monitoring personnel) (fixed cost)
Слайд 36
Application to oil pipelines
Electricity costs vary with throughput,
but the number of personnel does not.
The salary of
personnel is avoidable if the pipeline shuts down.
What are the variable costs?
What are the fixed costs?
Слайд 37
Economies of scale
Economies of scale impact the LRAC
Minimum
efficient scale = output level beyond which firms can
make no further savings in LRAC through further expansion.
Economies of scale
Indivisibilities
Learning economies
Purchasing economies
Transports economies
Diseconomies of scale
Long chains of command
Strained communications
Bureaucracy
Слайд 39
Empirical studies of economies of scale
Some firms have
U-shaped LRAC
However, manufacturing firms often have L-shaped LRAC
Estimates of
MES:
Слайд 40
Empirical studies of economies of scale
Survivorship studies: If
a particular plant size is efficient, eventually all plants
in that industry should approach that size.
Example from the beer industry:
Слайд 41
Economies of scope
Economies of scope are the cost
savings that arise when a firm produces two or
more outputs using the same set of resources.
Example 1: Manufacturing process
Oil refineries produce gasoline and kerosene as part of the refining process
Example 2: Knowledge gained from developing, producing, or marketing one product can be applied to another product
R&D investment for a specific software can benefit other categories of softwares
Слайд 42
Economies of scope
Example 3: Umbrella advertising
Advertising one Samsung
product will lead to more demand for other Samsung
products (even if they are not related).
New products are easier to introduce when there is an established brand with the desired image.
Virgin: 400+ companies, active in railways, airlines, soda, mobile, media etc.
Слайд 47
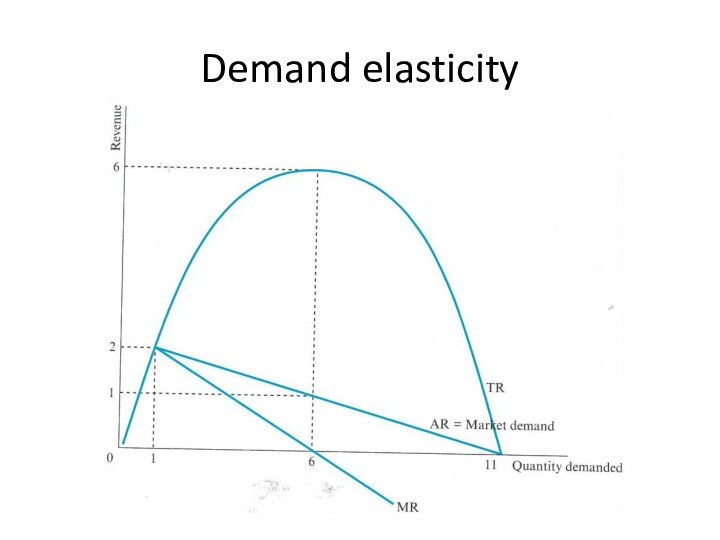
Cross-price elasticity of demand
CES>0. Goods 1 and 2
are substitute. As the price of Good 2 increases,
consumers switch from Good 2 to Good 1.
CES<0. Goods 1 and 2 are complement. As the price of Good 2 increases, demand for Good 1 decreases.
CED=0. Goods 1 and 2 are independent.