- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему Immunty system
Содержание
- 2. ORGANS OF IMMUNITY SYSTEM 1-Spleen2-Lymph node3-Glottis4-Mucosol node5-Thymus6-Reticula – Endothelial System
- 3. SpleenThe spleen involved in;- Degradation of old
- 5. TYPES OF IMMUNITY Immunity is maintained by two pathways;1-Non- specific immunity.2-Specific immunity.
- 6. IMMUNITY
- 8. Acquisition of immunityActive immunityPassive immunity
- 9. active immunity1. In the case of active immunity,
- 10. 2. Passive immunity2. Passive immunity is the acquisition by an
- 11. Furthermore, either active or passive immunity may
- 13. 1-NON-SPECIFIC IMMUNITY: It is maintained by
- 14. b) Phagocytosis:Leucocytes are involved in the maintance
- 15. c) Inflammatory Response
- 16. SPECIFIC IMMUNITY: Cells Involved in the Immune
- 17. Bacteria With Antigens on SurfaceMacrophageT cellB cellA
- 18. MacrophageT CellHelper T CellKiller T CellInfected CellAntigens
- 19. SPECIFIC IMMUNITY: It is maintained by two
- 20. ACQUISTION OF HUMARAL IMMUNITY ANTIGENS:Antigens consist of
- 21. SkinWoundBacteria enter the woundPhagocytes move into the
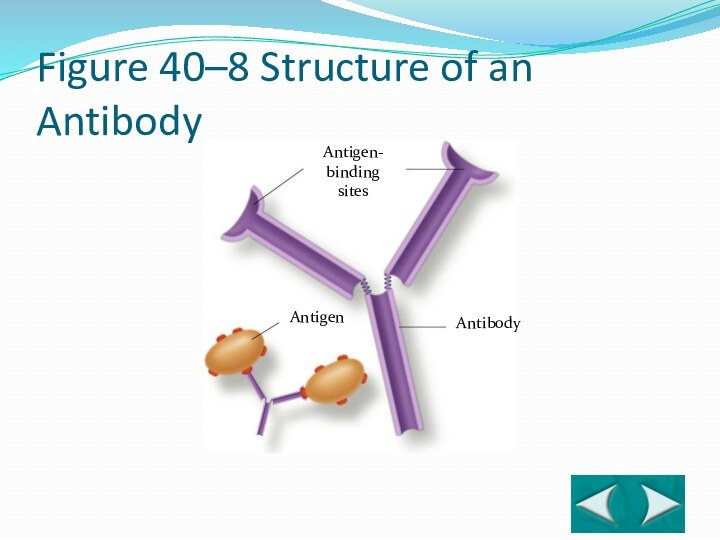
- 22. Antigen- binding sitesAntigenAntibodySection 40-2Figure 40–8 Structure of an Antibody
- 23. Specific Defenses, continuedRecognizing InvadersSome cells of the
- 24. ANTIBODIES:All vertabrates can synthesize antibodies. They are
- 25. The Immune Response Has Two Main PartsTwo
- 27. The structure of antibodies: Antibodies stuctrally are
- 28. The diseas causing organism
- 29. TOXIN – ANTITOXIN: The human immune system
- 30. ALLERGY: All allergies can be described as
- 31. VACCINES: They are composed of physological fluid
- 32. Скачать презентацию
- 33. Похожие презентации



















Слайд 2
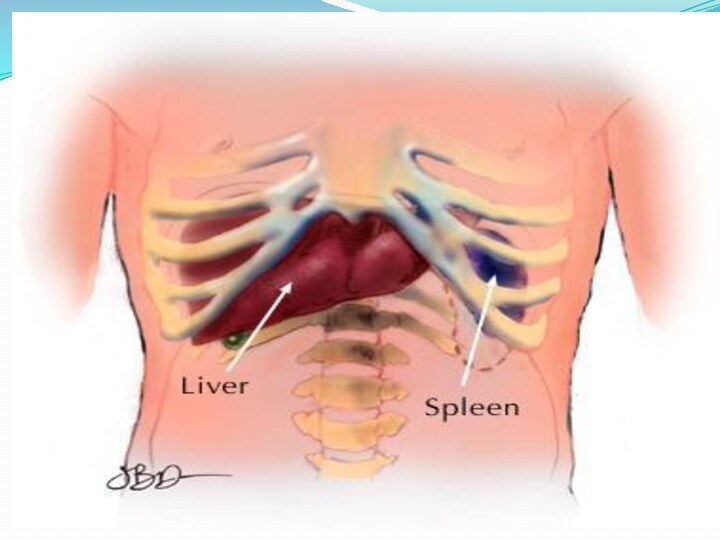
ORGANS OF IMMUNITY SYSTEM
1-Spleen
2-Lymph node
3-Glottis
4-Mucosol node
5-Thymus
6-Reticula –
Endothelial System
Слайд 3
Spleen
The spleen involved in;
- Degradation of old and
dead erythrocytes
- Production of lymphocytes active in the defense
of the body- It is then produce red bone marrow
Слайд 5
TYPES OF IMMUNITY
Immunity is maintained
by two pathways;
1-Non- specific immunity.
2-Specific immunity.
Слайд 6
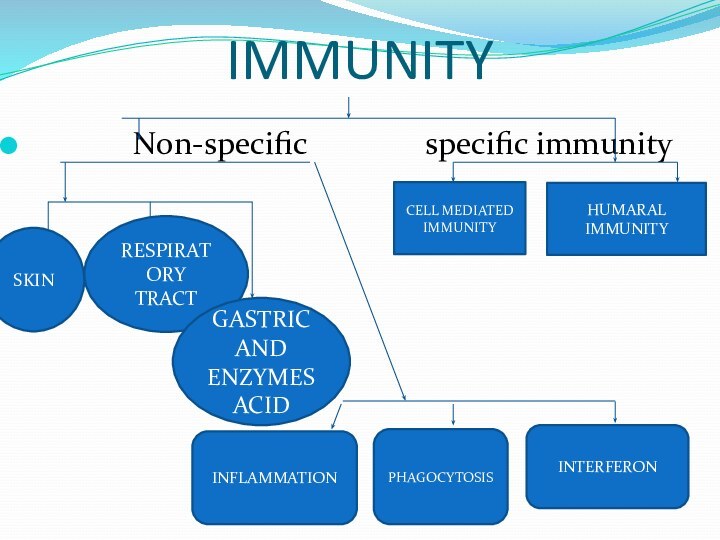
IMMUNITY
Non-specific
specific immunitySKIN
RESPIRATORY
TRACT
GASTRIC
AND ENZYMESACID
INFLAMMATION
PHAGOCYTOSIS
INTERFERON
CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
HUMARAL IMMUNITY
Слайд 9
active immunity
1. In the case of active immunity, the
animal undergoes an immunological response to an antigen and
produces the cells and factors responsible for the immunity, i.e., the animal produces its own antibodies and/or immuno-reactive lymphocytes. Active immunity can persist a long time in the animal, up to many years in humans.
Слайд 10
2. Passive immunity
2. Passive immunity is the acquisition by an animal
of immune factors which were produced in another animal,
i.e., the host receives antibodies and/or immuno-reactive lymphocytes originally produced during an active response in another animal. Passive immunity is typically short-lived and usually persists for only a few weeks or months.
Слайд 11
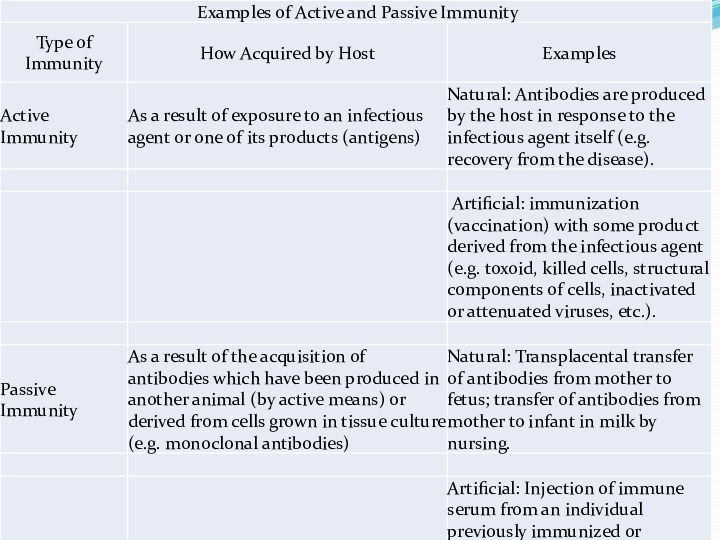
Furthermore, either active or passive immunity may be
acquired by naturalmeans (e.g. self production of antibodies during infection
or transfer of antibodies from mother to offspring) or by artificial means (i.e., vaccination and other immunization procedures). Some familiar examples of active and passive immunity are given in the table below.
Слайд 13
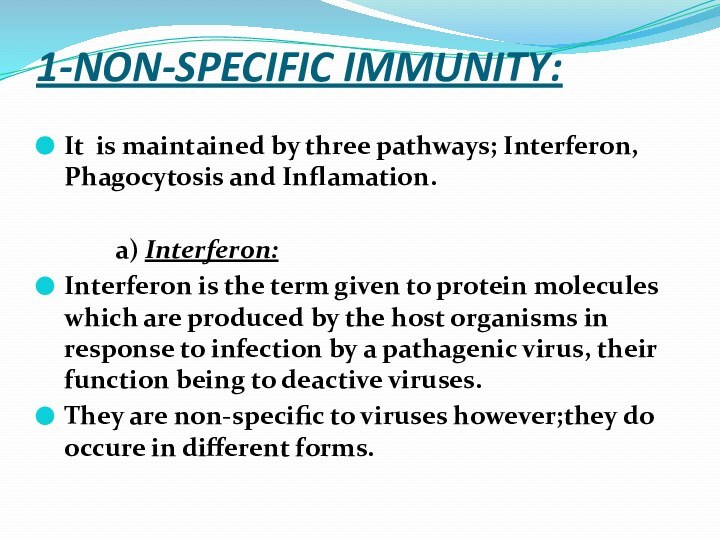
1-NON-SPECIFIC IMMUNITY:
It is maintained by three pathways;
Interferon, Phagocytosis and Inflamation.
a) Interferon:
Interferon is the term given
to protein molecules which are produced by the host organisms in response to infection by a pathagenic virus, their function being to deactive viruses. They are non-specific to viruses however;they do occure in different forms.
Слайд 14
b) Phagocytosis:
Leucocytes are involved in the maintance of
immunity againts pathogenic microbes.
Neuthropills are monocytes digest microbes by
Phagocytosis.
Слайд 16
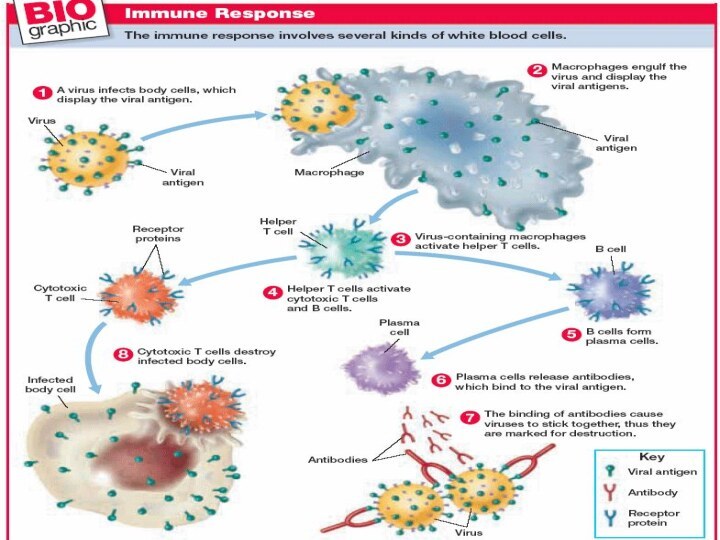
SPECIFIC IMMUNITY:
Cells Involved in the Immune Response
Cytotoxic T
cells attack and kill infected cells.
B cells label invaders
for later destruction by macrophages.Helper T cells activate both cytotoxic T cells and B cells.
Слайд 17
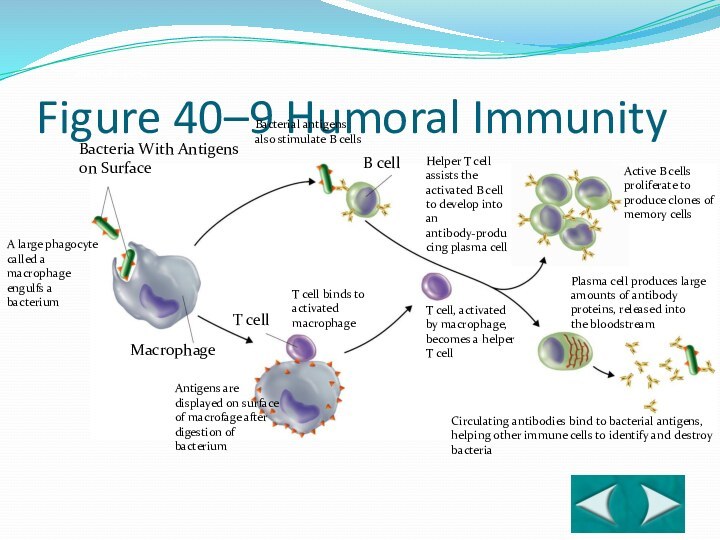
Bacteria With Antigens on Surface
Macrophage
T cell
B cell
A large
phagocyte called a macrophage engulfs a bacterium
Circulating antibodies bind
to bacterial antigens, helping other immune cells to identify and destroy bacteriaActive B cells proliferate to produce clones of memory cells
Helper T cell assists the activated B cell to develop into an antibody-producing plasma cell
T cell, activated by macrophage, becomes a helper T cell
Antigens are displayed on surface of macrofage after digestion of bacterium
T cell binds to activated macrophage
Section 40-2
Figure 40–9 Humoral Immunity
Bacterial antigens
also stimulate B cells
Plasma cell produces large amounts of antibody proteins, released into
the bloodstream
Слайд 18
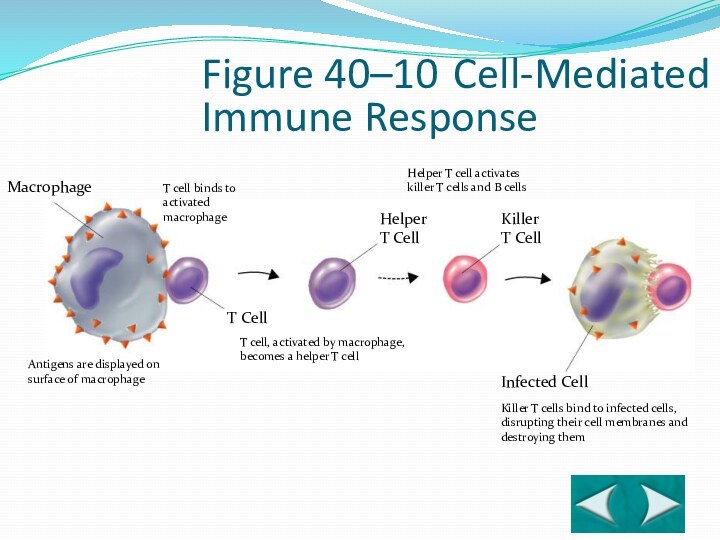
Macrophage
T Cell
Helper T Cell
Killer T Cell
Infected Cell
Antigens are
displayed on surface of macrophage
T cell binds to
activated
macrophageT cell, activated by macrophage, becomes a helper T cell
Helper T cell activates
killer T cells and B cells
Killer T cells bind to infected cells, disrupting their cell membranes and destroying them
Section 40-2
Figure 40–10 Cell-Mediated
Immune Response
Слайд 19 SPECIFIC IMMUNITY: It is maintained by two pathways; Humeral
immunity and Cell mediated immunity.
a) Humeral immunity:
This type of
immunity is the most effective immunity agains diseas such as typhoid and diphteria.
The factors which are effective in humaral immunity.
Слайд 20
ACQUISTION OF HUMARAL IMMUNITY
ANTIGENS:
Antigens consist of foreign substances
that intiated the formation of antibodies againts them.
When they
enter the body of humans or other animals. Antigens facilate the the formation of antibodies and also react with them go inside and outside of the body.
A factionally operational antigen should be;
in high molecular weight
recognise as hostile to the host organism
Persistant enough to remain in the host.
Слайд 21
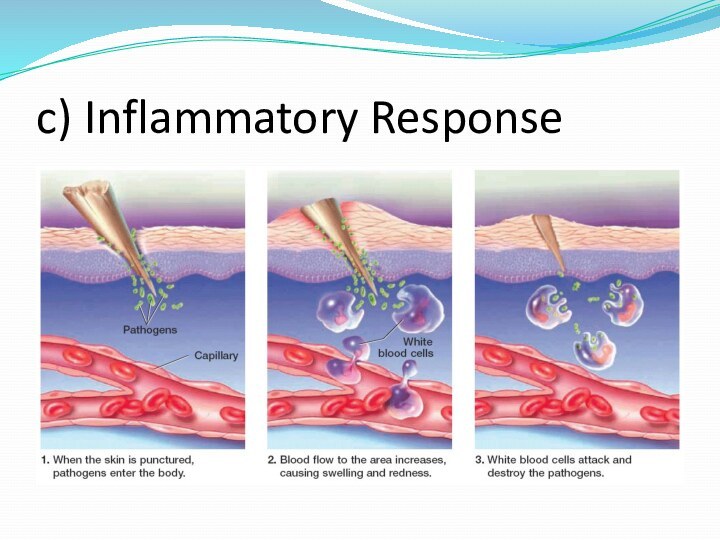
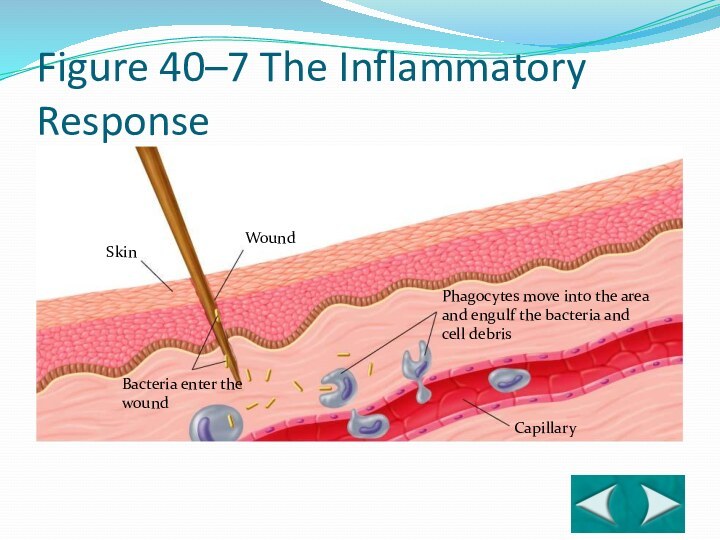
Skin
Wound
Bacteria enter the wound
Phagocytes move into the area
and engulf the bacteria and cell debris
Capillary
Section 40-2
Figure 40–7 The
Inflammatory Response
Слайд 23
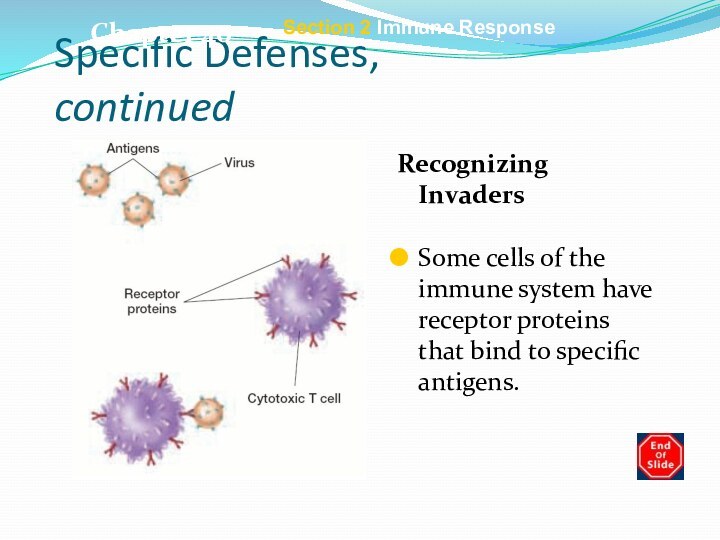
Specific Defenses, continued
Recognizing Invaders
Some cells of the immune
system have receptor proteins that bind to specific antigens.
Section
2 Immune ResponseChapter 40
Слайд 24
ANTIBODIES:
All vertabrates can synthesize antibodies.
They are formed
by stimulation by the antigen and react with them.they
are also known as immugloblins.
Слайд 25
The Immune Response Has Two Main Parts
Two distinct
processes work together in an immune response.
One is the
B cell response, a defense that aids the removal of extracellular pathogens from the body.The other is the T cell response, a defense that involves the destruction of intracellular pathogens by cytotoxic T cells.
Слайд 27
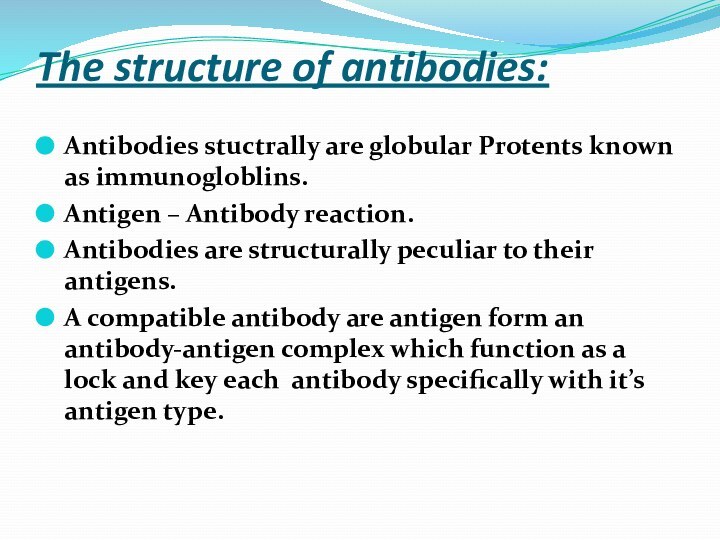
The structure of antibodies:
Antibodies stuctrally are globular Protents
known as immunogloblins.
Antigen – Antibody reaction.
Antibodies are structurally peculiar
to their antigens. A compatible antibody are antigen form an antibody-antigen complex which function as a lock and key each antibody specifically with it’s antigen type.
Слайд 28
The diseas causing organism
is referned to as the pathegon and it’s ability
to caused diseas is called virulance.Conerally,antibodies make dread contact with antigens.
Four different results of these reaction areas for follows: Aglulatiuation, Percipitation, Neutrilisation, Lysis.
Слайд 29
TOXIN – ANTITOXIN:
The human immune system can produse
antitoxing againts these exotoxins.
Antitoxin serum contains antitoxin antibodies.
Слайд 30
ALLERGY:
All allergies can be described as a type
of response by the immune system to infection from
diseases.The symptoms of an allergy originate from the activity of an antigens and antibodies in the lymphatic system.
A few bacteria such as tuberculosis bacillus produce an allergic response.
These bacteria are called allergens.
Слайд 31
VACCINES:
They are composed of physological fluid and weakened
or dead microbe.
Thus the body recognises the microbe
and produce antibodies or antitoxides to them. The vaccine for each illness is there fore unique, compound vaccines administrated to together are used againts two or more deceases.
Vaccines sustain active immunity and their effect is long term.