Слайд 2
Outline
The causes of global economic crisis
Channels of transmission
The
impact of crisis on global trade
Global crisis and trade
credit
Rising protectionism
Outlook
Role of trade policy
Слайд 3
Global Economic Crisis
In order to assess the role
that can be played by trade policy one has
to understand the causes of the crisis
Causes: Common elements: high credit growth, asset price appreciation (house price boom) large capital flows. New elements: increased financial integration, greater financial complexity, weakness in regulation and supervision
Channels: Financial and trade linkages
Слайд 4
Channels of transmission
Financial: As the crisis emerged in
the US subprime, it spread to other US financial
markets
International transmission: liquidity; banks with exposure to US, freezing of credits markets
Solvency: financial meltdown
Trade not a channel for contagion of the crisis, but casualty.
Слайд 5
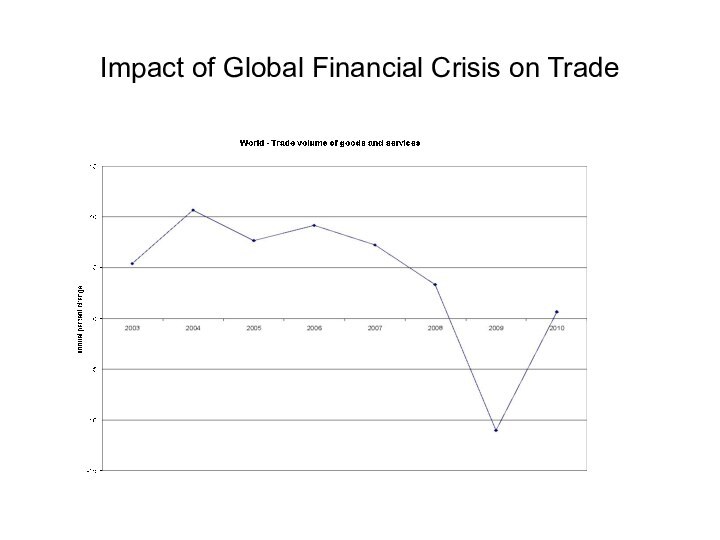
Impact on trade
Although the current crisis is a
financial crisis and is transmitted through the financial channel
internationally, it has an impact on both the supply-side and demand-side of trade.
Supply-side impact: Trade has collapsed due to drying up of trade finance; collapse of vertical integration; disruption in international capital markets
Demand-side: collapse of demand in advanced economies has a significant impact on emerging market economy exports
Слайд 6
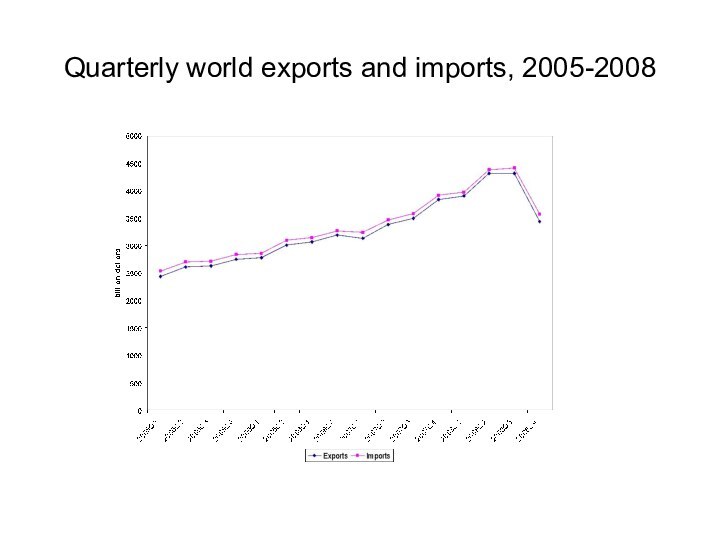
Impact on trade
Until mid-2008, slowing of OECD demand
offset by strong growth in exports of capital- and
high-tech products
Capital good producing economies: Japan, Germany, Taiwan, China and US-most affected by collapse of investment
GDP collapse in Japan 12.1 %, 21% in Korea and 25% in Taiwan and China
Слайд 7
Quarterly world exports and imports, 2005-2008
Слайд 8
Impact of Global Financial Crisis on Trade
Слайд 9
Global crisis and trade credit
Global financial crisis might
have reduced the trade finance (WTO, 2008)
G20 meeting on
2 April 2009: ensure $250 billion for trade finance to promote trade and investment over 2 years (through export credits and investment agencies)
Supply-side failure: sharp fall in trade finance in advanced economies; increase in credit prices
Possible explanations: herd behavior (S-T); global consolidation and concentration (L-T)
“perception that domestic local banks were no longer in a position to be reliable counterparts, and the absence of possibilities to "securitize" outstanding loans, convinced international banks that, despite an existing demand, the level of risk had become too high relative to its remuneration” (WTO, 2008).
Слайд 10
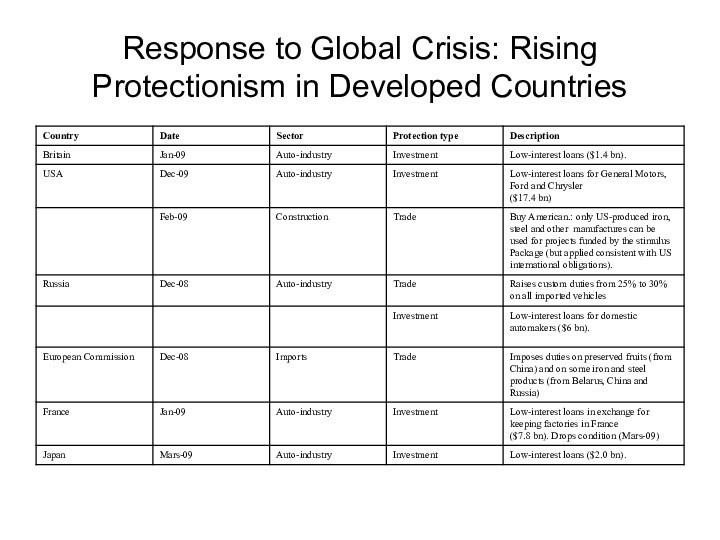
Response to Global Crisis: Rising Protectionism in Developed
Countries
Слайд 11
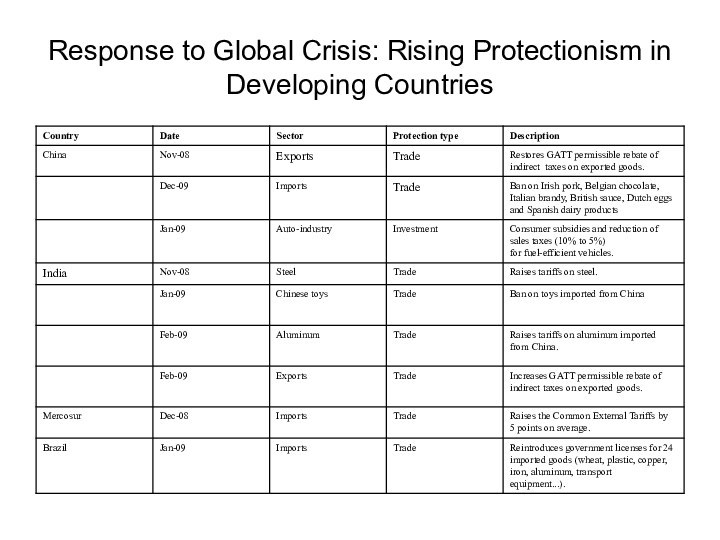
Response to Global Crisis: Rising Protectionism in Developing
Countries
Слайд 12
Road to Recovery
Emerging markets economies are key to
global recovery
Decoupling theory: A survey of the decoupling debate
(Kose, et al 2008) reveals that during the last period of globalization (1985-2005) there has been convergence of business cycles fluctuations among the group of industrial and emerging markets. While these groups have become more integrated within themselves they have become more disconnected from each other.
As in the case of the current crisis the emerging markets were not initially affected (except Eastern Europe that is highly exposed to the financial crisis through its mainly foreign owned banking system). In this case, the transmission of the crisis from advance economies to the emerging markets through trade linkages were caused by the collapse of demand in advanced countries.
Слайд 13
Road to Recovery
The idea that EMEs are decoupling
vis-à-vis advanced economies has been quite widespread until the
onset of the crisis; however, more recent developments have discredited this view.
Despite the improvement in the fundamentals of many EMEs (after the 1990s crises) and the decline in their vulnerability, it seems clear that EMEs are suffering the consequences of the crisis.
The World Economic Outlook and the Global Financial Stability Report have highlighted important heterogeneity among the group of EMEs but the increase in the risk aversion (and uncertainty) has hit all of them.
Слайд 14
Road to Recovery
Given the weight of these emerging
market economies in world output and trade, they have
a significant role to play in terms of recovery.
Although emerging economies and developing countries as a group are expected to experience sharp decline in GDP, they will still have positive growth rates unlike advanced economies, except the NIA (Hong Kong, Singapore, Korea and Taiwan).
Слайд 15
Road to Recovery
According to IMF estimates Developing Asia
is the only region that is expected to have
strong growth (4.8%) in 2009.
Developing Asia: China (6.5% in 2009, 10.2% in 2011) India (4.5% in 2009, 6.9% in 2011).
Claessens et al 2009: A recovery without credit-
Financial downturns tend to last longer than economic recessions
Episodes of credit crunches and equity price busts last twice as long as recessions and house price busts last more than 3 times as long
For recessions with credit crunches, real economy picks up while credit is still contracting.
Слайд 16
Conclusion
If the theory of creditless recovery holds: it
is mainly going to be driven by consumption.
Given by
the increasing weight of emerging market economies, they will be the key players in recovery: as consumption is restored in these economies, demand will be restored
As exports are a significant driver of growth in these economies and in some cases more than 40% of the value added of exports are imported:
Protectionism is the wrong approach to recovery. It is only a short-term solution.