- Главная
- Разное
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Государство
- Спорт
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Религиоведение
- Черчение
- Физкультура
- ИЗО
- Психология
- Социология
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое findslide.org?
FindSlide.org - это сайт презентаций, докладов, шаблонов в формате PowerPoint.
Обратная связь
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть
Презентация на тему к лекции №1 по дисциплине История английского языка
Содержание
- 2. THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE IN THE INDO-EUROPEAN FAMILY OF LANGUAGES
- 3. How many groups of languages belong to
- 4. AlbanianBalticCelticGallic2345689101112Italic later RomanceLanguages1IndianIranianArmenianOld PrusianSlavonicHellenicor GreekBlock-scheme Module 1 The Indo-European family of languages7GERMANIC
- 5. Languages can be classified according to different
- 6. The pre-written history of English and cognate
- 7. What is the parent language of Germanic
- 8. The history of the Germanic group begins
- 9. What do Greek and Roman writers say
- 10. Indo-European familyGermanic group of languagesThe Proto-GermanicIndo-European ParentThe Proto Germanic language (15th -10th c. B. C.)B.C.A. D.
- 11. Which Germanic languages are dead?Which Germanic languages
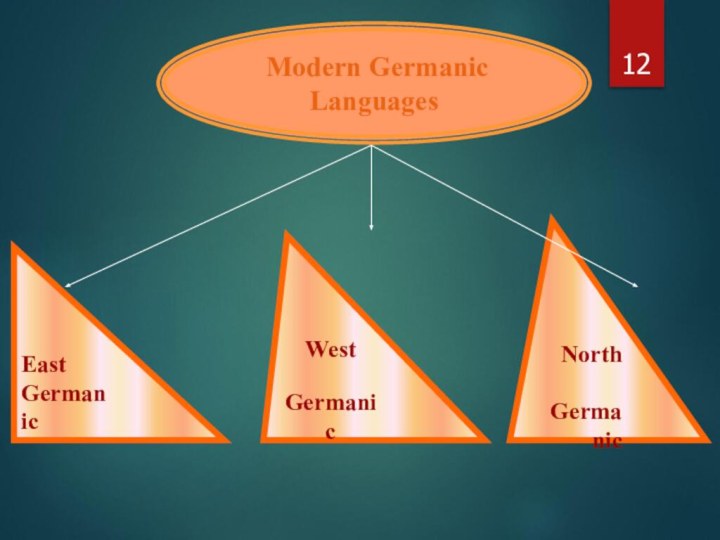
- 12. Modern Germanic LanguagesEast GermanicWest Germanic North Germanic
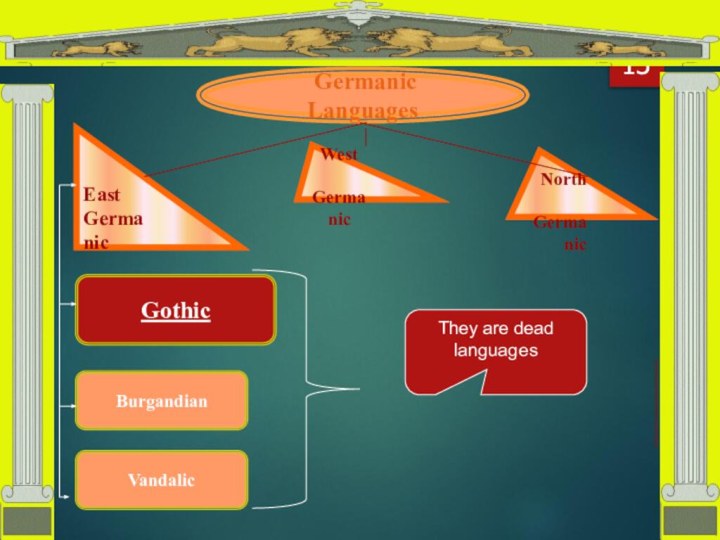
- 13. Germanic LanguagesEast GermanicWest Germanic North GermanicGothicBurgandianVandalicBlock-scheme They are dead languages
- 14. The Gothic languageBecause only the Gothic language
- 15. Germanic LanguagesEast GermanicWest Germanic North GermanicEastern branchWestern branchNorwegianSwedishDanishFaroesIcelandicBlock-scheme
- 16. The Icelandic languageAs compared with other North
- 17. Germanic LanguagesEast GermanicWest Germanic North GermanicLow BranchHigh BranchGermanYiddishFlemishFrisianEnglishAfricaansDutchBlock-scheme
- 18. The Africaans languageBecause the Africaans language is
- 19. GREAT BRITAINOn the Eastern Lesser Islands The USACANADAAUSTRALIANEW ZEALANDThe Continent of AFRICAENGLISH
- 20. Скачать презентацию
- 21. Похожие презентации



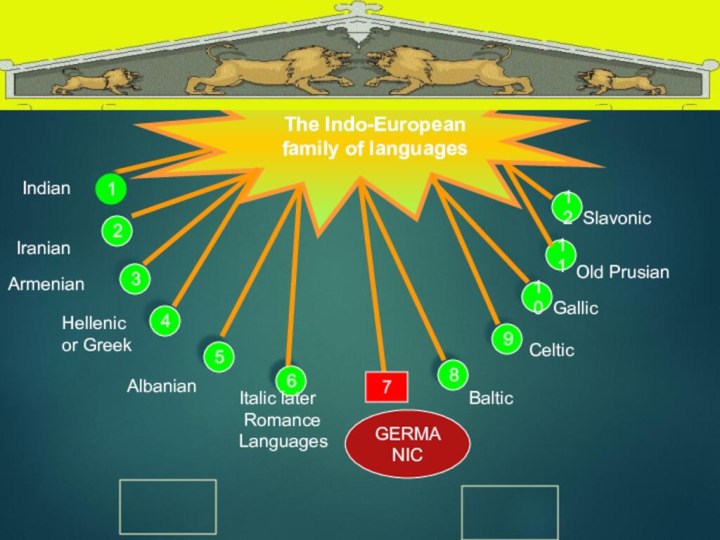











Слайд 3 How many groups of languages belong to the
Indo-European family of languages?
Why do we have to speak
about the Indo-European family of languages?What is the parent language of the Indo-European family of languages?
What do you know about the historical comparative method?
Brainstorming
activity
Слайд 4
Albanian
Baltic
Celtic
Gallic
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
Italic later
Romance
Languages
1
Indian
Iranian
Armenian
Old Prusian
Slavonic
Hellenic
or Greek
Block-scheme
Module 1
The
Indo-European family of languages
7
GERMANIC
Слайд 5
Languages can be classified according to
different principles.
The historical or
genealogical classification, groups of
languages in
accordance with their origin from a common linguistic ancestor. Genetically,
English belongs to the Germanic or
Teutonic group of languages,
which is one of the twelve groups
of the Indo-European linguistic family.
Most of the Area of Europe and large part of
other continents are occupied today by the
Indo-European languages,
and Germanic being one of their major group.
Слайд 6
The pre-written history of English and cognate
languages
was first studied by the methods of historico-comparative
linguistics
evolved in the 19th с. By applying these methods linguists discovered the kinship of what
is now known as the Indo-European (IE) family of
languages and grouped them into Germanic,
Slavonic, Romance, Celtic, and others. Modern linguistics
has improved on the method of historico-comparative linguistic research
applied in the 19th с.
Слайд 7
What is the parent language of Germanic languages?
Where
was the parent language of Germanic languages spoken?
By whom
was the parent language of Germanic languages spoken?What do you know about the ancestor of the Germanic tribes?
What did the famous scholars say about classification of the Germanic tribes?
Brainstorming
activity
Слайд 8 The history of the Germanic group begins with
the appearance of what is known, as the Proto-Germanic
(PG) language (also termed Common or Primitive
Germanic, Primitive Teutonic and simply Germanic).
PG is the linguistic ancestor the parent-language
of the Germanic group. It is supposed to have split
from related IE tongues sometime between the
15th and 10th c. B.C. There would be Germanic tribes
belonged to the western division of the IE speech
community. As the Indo-Europeans extended over a larger
territory, the ancient Germans or Teutons moved further
north than other tribes and settled on the southern coast of
the Baltic Sea in the region of the Elbe.
Слайд 9 What do Greek and Roman writers say about
the ancient Teutons?
1. The Roman general, statesman, and writer
Julius Caesar (100—44 B.C.). In the Commentaries on the War in Gaul (Commentarii de hello Gallico) Caesar wrote that the Germans lived in tribes and tribal unions. It was of particularly great value for the historians. It also follows from Caesar's account that the Teutons were nomads in his time. 2. In the 1st c. A.D. Pliny the Elder in NATURAL HISTORY (NATURALIS HISTORIA) made a classified list of Germanic tribes grouping them under six headings.
3. The Roman historian Tacitus compiled a detailed description of the life and customs of the ancient Teutons. In his work he reproduced Pliny's classification of the Germanic tribes.
4. F. Engels in ON THE HISTORY OF THE ANCIENT GERMANS and THE ORIGIN OF THE FAMILY, PRIVATE PROPERTY AND THE STATE. Having made a linguistic analysis of several Germanic dialects of later ages F. Engels came to the conclusion that Pliny's classification of the Teutonic tribes accurately reflected the contemporary dialectal division.
Слайд 10
Indo-European
family
Germanic group of
languages
The Proto-Germanic
Indo-European
Parent
The Proto
Germanic language
(15th -10th c. B. C.)
B.C.
A. D.
Слайд 11
Which Germanic languages are dead?
Which Germanic languages are
the most important from the point of territorial extent?
Which
Germanic languages are the most important from the linguistic point of view?Brainstorming
activity
Слайд 13
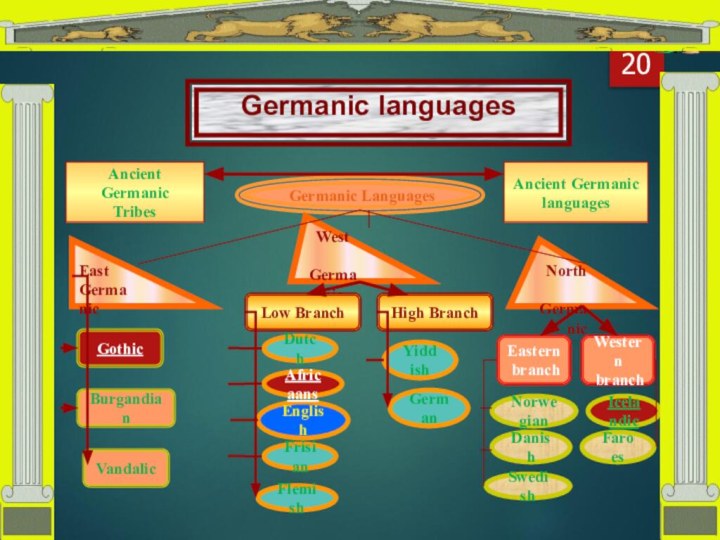
Germanic Languages
East
Germanic
West
Germanic
North
Germanic
Gothic
Burgandian
Vandalic
Block-scheme
They are dead languages
Слайд 14
The Gothic language
Because only the Gothic language left
it’s historical
written monument, which is called
SILVER CODEX
(CODEX ARGENTEUS).It was written by Ulfilas, a West Gothic bishop, in the 4th c.
It is written on red parchment with silver and golden letters,
and kept now in Uppsala, Sweden.
The SILVER CODEX is one of the earliest texts in the
languages of Germanic group; it represents a form of
language very close to PG and therefore throws light
on the pre-written stages of history of all the languages of
Germanic group, including English.
Слайд 15
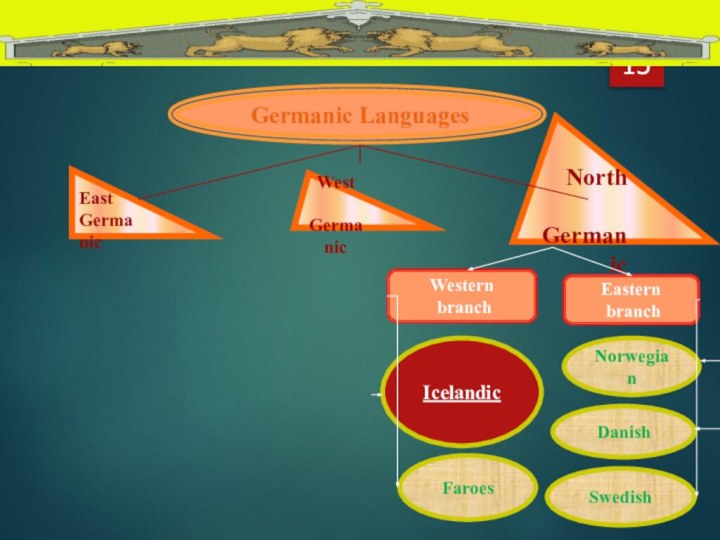
Germanic Languages
East
Germanic
West
Germanic
North
Germanic
Eastern
branch
Western
branch
Norwegian
Swedish
Danish
Faroes
Icelandic
Block-scheme
Слайд 16
The Icelandic language
As compared with other North Germanic
languages
Icelandic has retained a more archaic vocabulary
and
grammatical system. Modern Icelandic is very much like Old Icelandic and Old Norse,
for it has not participated in "the linguistic changes
which took place in the other Scandinavian
languages, probably because of its geographical isolation.
Old Icelandic written records date from the
12th and 13th c, an age of literary flourishing.
The most important records are:
the ELDER EDDA (also called the POETIC EDDA) —
a collection of heroic songs of the 12th c,
the YOUNGER (PROSE) EDDA
(a text-book for poets compiled by
Snorri Sturluson in the early 13th c.)
and the Old Icelandic sagas.
Слайд 17
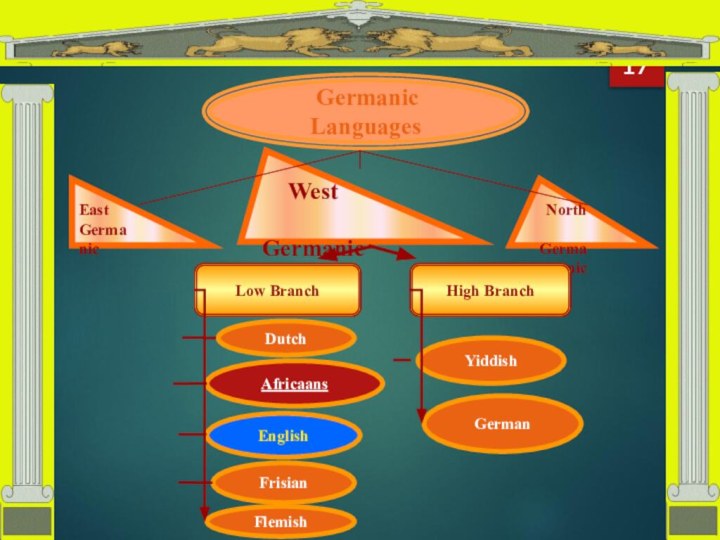
Germanic Languages
East
Germanic
West
Germanic
North
Germanic
Low Branch
High Branch
German
Yiddish
Flemish
Frisian
English
Africaans
Dutch
Block-scheme
Слайд 18
The Africaans language
Because the Africaans language
is the
youngest language among all the
languages of the West
Germanic group. It exist for about 200 years.
About three hundred years ago the Dutch language
was brought to South Africa by colonists from
Southern Holland. Their dialects in Africa eventually
grew into a separate West Germanic language,
Afrikaans. Afrikaans has incorporated elements
from the speech of English and German colonists
in Africa and from the tongues of the natives.
Writing in Afrikaans began as late as the end of the
19th с. Today Afrikaans is the mother-tongue of over
four million Afrikaners and coloured people and
one of the state languages in the
South African Republic (alongside English).